Android Activities, States, and Event Handlers
Learn about the lifecycle of Android activities, their states, and how event handlers can help monitor state changes. Explore designing a GUI for a TipCalculator app using TableLayout and event handling in this informative guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
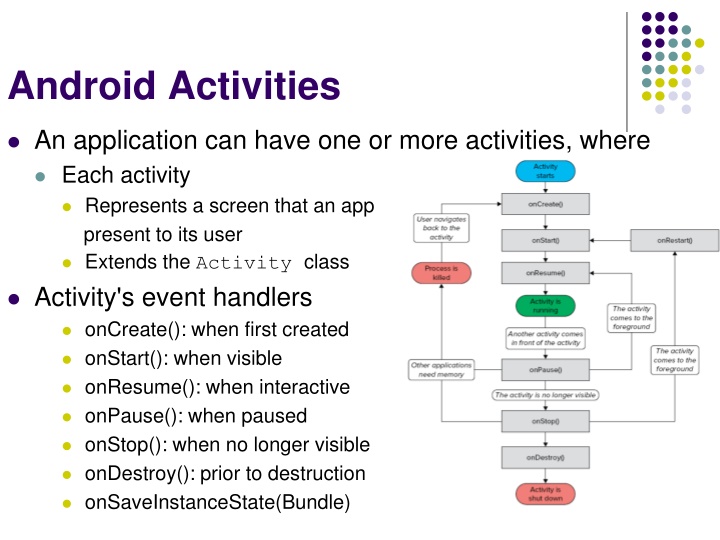
Android Activities An application can have one or more activities, where Each activity Represents a screen that an app present to its user Extends the Activity class Activity's event handlers onCreate(): when first created onStart(): when visible onResume(): when interactive onPause(): when paused onStop(): when no longer visible onDestroy(): prior to destruction onSaveInstanceState(Bundle)
Activity States The state of an activity depends on Its position in the Activity stack Activity states Active Activity at the top of the stack Paused Activity does not have focus Stopped Activity is not visible Inactive After an activity has been killed
Event Handlers to Monitor State Changes Event handlers are defined to Enable activities to react to state changes Full lifetime: Between onCreate and onDestroy Visible lifetime: Bound between onStart and onStop Active lifetime Starts with onResume and ends with onPause
TipCalculator App (Chapter 4 of Android how to Program book) Objectives Design a GUI using a TableLayout. Use the ADT Plugin s Outline window in Eclipse to add GUI components to a TableLayout. Directly edit the XML of a GUI layout to customize properties that are not available through the Visual Layout Editor and Properties window in Eclipse. Use TextView, EditText and SeekBar GUI components. Use event handling to respond to user interactions with an EditText and a SeekBar. Refer to TipCalculatorApp android project
