Arylation Reactions: Mechanism and Applications
Arylation reactions involving diazonium salts play a significant role in organic chemistry, specifically in the arylation of aromatic compounds. The Gomberg-Bachmann reaction and Sandmayer reaction are important examples, each with its specific mechanism and applications. Understanding these reactions is crucial for synthesizing aryl chlorides or bromides, and exploring their potential in organic synthesis.
Uploaded on Feb 24, 2025 | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The H.N.S.B. Ltd. Science College, Himatnagar Class Seminar Semester-2 Year: 2010-2011 Paper: CHN-502 Organic Chemistry Unit:4 (B) Chapter Name : Free Radical Reactions Topic Name : ARYLATION REACTION
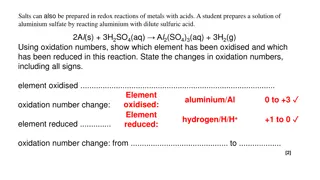
ARYLATION OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS BY DIAZONIUM SALTS - + - OH Ar H + ArN 2X Ar Ar When diazonium salt solution is made alkaline, the aryl portion of the diazonium salts can couple with another aromatic ring. This reaction is known as the Gomberg or Gomberg-Bachmann reaction, and has been performed on several types of aromatic rings and or quinones. When the Gomberg-Bachmann reaction is performed intramolecularly, either by the alkaline solution or by the copper ion procedure, it is called Pschorr ring closure. Z Z + N 2 [Z CH CH, CH 2CH 2, NH, C O, CH2]
Mechanism of Gomberg or Gomberg-Bachmann reaction: - Ar N N OH + - OH Ar N N OH ArN 2X -H 2O Ar N N O N N Ar (Anhydride) Ar . + O. N N Ar Ar N N O N N Ar The aryl radical thus formed attacks the substrate to give the intermediate II, from which the radical (I) abstracts hydrogen to give the product. It has been shown that whatever is the nature of a substituent (R) in the substrate, ortho or para substitution always predominates, but small amount of meta product is also formed.
Ar H Ar . Ar N N O. Ar. + + Ar N N OH R R Sandmayer Reaction : + - CuX ArX + N 2 ArN 2X Treatment of diazonium salts with cuprous chloride or bromide gives aryl chlorides or bromides, respectively. This reaction is called the Sandmayer reaction. The reaction can also be carried out with copper and HBr or HCl, in this case it called the Gattermann reaction. The Sandmayer reaction is not useful for the preparation of fluorides and iodides, but it is probably the best way of introducing bromine or chlorine into an aromatic ring.
Mechanism :The reaction involves two steps. The first step is the reduction of diazonium ion by cuprous ion to give an aryl radical : + - Ar. + N 2 + CuX 2 ArN 2X + CuX In the second step, the aryl radical abstracts halogen from cupric chloride, reducing it. CuX is regenerated and is thus, a true catalyst. Ar.+ CuX2 Ar X + CuX