Advanced Application of Electron Microscopes in Microbiology
Explore the advanced technology of electron microscopes by Dr. Nelson Xess at Bhanupratap Deo Govt. P.G. College in Chhattisgarh. Learn about the powerful imaging capabilities and applications of Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM) and Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM) in studying minute structures with unparalleled resolution. Discover the key differences between TEM and SEM, including resolution, electron types, sample preparation, and imaging techniques.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Electron microscope By Dr. Nelson Xess Department of Microbiology Bhanupratap Deo Govt. P.G College, Kanker, Chhattisgarh
Electron microscope Because the wavelength of an electron beam is 100,000 times shorter than the wavelength of visible light photons, electron microscopes have far greater detection power than optical or light microscope . These microscopes can provide a structural image of the smallest objects with a resolution better than 50 picometers. Electron microscopes have a magnification of more than 10 million times, while optical microscopes have a resolution of 200 nanometers and a magnification of less than 2000 times due to the limitation of the diffraction phenomenon.
Type of electron microscopes Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) A transmission electron microscope employs an electron beam produced at high voltage to brighten the specimen and produce an image to be viewed. The working principle of this microscope is that the electrons pass through the exhibit and create a projection image of the specimen. TEM is typically used to view thin samples such as molecules, tissue sections etc. TEM is similar to other microscope but it used to achieve a very degree of magnification thereby allowing the observation of specimens at a nanometer level.
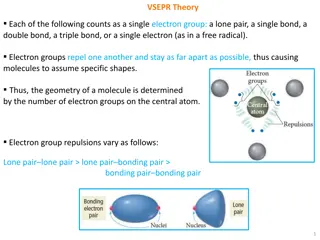
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) An SEM creates magnified images of the specimen by probing along a rectangular area of the specimen with a focused electron beam. This process is called the raster scanning. It is called a scanning electron microscope because the image is formed by scanning the surface of the specimen in a raster pattern using a focused electron beam. SEM relies on the secondary emission of electrons from the surface of the specimen to achieve magnified image to be viewed. The major advantage of a SEM over TEM is that it can produce detailed image of the whole organisms and surfaces of the cells.
Difference between Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) & Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Characteristics Resolution Information from cells visualized Type of electrons Sample preparation TEM 50 pm SEM 0.5 pm Inner surface Outer surface Transmitted Laborious Reflected Using heavy metals Mounting Scan Coils Back scattered electron detector Image Application Copper grids Absent Absent Alumina stabs Present Present 2-D 3-D Ultra structure Topography
Difference between Light microscopy, Transmission electron microscopy and Scanning electron Microscopy