ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
Acquired immunity involves active and passive mechanisms, cell-mediated and humoral responses, MHC proteins, and the distinction between Class I and Class II MHC proteins in immune recognition. Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet provide insights into the types of acquired immunity and the roles of antibodies in combating pathogens.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ACQUIRED IMMUNITY - Overview of the components of acquired immunity. - Overview of the different acquired immune responses. - Definition of pathogens and types of antigens and antigenic determinants. Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet
Acquired Or Adaptive Immunity Specific resistance Acquires during life time Increases with repeated exposures Has memory Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet
Types of Acquired immunity ACTIVE PASSIVE Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet
Active Developed as a result of an antigenic stimulus Involves the synthesis of antibodies Production of immunologically active cells Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet
Passive Resistance that is transmitted to a recipient in a readymade form Preformed antibodies are administered Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet
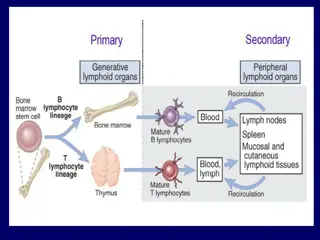
Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet Adaptive immunity mechanisms: Cell-mediated immune response T cells eliminate intracellular microbes that survive within phagocytes or other infected cells Humoral immune response B cells mediated by antibodies eliminate extra-cellular microbes and their toxins Plasma cell (Derived from B cells , produces antibodies)
Cell-Mediated Immune Response Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet
What are MHC & APC Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) MHC proteins, mark a cell as self The two classes of MHC proteins are: Class I MHC proteins found on virtually all body cells Class II MHC proteins found on certain cells in the immune response The main function of MHC molecules is to bind to peptide fragments derived from pathogens and display them on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet
Antigen-Presenting Cells B cells Dendritic cells Macrophages Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet
How do T cells know a cell is infected? Infected cells digest some pathogens and MHC proteins carry pieces to cell surface Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) Alerts Helper T cells MHC proteins displaying foreign antigens infected cell TH cell T cell with antigen receptors Dr. Sultan Alsharif & Dr. Iman Thabet