Analog to Digital Conversion Process
Learn about the differences between analog and digital signals, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and the process of converting analog signals into digital using sampling. Explore how digital signals are discrete and easier to work with, while analog signals offer infinite data and higher density but are more prone to noise and interference.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
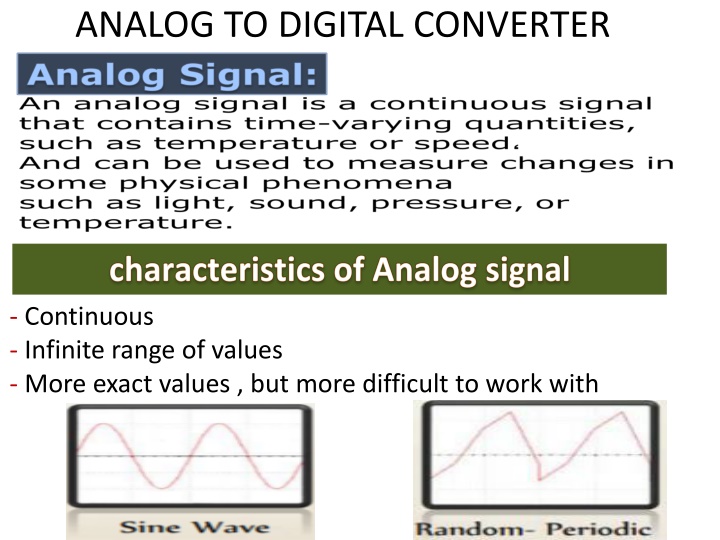
ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER - Continuous - Infinite range of values - More exact values , but more difficult to work with
1-Major advantages of the analog signal is infinite amount of data 2-Density is much higher. 3-Easy processing Disadvantages of Analog signal 1-Unwanted noise in recording. 2-If we transmit data at long distance then unwanted disturbance is there. 3-Generation loss is also a big con of analog signals.
Digital signal Is a type of signal that can take on a set of discrete values (a quantized signal) Digital signals can represent a discrete set of values using any discrete set of waveforms .. And we can represent it like (0 or 1) ,( on or off ) .. etc -Discrete - Finite range of values - Not as exact as analog , but easierto work with
Example: For a 3 bit A/D converter, you have 0-10V signals. Separate them into a set of discrete states
Sampling:- It is a process of taking a sufficient number of discrete values at point on a waveform that will define the shape of waveform. The more samples you take, the more accurately you will define the waveform. It converts analog signal into series of impulses, each representing amplitude of the signal at given point . Here we assign the digital value (binary number) to each state for the computer to read.