Adult Development and Needs: Exploring Life Stages
Discover the stages of adult development and corresponding needs from identity vs. role confusion in youth to intimacy vs. isolation in early adulthood. Gain insights into implications for staff development and ways to support adults in finding a balance between career and family responsibilities.
Uploaded on | 3 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Stages of Adult Development And Needs
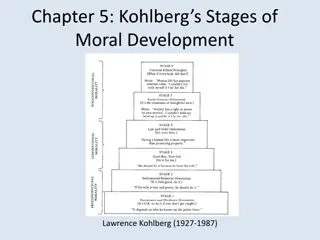
Identity Vs. Role Confusion (13-21 years) Concerns and Characteristics: Struggle for identity (who am I?) Changing self-image Breaking away from parents and transferring need to parental guidance to mentors Very active socially Considers possibility of teaching
Implications for Staff Development (needs) Provide clear expectations Provide opportunities for independence, but recognize the need for dependence Be sensitive to the ups and downs of intimate relationships During student teaching, provide support and feedback
Intimacy Vs. Isolation (21-39 years) Concerns and Characteristics (the 20s): Searching for a partner Parenting may begin for some Focus on education and careers Wanting to demonstrate competence on the job
Implications for Staff Development (needs): Provide mentor for new teachers Clearly define limitations of the job Offer on-site and specific training (classroom management, working with parents, etc.) Provide social activities for staff
Concerns and Characteristics (30s): Social life revolves around partnerships and family or around close friends More men and women choosing to postpone marriage Both men and women concerned about balancing work and family responsibilities Job advancement may be a goal for some
Implications for Staff Development (needs): Discuss relationship between career and family Build trust and respect Offer staff development, portfolio development, college-level coursework Encourage staff to become involved in professional associations Encourage staff to pursue graduate education Provide teacher leadership roles (head teach, advisor, or coordinator, administrator/supervisor internships, for those who are ready)
Generativity Vs. Stagnation (40-65 years) Concerns and Characteristics: Marriage each partner respects autonomy of the other Continues to try to balance work and family responsibilities Mental activities still in place Becoming a model in the next generation s eyes
Friends are important Signs of aging 43% of marriages break up within first 15 years Feeling creative, productive, and self- satisfied Begins to think about retirement
Implications for Staff Development (needs): Know teachers; individualize to meet teachers needs Jointly plan teacher development to facilitate growth Respect differences, skills, and knowledge base among teachers Offer training and support for those reentering the field Include teachers in decision making Encourage teachers to lead staff development, workshops
Concerns and Characteristics Beginning to accept self as part of elder generation Sharing wisdom Mental ability may diminish, but still effective Health and aging issues Enjoys old friends, family, grandchildren Still seeks work creative, or learning opportunities
Implications for Staff Development (needs): Prepare teachers for retirement Explore ways that teachers can pass on knowledge and expertise Provide individualized professional development and learning Help teachers recognize accomplishments
Support intergenerational community- wide programs and activities that bring children, teachers, and seniors together Offer part-time volunteer opportunities with training and support Teach children to care
Stages of Supervisors Supervisors undergo a process of growth and development over time. They face similar problems and frustrations in each phase, but their ability to handle problems changes as they gain experience and move towards maturity.
Phase/ Stage 1: Beginning/Survival Concerned with self: Anxious (will I be able to carry out the responsibilities?) Critical of self Seeks support from many sources
Copes in several ways: Plays the role of supervisor Avoids responsibility Uses trial and error Uncomfortable with authority Develops new realizations about self
Phase /Stage 2: Extending/Consolidation If only I Accepts leadership with uncertainty Can discuss problems and concerns more objectively Concerns are centered on others Better understanding of others and of program More comfortable with authority High expectations for self More confident, more relaxed
Phase/Stage 3: Maturity Knows self and can evaluate self openly Sense of being in charge Greater sensitivity toward and understanding of supervisees
Recognizes expertise of supervisees More realistic about job and what can be done Concerned with ideas Stimulated by outside contracts, gets rewards from solving problems Continues to be critical, but sees self as learner