Analyzing Projectile Motion Components
Explore the analysis of horizontal and vertical components of projectile motion, including determining time of flight and solving sample problems involving projectiles launched at various velocities and heights. Understand how initial velocities and accelerations influence the motion trajectory. Dive into calculating time to reach peak height and total flight time, along with solving problems related to objects in free fall.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Projectile Motion Analysis HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL COMPONENTS OF PROJECTILE MOTION
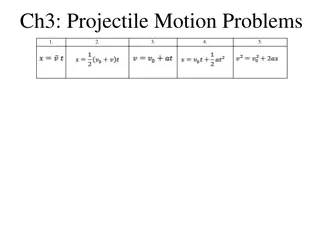
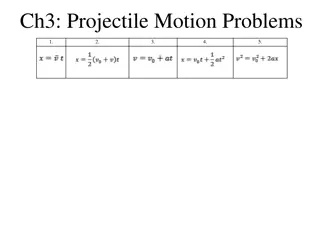
Projectile Motion The time for a projectile to rise vertically to its peak is a result of the initial vertical velocity and acceleration due to gravity. The upwards velocity of a projectile will decrease by 9.8 m/s every second. ??= ?? ?? For a cannon ball with an initial vertical velocity of 39.2m/s 39.2 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? 1? = 29.4 ? ?
Determining Time of Flight Imagine a ball thrown upwards with an initial velocity of 29.4m/s ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 29.4 29.4 29.4 29.4 29.4 29.4 29.4 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 0.5? = 24.5 ? ? + 1? = 19.6 ? ? + 1.5? = 14.7 ? ? + 2? = 9.8 ? ? + 2.5? = 4.9 ? ? + 3? = 0 ? ? + 3.5? = 4.9
Determining Time of Flight Imagine a ball thrown upwards with an initial velocity of 29.4m/s ? ? ? ? 29.4 29.4 29.4 29.4 29.4 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 9.8 ? ? + 4? = 9.8 ? ? + 4.5? = 14.7 ? ? + 5? = 19.6 ? ? + 5.5? = 24.5 ? ? + 6? = 29.4 ? ? ? ? ? ? Rearranging the above equation results in a formula for determining time to peak ?? ? ? = Once rise time is determined, total flight time can be established
Sample Problem #1 A pool ball leaves a 0.60-meter high table with an initial horizontal velocity of 2.4 m/s. Predict the time required for the pool ball to fall to the ground and the horizontal distance between the table's edge and the ball's landing location. ? ?2 ? = 9.8 Begin by determining time of flight using ? = ?? ? + 0.5 ? ?2 ? ?2 ?2 0.6? = 0 ? ? ? + 0.5 9.8 ? ?2?2 0.6? = 4.9 1.22?2= ?2 1.22?2= ? = 0.35?
Sample Problem #1 cont., A pool ball leaves a 0.60-meter high table with an initial horizontal velocity of 2.4 m/s. Predict the time required for the pool ball to fall to the ground and the horizontal distance between the table's edge and the ball's landing location. Once the time has been determined, the distance the pool ball travels can be determined using the formula ? = ?? ? ? = 2.4 ? ? 0.35? = 8.4?
Sample Problem #2 A soccer ball is kicked horizontally off a 22.0-meter high hill and lands a distance of 35.0 meters from the edge of the hill. Determine the initial horizontal velocity of the soccer ball. With zero initial vertical velocity we determine the time of flight ? ?2?2 22.0? = 4.9 4.5?2= ?2 4.5?2= ? = 2.1?
Sample Problem #2 cont., A soccer ball is kicked horizontally off a 22.0-meter high hill and lands a distance of 35.0 meters from the edge of the hill. Determine the initial horizontal velocity of the soccer ball. Once the time has been determined, the distance the ball travels can be determined by rearranging the formula for determining horizontal distance ? = ?? ? ? ?= ?? 35? 2.1?= ??= 16.7 ? ? What about projectiles launched at an angle, that rise to a peak?
Sample Problem #3 A football is kicked with an initial velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 45- degrees with the horizontal. Determine the time of flight, the horizontal distance, and the peak height of the football. ?? ? ? = will allow us to determine the time to the peak and multiplying that by 2 will give the time of flight Begin by substituting ?sin? for ?? ? sin ? ? ? = 2 25 ? ? sin 45 9.8 ? ?2 ? = 2 = 3.6?
Sample Problem #3 A football is kicked with an initial velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 45- degrees with the horizontal. Determine the time of flight, the horizontal distance, and the peak height of the football. ? = 3.6? To determine the horizontal distance, use the formula ? = ?? ????? ? Substituting ?cos? for ?? ? = ?cos? ????? ? ? = 25 ? ?cos45 3.6? = 63.7?
Sample Problem #3 A football is kicked with an initial velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 45- degrees with the horizontal. Determine the time of flight, the horizontal distance, and the peak height of the football. ? = 3.6? ? = 63.7? To determine the peak height of the football, use the formula ? = ?? ? + 0.5 ? ?2 Determine initial vertical velocity ??= ?sin? = 25 ? ? sin45 = 17.7 ? ? ? ?2 1.8?2= 15.9? ? = 17.7 ? ? 1.8? + 0.5 9.8