Adrenal Medulla Hormones and Their Effects
Explore the role of adrenal medulla hormones in the fight-or-flight response, their impact on body functions like glycogenolysis, heart rate, and metabolic rate, as well as the secretion of catecholamines. Learn about the functions and outcomes related to these crucial hormones.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Learningoutcomes AfterreviewingthePowerPointpresentation,lecturenotesandassociatedmaterial,the student should be ableto: Summarize the actions of adrenalandrogens. Describe the causes and major manifestations of hyperadrenocorticism andHypoadrenocorticism Describe circumstances in which catecholamines are released from the adrenalgland. List the major actions ofcatecholamines.
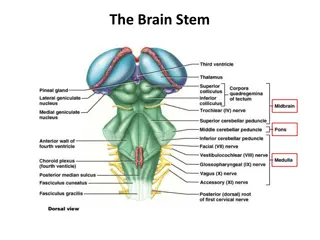
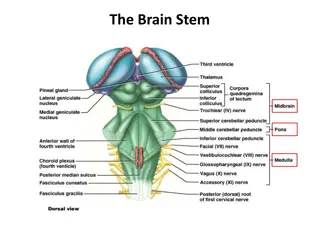
Adrenalmedulla Theadrenalmedullaistheinnerpartorcoreofeachadrenalgland. Itisconsideredaspartofsympatheticnervoussystem. It secretescatecholamines: Adrenaline (epinephrine) --80% of the secretion. Noradrenaline(norepinephrine)--20% ofthesecretion. small amount ofdopamine They are released from chromaffincells
Adrenalmedulla Secretion of these hormonescauses: Bloodtobedivertedtothebrain,heart,andskeletalmuscle Epinephrineisthemorepotentstimulatoroftheheartandmetabolic activities Norepinephrineismoreinfluentialonperipheralvasoconstrictionand bloodpressure
Role of the adrenal medullaryhormones 1.Enhance the effects of the sympathetic nervoussystem. 2.Prepare the body for a stressfulevent. Theresponseisknownasthe fightorflight response.
Effects ofCatecholamines 1-Glycogenolysisinliverandskeletalmuscle(canlead to hyperglycemia)whichincreasesblood glucose level 2-Increaseheartrateand bloodpressure 3-Cause vasoconstriction of bloodvessels 4-Mobilization of free fattyacids 5-Increase metabolic rate 6-Increase O2consumption
Actions of adrenal medullaryhormones Theeffectsoftheadrenalmedullary hormonesunderlietheroleofthesehormonesinpreparation ofbodyforfight orflight. Theoveralleffectistoensuethatallrequirementsforincreasedmuscleactivityareavailable.Whatarethese?
Control of secretionof adrenal medullaryhormones The adrenal medulla is innervated bythe sympathetic nervoussystem. Adrenal hormones are released from the medulla inresponseto signals from thesympatheticnervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is activated in response to stress also know as the fight orflight response. Stress can be physical (exercise), physiological (hypoglycemia, hemmorhage), or emotional, Cortisol, when secreted from the adrenal cortex in responseto stress,causesreleaseof thesehormones fromthemedulla.
The adrenal medulla is, functionally , integral part o f the sympathetic system . 80% of its secretion is Epinephrine ( EP) and 20% of its secretion is Norepinephrine (NE ). EP in the bloodstream , on the other hand , comes solely from the adrenal medulla . BUT NE in blood comes from BOTH adrenal medulla and postganglionic sympathetic nerves This is because postganglionic sympathetic nerves can not synthesize EP from its precursor NE , because they lack the enzyme ( PNMT) needed for conversion of NE into EP .
Pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma is a tumor of adrenal medulla . It can be life threatening if not recognized & not t Most often occurs in middle age. Symptoms & signs reated.
Pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma chromaffin cells (arise from crest). is derived from neural Most tumors secrete epinephrine, NE, and dopamine and can cause episodic hypertension. Urinary vanillylmandelic acid, VMA (a breakdown product of norepinephrine) and plasma catecholamines elevated. are Associated withneurofibromatosis.
Signs and Symptoms ofPheochromocytoma resistant hypertension (95%) classic triad headache sweating palpitations chest pain anxiety glucose intolerance increased metabolic rate
Diagnosis andTreatment High plasmacatecholamine. Increased metabolites [VMA] in urine Treatment issurgical resection