Geopotential and Geopotential Height in Atmospheric Thermodynamics
Explore the concept of geopotential and geopotential height in atmospheric sciences, focusing on their significance in understanding gravitational and centrifugal forces on Earth. Learn about the definition, calculation, and applications of geopotential height in relation to atmospheric properties a
5 views • 14 slides
Atmospheric Thickness and Its Applications
Atmospheric thickness refers to the difference in geopotential height between two pressure surfaces, which is dependent on the mean virtual temperature of the layer in between. This concept plays a key role in determining temperature gradients, identifying fronts, and aiding in weather forecasting,
3 views • 11 slides
Geopotential and Geopotential Height in Atmospheric Thermodynamics
This lecture discusses the concepts of geopotential and geopotential height in atmospheric thermodynamics, including their definitions, significance, and relationship with gravity. It explains how geopotential is a measure of potential energy relative to sea level and how geopotential height serves
6 views • 17 slides
Decadal Changes in Caribbean Low-Level Jet and Atmospheric Dynamics
Analysis of decadal changes between the 1990s and 2010s in the Caribbean region focusing on the low-level jet, rainfall patterns, 925 hPa geopotential, winds, and surface temperatures during dry and rainy seasons. Significant variations observed in wind strengths, pressure gradients, and surface tem
4 views • 9 slides
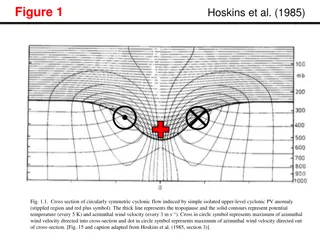
Cyclonic Flow Analysis in Atmospheric Dynamics Study
The figures presented in this study showcase cross-sections and composite sections of cyclonic flow induced by upper-level potential vorticity (PV) anomalies. Various parameters such as potential temperature, wind velocity, geopotential height, and relative humidity are analyzed to understand the st
3 views • 9 slides
Decoding SYNOP Code and Plotting Surface Data for Meteorological Analysis
Learn how to decode the SYNOP code and plot observational data on surface charts for weather analysis. Understand the elements observed, such as present and past weather, wind speed and direction, cloud type and coverage, visibility, temperature, humidity, and pressure at surface weather stations. E
5 views • 42 slides
Atmospheric Thermodynamics Essentials
This lecture covers forms of energy, Earth's atmosphere overview, atmospheric composition, vertical structure, pressure, temperature variations, density, geopotential height, and the hydrostatic equation. Explore the fundamental principles governing atmospheric behaviors.
5 views • 5 slides