Strategic Planning Analysis for Starbucks Hong Kong
Conducting a strategic planning analysis for Starbucks in Hong Kong, focusing on Porter's Five Forces, PEST analysis, and market trends within the coffee and snacks store industry. Evaluate aspects such as threat of new entrants, supplier power, buyer power, rivalry, and threat of substitute products or services in this competitive market.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Strategic Planning Strategic Planning http://www.quickmba.com/strategy/strategic-planning/
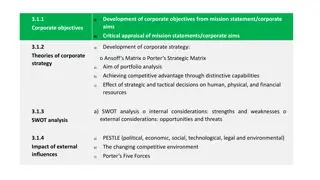
Strategic Planning Strategic Planning Strategic Planning Strategic Analysis Strategic Formulation SWOT External Environment Internal Capabilities PEST Boston Matrix Porter s Five Forces
Starbucks Hong Kong Starbucks Hong Kong Background Information Background Information The retail coffee and snacks store industry / food and beverage industry General trends of the industry: Overview of the industry Market share: Compare Starbucks with competitors Demand and profitability drivers: Disposable income, prices, culture and attitudes
Starbucks Hong Kong Starbucks Hong Kong Porter s Five Forces Analysis (Industry) Porter s Five Forces Analysis (Industry) THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS: Moderate Barriers to entry: Not considered to be high (many existing competitors, localized small shops) Brand identity: Strong brand identity Capital requirements: Considered to be moderate Absolute cost advantages: learning curve advantages exist Switching costs: Essentially none SUPPLIER POWER: Low to moderate Switching costs of suppliers and firms in the industry: Relatively low to moderate as inputs are standard coffee beans Presence of substitute inputs: Available Threat of forward integration with respect to threat of backward integration by firms in the industry: Backward integration through direct purchase agreement and the establishment of coffee roasting plants. Forward integration through retail stores BUYER POWER: Low to moderate Buyer volume: Large number of individual buyers with low volume purchases Buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs: Essentially none Buyer information: Open Substitute products availability: Many Price sensitivity: Price related to quality Brand identity: Strong RIVALRY: High to Moderate Industry growth: Market is mature with slow growth rate Intermittent overcapacity: No Product differences: Differentiation with products and services Brand identity: Strong brand identity Switching costs: None THREAT OF SUBSTITUTE PRODDUCTS OR SERVICES: High Many alternative possible substitutions (e.g. tea, cocktails, soda, , etc) Essentially no switching cost Much cheaper to make one s own coffee Countermeasures possible?
Starbucks Hong Kong Starbucks Hong Kong PEST (External Analysis) PEST (External Analysis) Political Factors No major changes to the legal system after the handover Still common law based Economic Factors Asia s major financial center Many visitors form other countries especially from the mainland Willing to spend for Starbucks? Social-Cultural Factors Interpersonal skills highly valued Trend not to plan ahead for purchases Loyal to a brand once trust has been established
Starbucks Hong Kong Starbucks Hong Kong PEST (External Analysis) PEST (External Analysis) Technological Factors Most people are technological capable Good technological infrastructure Analysis Favorable conditions for western companies like Starbuck May formulate strategies in leveraging the technological environment (how?)
Starbucks Hong Kong Starbucks Hong Kong SWOT (Internal Analysis) SWOT (Internal Analysis) Strength Strong brand identity and market shares Diverse and high quality products Store locations and decorations Strong team building and HR management Social responsibilities Good mobile applications and established customer loyalty program Weaknesses Expensive Too many outlets Stereotype of large corporation
Starbucks Hong Kong Starbucks Hong Kong SWOT (Internal Analysis) SWOT (Internal Analysis) Opportunities Diversify products and expand into retail operation Further enhancement of the existing mobile and technological applications Threats Increased competition Market saturation Price volatility
Starbucks Hong Kong Starbucks Hong Kong Value Chain Analysis Value Chain Analysis Primary Activities Inbound logistics Select beans and perform roasting Operations Has both retail and licensed stores Outbound logistics Little presence of intermediaries Marketing and Sales Achieve mainly through good quality Service Provide unique Starbucks experience Support Activities Infrastructure Well-established infrastructure to support the business HR Management Well known for good HK management Technology Well known in using technology for management and services Procurment Form good strategic partnerships with suppliers
Starbucks Hong Kong Starbucks Hong Kong Strategies Strategies Offer diversity Use hedging strategies to deal with price volatilities Further development in the retail sector Reference: https://scholar.harvard.edu/files/nithingeereddy/files/starbucks_case_analys is.pdf