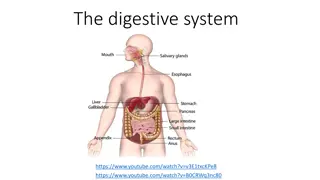
An Overview of the Digestive System
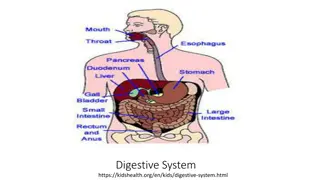
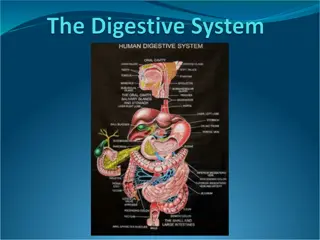
The digestive system, a vital system in our body, includes various organs such as the stomach, small intestine, and more. Understanding its components, functions, and processes can help maintain overall health and well-being. From nutrient absorption to waste elimination, each part plays a crucial role in ensuring proper digestion and nutrient uptake, ultimately supporting our body's energy needs and growth.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Digestive System Dr. Dalia Abd Alkader Ph.D Pharmacology
Word Roots Specific to the Digestive System Root or Suffix Refers to cholecyst/o gallbladder duoden/o duodenum enter/o small intestine hepat/o liver pancreat/o pancreas phag/o eating; swallowing
The Muscular Apparatus of the Digestive System Digestion starts in the mouth and proceeds through the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The apparatus as a whole has several names: alimentary canal, digestive tract, and gastrointestinal (abbreviated GI) tract.
The Pharynx The pharynx has dual citizenship. It belongs to both the respiratory and digestive systems because it is a passageway for both air and for food and drink. Liquid and chewed food enters the pharynx from the oral cavity, and muscular action sends it to the esophagus.
The Esophagus The esophagus is a muscular tube connecting the pharynx with the stomach. It is lined by moist pink tissue called mucosa. The esophagus runs behind the trachea.
The Stomach It has four main areas are the fundus, cardia, body, and antrum. The functions of stomach are: A. Temporary storage place for the food B. Secreting acid and enzymes to help break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
The Small Intestine Ninety percent of nutrient absorption occurs in the small intestine, and the other 10% occurs in the large intestine. The first 10 inches of the small intestine is called the duodenum.
The segment coming right after the duodenum is the jejunum. The jejunum is the segment from which most nutrients are emptied into the bloodstream. The final segment of the small intestine is called the ileum.
The Large Intestine (colon) Besides absorbing 10% of nutrients, the large intestine compacts waste material for elimination. colon can be subdivided into the ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon.
Other Organs of Digestion The Salivary Glands There are three separate pairs of salivary glands, located in different parts of the oral cavity. They are called the parotid, sublingual, and submandibular salivary glands. Although saliva is more than 99% water, it contains essential enzymes that break down complex carbohydrates. Saliva also contains antibodies that kill bacteria.
The Pancreas The pancreas acts as both an endocrine and an exocrine gland. The pancreas provides insulin directly to the bloodstream (endocrine function) and secretes a fluid containing enzymes into the small intestine (exocrine function). Both of these pancreatic secretions are essential to digestion.
The Liver The liver keeps the body's metabolism balanced and promotes good health by releasing fat-soluble vitamins, such as A and D, when the body needs them. The liver also produces bile, which helps in breaking down the lipids (fats).
The Gallbladder It is a small pouch that locates just under the liver. The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver and delivers it to the small intestine.
Common disorders and procedures associated with the digestive system Term Definition excision of the gallbladder inflammation of the gallbladder inflammation of the colon cholecystectomy cholecystitis colitis enteritis inflammation of the intestine painful peristalsis enterospasm
gastrectomy excision of part of the stomach gastritis inflammation of the stomach hepatitis inflammation of the liver pancreatitis inflammation of the pancreas enterogastritis inflammation of the intestine and stomach enterostenosis narrowing within the intestinal tract
Common Abbreviations: Abbreviation DM diabetes mellitus GB gallbladder Meaning GERD gastroesophageal reflux disorder GI gastrointestinal NGT nasogastric tube