Access to COVID-19 Tools Accelerator: Civil Society Representation
This content discusses the involvement of civil society and communities in the Access to COVID-19 Tools Accelerator (ACT-A), focusing on representation in various pillars such as therapeutics, diagnostics, health system strengthening, and vaccines. It provides an overview of the progress made, opportunities for collaboration, and next steps in the initiative.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
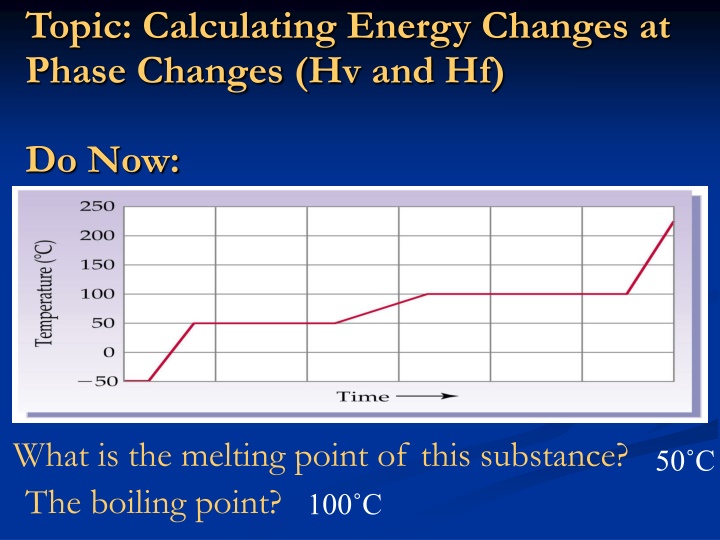
Topic: Calculating Energy Changes at Phase Changes (Hv and Hf) Do Now: What is the melting point of this substance? 50 C 100 C The boiling point?
It takes energy to heat stuff up! for pure substance in single phase - can calculate how much E needed using: Q = mC T Q = energy in Joules m = mass in grams C = specific heat capacity T = change in temperature = Tf - Ti on other hand, when something cools down, energy is released!
Q = mCliquid T Q = mCgas T Q = mCsolid T Temperature IV I II III V C = specific heat capacity (amount heat required to raise temp of 1g of pure substance by 1 C) C is a physical constant unique for every pure substance CAN YOU FIND THE SPECIFIC HEAT OF WATER ON YOUR REFERENCE TABLE? Time
Why cant I use Q = mCT for II and IV?? Temperature IV I II III V Because T = 0, temp isn t changing!!!! Time
So, how do we calculate the amount of energy required during a phase change? HF = Heat of Fusion (Q = mHF) HV = Heat of Vaporization (Q=mHV) We use one of these two constants instead of specific heat and delta T Q = mC T
Hf =Heat of Fusion is amount energy required to change 1 gram of pure substance from solid to liquid at its MP (meaning you aren t changing the temperature) Is a physical constant Check out Reference Table B, what is the heat of fusion for water? The Equation Q = mHf
How much heat is absorbed when 10 grams of ice melts at 0oC? Heat absorbed = mass of substance x heat of fusion of substance Q = mHf = (10 g)(334 J/g) = 3340 J Where does this energy go? Particles must overcome forces of attraction to move farther apart during phase change (s l)
HV = Heat of Vaporization is the amount energy required to convert 1 gram of pure substance from liquid to gas at its BP (meaning you aren t changing the temperature) Is a physical constant Check out Reference Table B, what is the heat of vaporization for water? The Equation Q = mHv
How much energy does it take to vaporize 10 g of water? Q = mHv Q = (10 g)(2260 J/g) = 22600 J
It takes a lot more energy to go from liquid to gas than from solid to liquid. Why? H2O changing from liquid to gas requires 22,600J/g H2O changing from solid to liquid requires 3,340J/g * greater energy required to change from liquid to gas because particles are spreading farther apart!
Q = mCsolidT Q = mCLIQUID T Q = mCgas T Q = mHV Q = mHF Temperature IV I II III V Time
3 equations for Q 1. Q = mC T 2. Q = mHf 3. Q = mHv figure out which to use depends on section of heating curve look for hints in word problem
Q = mC T Temperature changed T T Initial temperature Start temperature Final temperature Ending temperature From __ C to __ C Water
Q = mHf Ice Freezing Melting Occurs at 0 C (for H2O) At constant temperature
Q = mHv Steam Boiling Condensation Occurs at 100 C (for H2O) At constant temperature
heating rate = 150 J/min If the substance takes 4 minutes to melt, how much heat energy was used to melt it? 150J/min x 4min = 600J