Actinobacillus: Characteristics and Diseases in Animals
Actinobacillus, a G- pleomorphic bacterium, was first reported in 1902 from bovine abscesses. It is variably hemolytic, nonmotile, and requires CO2 for growth. Diseases attributed to Actinobacillus occur sporadically in animals, with species like A. lignieresii causing actinobacillosis in ruminants. The bacteria are primarily found in the upper respiratory tract and oral cavity, transmitted by carrier animals. A. equuli also causes diseases in horses, such as septicemia and arthritis, highlighting the importance of understanding these pathogens in veterinary medicine.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
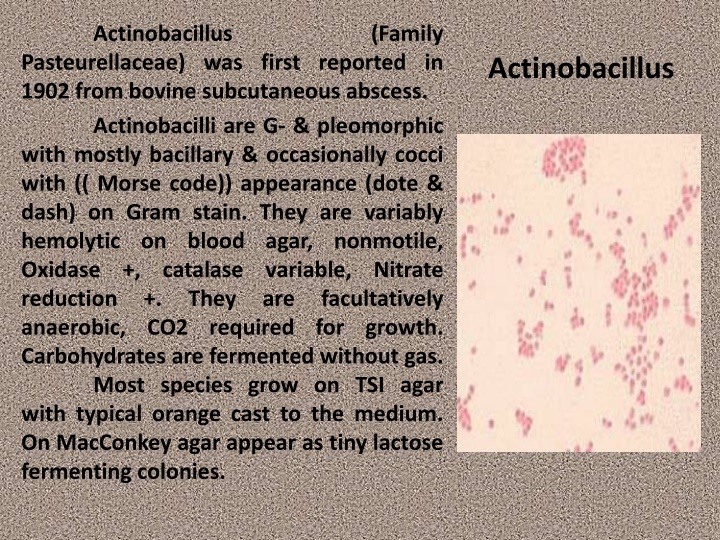
Actinobacillus (Family Pasteurellaceae) was first reported in 1902 from bovine subcutaneous abscess. Actinobacilli are G- & pleomorphic with mostly bacillary & occasionally cocci with (( Morse code)) appearance (dote & dash) on Gram stain. They are variably hemolytic on blood agar, nonmotile, Oxidase +, catalase reduction +. They anaerobic, CO2 required for growth. Carbohydrates are fermented without gas. Most species grow on TSI agar with typical orange cast to the medium. On MacConkey agar appear as tiny lactose fermenting colonies. Actinobacillus variable, are Nitrate facultatively
Diseases attributed to these bacteria occur sporadically. The URT & oral cavity are the natural habitats of most actinobacillus spps are incapable of long survival in the environment, carrier animals are important in disease transmission. Actinobacillus lignieresii is a commensal of the ruminant oropharynx & can be isolated from rumen contents. Actinobacillosis or Wooden tongue in ruminants result in the formation of hard tumorous masses in the tongue. Affected animals suffering from dysphagia & weight loss. The disease is often actinomycosis, but true actinomycosis is found in bone, whereas actinobacillosis affects soft tissues. A. lignieresii isolated from pneumonic sheep lung, tongue lesion of dogs & bovine mastitis. Trauma is an important predisposing factor because the organism gain entry into the underlying soft tissues through penetration of the mucosal or epithelial barrier. Diseases & Epidemiology actinobacilli. Because confused with
A. equuli has been divided into ssp equuli & hemolyticus. A. equuli ssp equuli reside in the mucous membrane of of normal horses & pigs, whereas A. equuli ssp hemolyticus has been recovered from horses only where it is a component of oral & alimentary microflora. B. equuli ssp equuli is associated with septicemia in neonatal foals (sleepy foal disease), purulent arthritis (joint ill) & nephritis. Nearly one third of equine neonatal mortality may be associated with this organism. The mare serves as the source of infection via the oral, umblical or respiratory routes either in utero, during parturition or shortly after birth. Colostrum deprivation, stress or parastism may predispose to illness. C. equuli ssp hemolyticus is strictly an equine pathogen associated with sporadic cases of endocarditis, meningitis, metritis, abortion & respiratory & wound infections. Human infections with actinobacilli are limited to periodental disease. Diseases & Epidemiology
Lesions typically begins several days after the inoculation of A. lignieresii usually through a traumatic injury with leukocytosis followed by granulomatous reaction, purulent foci containing club-shaped clusters of A. lignieresii microcolonies form within the center of the lesion & enlarge into tumorous masses as they become surrounded by layers of connective tissues. The organism may disseminate via the regional lymphatics to internal organs such as lung. The pathogenesis of equine actinobacillosis, the organism disseminates by the blood to many organs in infected foals, & these septic emboli lead to microabscess formation in affected tissues. Bacterial colonies are most frequently observed in the glomeruli & intertubular capillaries, where there is intense suppuration. Polyarthritis result from an increase in synovial fluid, followed by congestion & swelling of the joint capsule & leukocytosis. Virulence factors capsule, pore-forming exotoxins, lipopolysaccharide, unease & , protease production, Pathogenesis include polysaccharide
The capsule protect the bacteria from phagocytosis & lysis by complements. The host-cell-specific toxins act on immune cells, either by inducing production of inflammatory mediators or exerting cytotoxic effect that result in inflammation or cell death by apoptosis or necrosis. Urease activity consider a mechanism by which actinobacilli obtain preferred source of nitrogen. Urease may enable the bacteria to survive inside the macrophage. Protease hemoglobin. Degradation of IgA may facilitate mucosa spread of the organism. Pathogenesis has been ammonia, a degrade IgA &
1. Direct examination of Gram stain smear from pus from tongue lesion may reveal club- shaped forms (sulfur granules) that contain centreal masses of pleomorphic G- rods. 2. Culture of actinobacilli from infected tissues is the most reliable method for diagnosis. 3. Species differentiation by biochemical test s may be helpful. 4. Differenttion of actinobacilli may be based on hemolytic poperties, their ability to grow on MacConkey agar & hydrolysis of esculin & their ability to produce oxidase, catalase, urease & acids in carbohydrate fermentation. 5. Serotyping using specific antisera. 6. ELISA technique Laboratory Diagnosis