Anatomy of the Ear and Its Surroundings
Explore the intricate anatomy of the ear, including the auricle, external auditory canal, tympanic membrane, nerve, blood supply, middle ear cleft, and more. Learn about sensory and motor nerve supplies, arterial supply, venous drainage, and lymphatics of the ear. Delve into the structures of the middle ear and inner ear, including the bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth. Discover the complexities of this vital sensory organ and its functions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
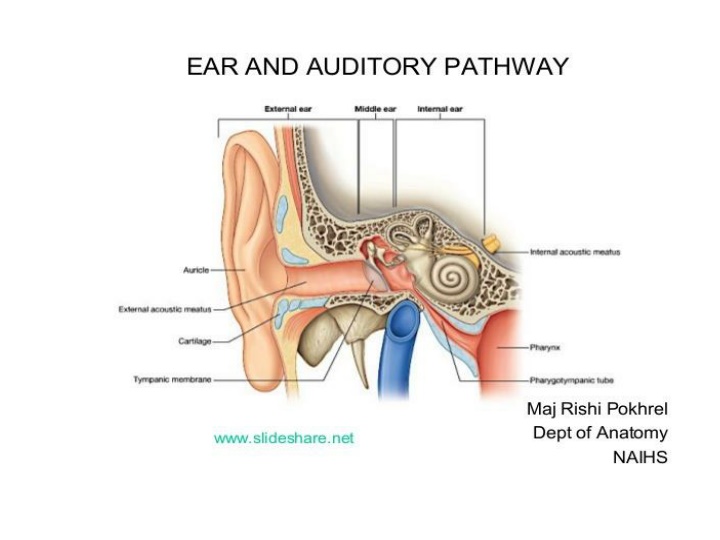
The Auricle: helix, crus of helix, tragus, lobule, antihelix, triangular fossa, antitragus, concha, Ext. aud. Canal opening
The External Auditory Canal (EAC): 24 mm 1-Outer 1/3: Cartilaginous part: hair follicles, sebaceous glands, cerumen glands The wax: is hydrophobic, acidic & with antibacterial properties, the epithelium of the EAC has the capacity to migrate. 2- Inner 2/3: Bony part
NERVE SUPPLY OF EXTERNAL EAR: 1. Auriculo-temporal nerve (V3) 2. Greater Auricular (C2, 3) 3. Lesser Occipital (C2 ) 4. Arnold`s nerve (X) 5. Facial nerve (sensory twigs) BLOOD SUPPLY OF EXTERNAL EAR: branches of external carotid artery Venous drainage: to posterior auricular & superficial temporal veins Lymphatic drainage: to pre-auricular, infra- auricular & mastoid lymph nodes.
THE MIDDLE EAR CLEFT Comprises of: 1. Middle Ear Proper 2. Aditus & Mastoid Antrum and Mastoid air cells 3. Eustachian Tube Upper 1/3: Bony Lower 2/3: Cartilaginous
THE MIDDLE EAR PROPER: a box of 6 walls, is an air-containing space with bony walls except laterally by TM. Lateral, medial, anterior, posterior, superior, inferior boundieries
Sensory nerve supply of the middle ear: Jocobson`s nerve, a branch of IX (Glossopharyngeal nerve), Motor supply of middle ear muscles: by V & VII cranial nerves. Arterial supply of middle ear: from branches of external & internal carotid arteries Venous drainage: to pterygoid plexus or superior petrosal sinus Lymphatics: to retropharyngeal lymph node
Inner ear 1. Bony Labyrinth :comprises of A. Bony Semicircular Canals (SCCs) , B. vestibule, C. Cochlea
2. Membranous Labyrinth: comprises of A. Membranous SCCs, B. Utricle & Saccule , C. Cochlear Duct triangular in cross section ( Organ of Corti ), D. Endolymphatic Duct & Sac , E. Ductus Reuniens