Arduino Microcontroller Workshop at UMBC Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Presentation
"Join the technical skills series presentation at UMBC Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers on Arduino programming with Piezo. Topics covered include Arduino coding basics, analog & digital signals, piezoelectric sensors, and pulse width modulation. Learn important functions and practical applications. Check out the program details and essential concepts discussed in this engaging workshop."
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
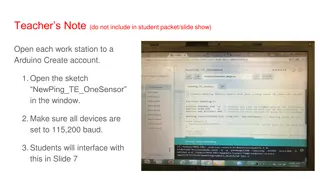
Arduino Microcontroller Workshop UMBC Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Sekar Kulandaivel sekark1@umbc.edu Week 2: Arduino Programming with Piezo Technical Skills Series Presentation Arduino UMBC IEEE April 8th 9th, 2014
Topics to Cover Arduino Coding Basics & Functions Analog & Digital Signals Piezoelectric Sensors Pulse Width Modulation
4th band is Tolerance. L R Color Black Brown Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Violet Gray White 1st Digit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2nd Digit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Multiplier 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109
330 x 101 = 3 3 10k x 103 = 0 1 2k x 102 = 0 2 1M x 105 = 0 1
Important Functions int val, time; void setup() { } void loop() { } Serial.begin(9600); Serial.print( Hello ); Serial.println( Hi ); delay(1000); map(var, testLow, testHigh, mapLow, mapHigh); tone(8, pitch, time); pinMode(8, INPUT); pinMode(9, OUTPUT); val = digitalRead(8); digitalWrite(9, out); val = analogRead(A0); analogWrite(9, out); time = millis();
const int sensorPin = 8; int sensorValue; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); } void loop() { sensorValue = digitalRead(sensorPin); Serial.println(sensorValue); delay(25); }
const int sensorPin = 8; const int outputPin = 9; int sensorValue; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); pinMode(outputPin, OUTPUT); } void loop() { sensorValue = digitalRead(sensorPin); Serial.println(sensorValue); if (sensorValue == HIGH) { digitalWrite(outputPin, HIGH); delay(500); digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); } delay(25); }
const int sensorPin = A0; const int outputPin = 9; int sensorValue; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); pinMode(outputPin, OUTPUT); } void loop() { sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); Serial.println(sensorValue); analogWrite(outputPin, sensorValue); delay(25); }
const int sensorPin = A1; const int outputPin = 9; int sensorValue; int low = 300; int high = 450; int range[2] = {0, 255}; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); pinMode(outputPin, OUTPUT); } void loop() { sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); Serial.println(sensorValue); sensorValue = map(sensorValue, low, high, range[0], range[1]); analogWrite(outputPin, sensorValue); delay(25); }
const int sensorPin = A1; const int outputPin = 11; int wait = 25; int sensorValue, pitch; int range[2] = {1023, 0}; int minTone = 500; int maxTone = 1500; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); pinMode(outputPin, OUTPUT); while (millis() < 3000) { sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); if (sensorValue < range[0]) { range[0] = sensorValue; } if (sensorValue > range[1]) { range[1] = sensorValue; } } }
void loop() { sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); Serial.println(sensorValue); pitch = map(sensorValue, range[0], range[1], minTone, maxTone); tone(outputPin, pitch, wait); delay(wait); }
Challenge Requirements: 1. Sense a knock using the piezoelectric sensor. 2. Flash LED once for a soft knock. 3. Flash LED twice for a loud knock. Analog Notes: Remove photoresistor and potentiometer circuits from your board. Knock on the breadboard or tap the piezo for the best results. Utilize previous code as a guide for your project.