Angle Modulation: Frequency and Phase Variations
Angle modulation involves varying the frequency or phase of a carrier signal based on the modulating signal. Frequency Modulation (FM) and Phase Modulation (PM) are types of angle modulation that offer better noise discrimination. This results in improved robustness against interference but comes at the expense of increased bandwidth. By exchanging channel bandwidth for noise performance, angle modulation provides a trade-off not possible with Amplitude Modulation (AM). Explore the relationship between angle and frequency signals, as well as the distinction between FM and PM in carrier signal modulation. Gain insights into the instantaneous frequency and phase deviations in angle modulation systems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
FREQUENCY AND PHASE MODULATION (ANGLE MODULATION)
ANGLE MODULATION When frequency or phase of the carrier is varied by the modulating signal , then it is called angle modulation. Frequency Modulation When the frequency of the carrier varies as per amplitude of modulating signal, then it is called frequency modulation (FM). Phase Modulation - When the phase of the carrier varies as per amplitude of modulating signal, then it is called phase modulation (PM). Amplitude of the modulated carrier remains constant in both modulation systems. BDG(xx) 2
An important feature of angle modulation: It can provide a better discrimination (robustness) against noise and interference than AM. This improvement is achieved at the expense of increased transmission bandwidth. In case of angle modulation, channel bandwidth may be exchanged for improved noise performance Such trade-off is not possible with AM BDG(xx) 3
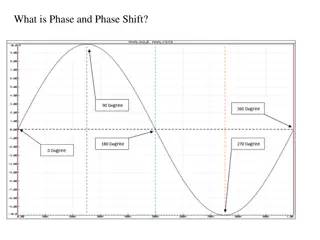
BASIC DEFINITIONS -Relationship between the angle and frequency of a sinusoidal signal Sinusoidal carrier c(t) =Ac cos[ i(t)] Angle of carrier i(t)[rad] Instantaneous frequency of carrier fi(t) =(1/2 ) i(t) =(1/2 )di(t)/dt =(1/2 ) i(t)[Hz]. In the case of an un-modulated carrier, the angle becomes i(t) = 2 fct + c BDG(xx) 4
Time domain representation BDG(xx) 5
Compare FM-PM The basic difference between FM & PM lies in which property of the carrier is directly varied by modulating signal. In FM, the frequency of carrier is varied directly. In PM, phase of the carrier is varied directly. Instantaneous phase deviation is represented by (t). Instantaneous phase= ct + (t) rad. BDG(xx) 6
Instantaneous frequency deviation = d/dt { (t)} = (t) Hz. The instantaneous frequency deviation is the instantaneous change in carrier frequency and is equal to the rate at which instantaneous phase deviation takes place. Instantaneous frequency is defined as frequency of the carrier at a given instant of time and is given as i(t) =d/dt [ c.t + (t)] = c + (t) rad/sec. BDG(xx) 7
Instantaneous phase deviation (t) is proportional to modulating signal voltage, (t) = k em(t) rad. ( k is deviation sensitivity of phase). Instantaneous frequency deviation (t) is proportional to modulating signal voltage, (t) = k1 em(t) rad. ( k1 is deviation sensitivity of frequency. BDG(xx) 8
Observations from the FM & PM waveforms 1. Both FM & PM waveforms are identical except the phase shift. 2. For FM, the maximum frequency deviation takes place when modulating signal is at +ve and ve peaks. 3. For PM, the maximum frequency deviation takes place near zero crossing of the modulating signal. 4. It is difficult to know from modulated waveform whether the modulation is FM or PM. BDG(xx) 11
Bandwidth Requirement for FM- The BW requirement can be obtained depending on the modulation index (M.I). The M.I. can be classified as high(more than 10), medium (1 to 10) and low (less than 1). The low index systems are called narrowband FM in which frequency spectrum resembles AM. BW (fm) =2fm Hz. For high index modulation, BW = 2* .(Freq. dev.) BW can also be found out by Bessel table- BWfm = 2.n.fm where n is the number of sidebands obtained from table. BDG(xx) 12
Carsons Rule Rule gives approximate minimum BW of angle modulated signal as BW fm = 2{ + fm(max)} Hz. From the above equation, it is found that the BW accommodates almost 98% of the total transmitted power BDG(xx) 13
Bandwidth for PM BW for PM is expressed as BWpm = 2(mp+1)fm. BDG(xx) 14
Wideband Frequency Modulation If the modulation index is higher than 10, then it is called wideband FM. Spectrum contains infinite numbers of sidebands and carrier as against two sidebands and carrier in NBFM. BW is = 2{ +fm(max)} as against 2fm for NBFM. Used for broadcast and entertainment as against for mobile communication for NBFM. BDG(xx) 16
Advantages of Angle Modulation over AM- 1. As the amplitude of FM carrier is constant, the noise interference is minimum. 2. The amplitude of FM carrier is constant and is independent of depth of modulation. Hence transmitter power remains constant in FM whereas it varies in AM. 3. As against the limitation of depth of modulation in AM, in FM depth of modulation can be increased to any value, without causing any distortion. BDG(xx) 17
4. Because of guard bands provided in FM, adjacent channel interference is very less. 5. Since FM uses VHF and UHF bands of frequencies, the noise interference is minimum as compared to AM which uses MF and HF ranges. 6. Radius of propagation is limited as FM uses space waves with line of sight. So it is possible to operate many independent transmitters on the same frequency with minimum interference. BDG(xx) 18
Disadvantages of FM compared to AM- 1. BW requirement of FM is very high as compared to AM. 2. FM equipments are more complex and hence costly. Area covered by FM is limited, to line of sight area but AM coverage area is large. BDG(xx) 19
Comparison between FM and AM - Parameter AM FM Origin AM method of audio transmission was first successfully carried out in the mid 1870s. FM radio was developed in the United states mainly by Edwin Armstrong in the 1930s. Modulating differences In AM, a radio wave known as the "carrier" or "carrier wave" is modulated in amplitude by the signal that is to be transmitted It is used in both analog and digital communication and telemetry In FM, a radio wave known as the "carrier" or "carrier wave" is modulated in frequency by the signal that is to be transmitted. It is used in both analog and digital communication and telemetry Importance Frequency Range AM radio ranges from 535 to 1705 KHz (OR) Up to 1200 Bits per second. FM radio ranges in a higher spectrum from 88 to 108 MHz. (OR) 1200 to 2400 bits per second. BDG(xx) 20
Comparison between FM and AM - Parameter AM FM Bandwidth Requirements Twice the highest modulating frequency. In AM radio broadcasting, the modulating signal has bandwidth of 15kHz, and hence the bandwidth of an amplitude-modulated signal is 30kHz. Twice the sum of the modulating signal frequency and the frequency deviation. If the frequency deviation is 75kHz and the modulating signal frequency is 15kHz, the bandwidth required is 180kHz. Complexity Transmitter and receiver are simple but synchronization is needed in case of SSBSC AM carrier. Transmitter and receiver are more complex as variation of modulating signal has to be converted and detected from corresponding variation in frequencies.(i.e. voltage to frequency and frequency to voltage conversion has to be done). FM is less susceptible to noise because information in an FM signal is transmitted through varying the frequency, and not the amplitude. Noise AM is more susceptible to noise because noise affects amplitude, which is where information is "stored" in an AM signal. BDG(xx) 21
Comparison between FM and PM - Sr No. FM PM 1 The max frequency deviation depends on amplitude of modulating signal and its frequency The max phase deviation depends on amplitude of modulating signal 2 Frequency of the carrier is modulated by modulating signal. Phase of the carrier is modulated by modulating signal. 3 Modulation index is increased as modulation frequency is reduced and vice versa. Modulation index remains same if modulating signal frequency is change. BDG(xx) 22
TWO types of FM Modulators 1. Indirect FM Modulation is obtained by phase modulation of the carrier. An instantaneous phase of the carrier is directly proportional to the amplitude of the modulating signal. 2. Direct FM- The frequency of carrier is varied directly by modulating signal. An instantaneous frequency variation is directly proportional to the amplitude of the modulating signal. BDG(xx) 23
FM Transmitters Two types of transmitters Indirect FM and Direct FM Transmitters. Indirect FM Transmitters Produces the FM whose phase deviation is directly proportional to modulating signal amplitude. Frequency of oscillator is not directly varied. Hence crystal oscillators can be used. Direct FM Transmitters Frequency deviation is directly proportional to modulating signal. Carrier frequency is directly deviated. BDG(xx) 24
Need for Automatic Frequency Correction In FM transmitters, the frequency of the oscillator is directly varied. To obtain very stable frequency of oscillator, automatic frequency correction technique is employed. BDG(xx) 25