Aromatic Electrophilic Substitution: Nitration Mechanism
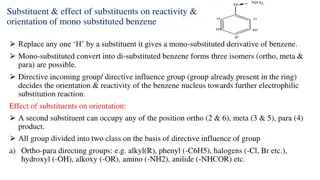
Aromatic electrophilic substitution involves nitration of arenes by introducing a nitro functional group using nitric and sulfuric acid. This process generates a reactive electrophile known as nitronium ion. The mechanism of nitration shows the generation of nitronium ion from various nitrating agents.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Aromatic Electrophilic Substitution by Dr. Atul Kumar Singh Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry M. L. Arya College, Kasba Purnia -854330 India
Nitration Introduction of an nitro functional group into an aromatic ring using a mixture of nitric and sulphuric acid (or other reagent) is known as nitration of arenes.
The reactive electrophile i.e. the active nitrating agent is a nitronium ion. Generation of nitronium ion from Conc. or fuming Nitric acid Generation of nitronium ion from N2O5 and CCl4
Generation of nitronium ion from mixture of Nitric acid and sulphuric acid