Arterial Blood Pressure Regulation Mechanisms and Long-Term Control
Learn about the short-term and long-term regulation of arterial blood pressure through baroreceptor mechanisms and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Explore the role of carotid sinus, low-pressure receptors, and chemoreceptors in maintaining blood pressure stability.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
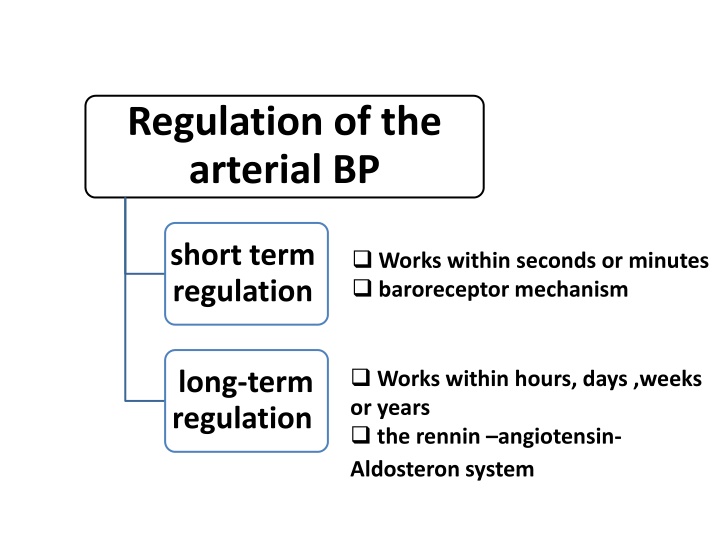
Regulation of the arterial BP short term regulation Works within seconds or minutes baroreceptor mechanism Works within hours, days ,weeks or years the rennin angiotensin- Aldosteron system long-term regulation
Baroreceptor mechanism Baroreceptors high pressure receptors Low pressure receptors Right atria Left atria pulmonary veins carotid sinus aortic arch
carotid body Int carotid A Ext carotid A carotid sinus Common carotid A Aortic body Aortic arch
Mechanism of transduction AP Stretch receptor stretch activated Na channels
Reflexes initiated by stretching of the baroreceptors NTS Medulla oblongata VMC CIC CEC
rate Medulla oblongata Cardiorequlatory center & VMC rate Symp n rate Symp chain Blood vessels
Function of the baroreceptors during changes in body posture. Standing BP pooling of blood in the lower extremities C.O. symp outflow. C.O. baroreceptors discharging rate BP
carotid sinus massage press on the carotid sinus baroreceptors discharging rate inhibition of CEC stimulation of CI.C HR & BP
Control of arterial pressure by the carotid & aortic chemoreceptors carotid body aortic bodY
Long-term regulation The rennin angiotensin aldosteron system Lets start the journey
Structure of nephron Distal convoluted tubules Afferent a.a Glomerulus Bowman's capsule Collecting duct efferent a.a Juxtaglomerular apparatus Proximal convoluted tubules Loop of Henle
The liver circulation Renin
In the lung 00 Angiotensin I Angiotensin II ACE 00
Adrenal gland Adrenal cortex Z. Glomerulosa Adrenal medulla Mineralocorticoids Mainly aldosteron Z. Fasiculata glucocorticoids Z. Reticularis androgens
Mechanism of action of aldosterone Interstitial renal fluid Tubular lumen Tubular cell K K K Na-k pump Na Na water Na water
kidney angiotensinogen liver Renin Angiotensin I ACE Vasoconstriction Stim. thirst center + Vasopressin Na and water reabsor. blood volume BP
