Adipic acid
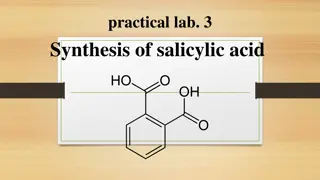
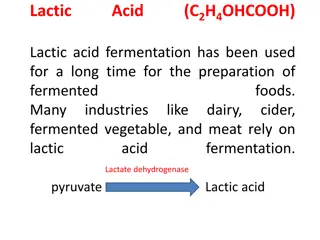
Adipic acid is a key industrial chemical primarily used in the production of nylon, with annual production reaching billions of kilograms. It has limited occurrence in nature and is known for its tart taste. Apart from nylon production, adipic acid also serves as an additive and gelling agent in products like jello and gelatins. Its physical properties include a melting point of 152.1°C and a molar mass of 146.142 g/mol. The chemical formula is C6H10O4, and it exhibits varying solubility in water at different temperatures.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Adipic dicarboxylic acid with about 2. 5 billion kilograms produced per year. It is used mainly in the production of nylon. It occurs relatively rarely in nature. It has a tart taste and is also used as an additive and gelling agent in jello or gelatins. acid is an important inudstrial
Physical properties Chemical formula: C H O Melting point: 152.1 C (305.8 F; 425.2 K) Molar mass: 146.142 g mol 1 Solubility in water: 14 g/L (10 C), 24 g/L (25 C), 1600 g/L (100 C)