Beneficial Resource Unit Allocation in IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Document
"Explore the advantages of multiple resource unit allocation in the IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 document for TGax OFDMA systems, highlighting system simulations and interleaver design enhancements. The content delves into both contiguous and non-contiguous RU allocation scenarios, addressing questions on interleaver impact and system throughput."
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
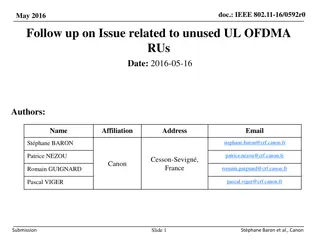
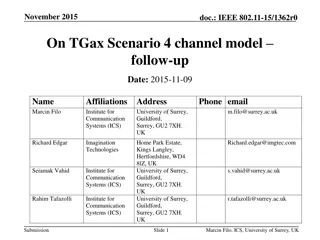
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Multiple Resource Unit Allocation for TGax OFDMA Date: 2015-09-12 Authors: Name Kome Oteri Alphan Sahin Affiliations Address InterDigital Communication Inc. Phone 858 210 4826 Kome.oteri@interdigital.com email 9710 Scranton Road, San Diego, CA, 92121 Chunhua Geng Rui Yang Robert Olesen Submission Slide 1 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Outline Motivation Existing design and open questions System Level Simulation assumptions and results Link Level Simulation assumptions and results Conclusion Submission Slide 2 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Motivation Show potential benefits of multiple RU allocation over single user allocation via system simulations. Identify need for updated interleaver design to enable multiple RU allocation Show potential benefits of non-contiguous multiple RU allocation over contiguous multiple RU allocations via system and link level simulations Submission Slide 3 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Existing Design OFDMA Numerology and Structure [1] PHY #10: Define 20MHz, 40 MHz, 80MHz, 160MHz / 80MHz + 80MHz OFDMA building blocks Numerology for 20MHz Interleaver and Tone Mapper for OFDMA [2] PHY #33: The BCC interleaver and LDPC parameters to be defined in the table below tone mapper BCC Interleaver and LDPC Tone Mapper Submission Slide 4 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Open Questions Q: Should we allocate more than one RU per user ? Q: If multiple RUs can be allocated per user, how does this affect the interleaver design? Observation: current design does not take all multiple RU allocation scenarios into consideration e.g. 3 x 26-tone RU allocation Q: If multiple RUs per user are allocated, should those RUs be contiguous or non-contiguous ? DL OFDMA Signalling [3] SP1: Do you think we should be able to express non-contiguous RU allocation? Y:N:A = 46:22:54 Submission Slide 5 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Study Outline Study system throughput performance in SS1 and SS3 for Single RU allocation Multiple RU allocation : contiguous Multiple RU allocation : non-contiguous Study link level performance for MCS 7 in Channel D Multiple RU allocation : contiguous Multiple RU allocation : non-contiguous Submission Slide 6 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 System Throughput Simulation Assumptions No MAC protocol overhead assumed STAs are located based on specific TGax simulation scenarios [4] 20 MHz 80 MHz Table derived from [8] Submission Slide 7 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Scheduler (20 MHz) 20 MHz Numerology Resource allocation for single RU allocation Resource allocation for Contiguous Case Resource Allocation for Non-contiguous Case Submission Slide 8 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 20 MHz Results (System Simulations) bps Legend sRU: Single RU Allocation C: Multiple RU Contiguous Allocation NC: Multiple RU Non-contiguous Allocation Performance gains for multiple RU non-contiguous allocation over single RU and multiple RU contiguous allocation can be observed Submission Slide 9 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 80 MHz Results (System Simulations) bps Legend sRU: Single RU Allocation C: Multiple RU Contiguous Allocation NC: Multiple RU Non-contiguous Allocation Larger gains for multiple RU non-contiguous allocation over single RU and multiple RU contiguous allocation overlargerbandwidth can be observed Submission Slide 10 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Link Level Simulation Assumptions Submission Slide 11 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Link Level Contiguous/Non-Contiguous Allocation Gains observed for non-contiguous over contiguous at the link level Submission Slide 12 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
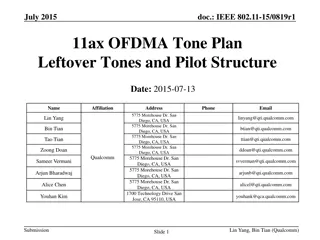
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Multiple RU Interleaving Q: How do we perform interleaving in multiple RU allocation ? Reuse design in [2] with a multiplexer (S/P) and de-multiplexer (P/S) Interleaver Frequency RU1 . . . Parser S/P P/S Space-Time Block Encoder Spatial Stream Parser RUM Interleaver Scrambler BCC Encoder Antenna Map . . . Interleaver Frequency RU1 QAM Map Parser . . . S/P P/S RUM Interleaver Submission Slide 13 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Conclusions Multiple RU allocation shows benefits over single RU allocation in some system level simulation scenarios (SS3) Non-contiguous multiple RU allocation shows benefits over contiguous multiple RU allocation The interleaver design should be updated to allow for multiple RU allocation Submission Slide 14 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Straw Poll #1 Do you agree to add to the TG Specification Framework? The amendment shall allow multiple RUs to be allocated to a single user Y/N/A Submission Slide 15 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Straw Poll #2 Do you agree with the following? The design of the interleaver shall be updated to allow for multiple RU allocations that are not captured in the current interleaver design Y/N/A Submission Slide 16 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Straw Poll #3 Do you agree to add to the TG Specification Framework? The amendment shall allow for non-contiguous allocation of multiple RUs to a single user Y/N/A Submission Slide 17 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 11-15-0330-05-00ax-ofdma-numerology-and-structure.pptx 11-15-0816-00-00ax-interleaver-and-tone-mapper-for-ofdma.pptx 11-15-0854-02-00ax-dl-ofdma-signalling.pptx 11-14-0980-14-00ax-simulation-scenarios.docx 11-14-0882-04-00ax-tgax-channel-model-document.docx Submission Slide 18 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Additional Material Submission Slide 19 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Granularity Definition @ Receiver: Instantaneous rates on the sub-channels (based on feedback granularity (FG)) are calculated and fed back to the transmitter. @ Transmitter: Instantaneous rates on the RUs (based on RU granularity (RG)) are calculated for each station and proportional fair scheduling is performed. Other users may use different granularity. Submission Slide 20 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Gain Definitions %28.5 %29.5 %1.9 Ref:C Ref:R NC: Non-contiguous allocation C: Contiguous allocation R: Random allocation Submission Slide 21 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 SISO Result Details NC: Non-contiguous allocation C: Contiguous allocation R: Random allocation Submission Slide 22 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 MIMO Result Details NC: Non-contiguous allocation C: Contiguous allocation R: Random allocation Submission Slide 23 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)
Sept 2015 doc.: IEEE 802.11-15/1057r0 Simulation Methodology of System Throughput Obtain per tone SINR of STAs based on path loss and shadowing of specific simulation scenario [12] and fading channel [2] Estimate effective SINR of sub-channels based on the specific numerology using the capacity mapping in [11] at the receiver Send these to the transmitter using the desired FG Perform proportional fair scheduling at the transmitter based on effective SINR of different sub-channels at the desired RG [9] Assign users to sub-channels Estimate PHY layer system throughput based on capacity of chosen users Average over multiple drops Submission Slide 24 Kome Oteri (InterDigital)