Beta Adrenergic Blockers
Outline the mechanisms of action of Beta-blockers, classify them into selective & non-selective categories, understand their pharmacokinetic aspects, and identify specific uses. Explore mnemonics for drug names, pharmacodynamic effects, and pharmacokinetic classification based on lipid solubility. Learn about the pharmacological actions of Beta-adrenergic blockers on cardiovascular function and receptor distribution in various tissues.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
8 # Beta Adrenergic Blockers Objectives: Outline the mechanisms of action of B-blockers. Classify B-receptor blockers into selective & non- selective. Know the pharmacokinetic aspects & pharmacodynamic effects of B- adrenergic blockers. Identify the specific uses of non selective and selective B -adrenergic blockers. Editing File Main Text Female Slides Male Slides Important Doctors Notes Extra Foda s videos: Click here for video timestamps First Second
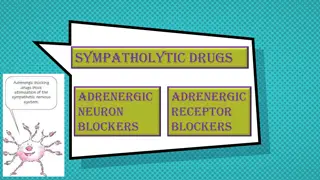
-Adrenoceptor Blockers Mnemonics (only for drugs mentioned in this lecture): All -blockers end in olol exceptmixed All cardioselective Cardioselectively thanks to Abdullah Alomran! All non-selective srekcolb end in lol only . - A srettel eht htiw nigeb srekcolb M Exclusive Beta Blockers Are Acting Mainly O srettel eht htiw nigeb srekcolb - Z ( . )tebahpla eht fo flah dnoces = 2 Pharmacodynamic Classification According to selectivity Non-selective -antagonists blocks 2 & 1 receptors stop O Z (Sotalol, Timolol (eye),Oxprenolol, Propranolol, Pindolol) Selective 1 antagonists )cinegoidraC( Acebutolol,Atenolol,Bisoprolol,Betaxolol,Celiprolol,Esmolol,Metoprolol A M ABCEM Mixed , Receptors Blockers Carvedilol,Labetalol According to presence of agonistic/antagonistic action Intrinsic Sympathomimetic Activity )ASI( Without ISA)stsinogatna eruP( Atenolol,Bisoprolol,Metoprolol,Propranolol,Sotalol,Timolol,Carvedilol With ISA )rotpecer ateb etavitca yam( Acebutolol,Pindolol,Oxprenolol,Celiprolol According to presence of membrane stabilizing effects Effect : - Block Na Channels( makes muscle cells unresponsive to pacemaker stimulation potential -Quinidine-like action (Quinidine is a class of antiarrhythmic drugs) -Antiarrhythmic action. excitability no action contraction of muscles) Drugs: Propranolol,Labetalol -Mnemonic : COntainPartial AgonisticActivity : Celiprolol+ Oxprenolol+ Pindolol+ Acebutolol -Extra note .noitcirtsnocosav larehpirep ssel & aidracydarb ssel esuac yehT .IM fo noitneverp yradnoces ro aidracydarb citamotpmys poleved ohw stneitap ni lufesu eb yam siht ,revewoH ralucitrap ni elbarovaf ASI sekam hcihw ,srekcolb sesac -Never use ISA drugs with angina, arrhythmia, & myocardial infarction (we do not want any simple stimulation). srekcolb - ateB : with ISA eht ni stsinogatna erup eht sa evitceffe sa eb ton yam With ISA = yllaitrap B etavitca srotpecer yam - ateb ot esnopser ni noitcirtsnocohcnorb .
Pharmacokinetic Classification According to lipid solubility Oral absorption Liver metabolism (most are excreted in urine) t1/2 CNS side effects CNS depressant effects i.e. Sedative effect Anxiety Drugs Drug Lipophilic Complete given orally Yes Short High Metoprolol,Labetalol ,Propranolol,Carvedilol, Timolol undergo hepatic clearance Hydrophilic Irregular given IV No Long Except Low Bisoprolol,Atenolol, Sotalol, Esmolol undergo renal clearance Esmolol(10min. given IV Most blockers are lipid soluble To sum up thanks to team411 Drugs: 14 Membrane stabilizing effects Sympathomimetic Activity )ASI( Selectivity Lipid solubility ) ( Sotalol without ISA Hydrophilic without ISA Lipophilic Timolol Non selective - Antagonists Oxprenolol with ISA Propranolol without ISA Present Lipophilic Pindolol with ISA Acebutolol with ISA Atenolol without ISA Hydrophilic Bisoprolol without ISA Hydrophilic Betaxolol Selective -1 Celiprolol with ISA Esmolol Hydrophilic Metoprolol without ISA Lipophilic Mixed Carvedilol without ISA Lipophilic nonselective - Labetalol with ISA Present Lipophilic
Pharmacological actions CVS have negative inotropic (force of contraction), chronotropic (HR), dromotropic (conduction velocity) COP (cardiac output) 1 receptors are found in the heart & JG cells in the kidney 2 receptors are found in the bronchi, blood vessels, liver, skeletal muscles 3 receptors are found in adipose tissue CVS 1 -Antianginal effects (ischemic heart disease): consumption due to bradycardia -Anti-arrhythmic effects: excitability, automaticity & conductivity (due to its sympathetic blocking.) Heart rate (bradycardia) Oxygen Force of contraction Cardiac work -Blood pressure: Antihypertensive BP in hypertensive patients due to effects on: Inhibiting heart properties secretion ( 1 ) Presynaptic inhibition of NE release from adrenergic nerves cardiac output ( 1 ) edakcolB renin secretion Ang II & aldosterone sympathetic -Blood vessels ( 2 ) : Block vasodilatory effect of extremities contraindicatedin peripheral diseases like Raynaud's disease Eye 2 peripheral resistance (PR) blood flow to organs cold 2 Aqueous humor production from ciliary body thus reduces intraocular pressure( IOP) e.g. Timolol (The only drug from blockers used for glaucoma) )pord eye rof emit : cinomenm ( spord eye sa 3 Respiratory tract 2 Bronchoconstriction contraindicated in asthmatic patients (unless if selective 1 blockers were given not 2 ) Metabolic effects & intestine 4 Hypoglycemia due to Glycogenolysis in liver & Glucagon secretion in pancreas All mask hypoglycemic manifestations in diabetic patients COMA Na+ retention 2ndry to BP srekcolb as a reflex (to restore BP). Renin will aldosterone, which in turn causes Na & water retention . Lipolysis in adipocytes renal perfusion. cardiac output, which lowers the BP & renal perfusion.This will cause renin to be Intestinal motility
Cardiovascular disorders Clinical Uses In supraventricular Bisoprololand Carvedilol are preferred B-blockers are class II antiarrhythmic agents & are used for tachyarrhythmias only. (Give ones with a quinidine like effect) . saimhtyhrra ralucirtnev & )selcirtnev ni( )selcirtnev evoba( Cardiac Arrhythmias Propranolol, Atenolol, Bisoprolol Labetalol: , blocker in hypertensive pregnantnseod( it crosses BBB, if methyldopa doesn t work) & hypertensive crisis parenterally).[very important] t harm the baby although ti esuaceb Hypertension ( s given heart rate, cardiac work & oxygen demand. the frequency of angina episodes. Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Metaprolol ( 1 selective) Angina: a condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often also spreading to the shoulders, arms, and neck, owing to an inadequate blood supply to the heart. Angina pectoris Congestive heart failure )Heart failure with edema) Bisoprolol & Metoprolol ( 1 selective) Carvedilol & rekcolb , evitceles noN: antioxidant fo gurd( choice), artxe na effect ) ( myocardial remodeling & risk of sudden death infarct size, morbidity & mortality, myocardial O2 demand. (Cardioprotective effect) Antiarrhythmicaction . Myocardial infarction incidence of sudden death. Other disorders e.g. Timololas eye drops Chronic Glaucoma secretion of aqueous humor by ciliary body. Intraocular pressure (IOP) Anxiety (Social & performance type) eg. Propranolol Controlssymptoms due to sympathetic system stimulation as tachycardia, tremors, sweating (somatic symptoms ) ( ) Protect the heart against sympathetic overstimulation cause by overproduction of thyroid hormone (thyrotoxicosis) Controls symptoms; Tachycardia - Tremors -Sweating Propranolol is the drug of choice. Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis) Prophylactic propranolol. A migraine is due to vasodilation episodes of chronic migraine catecholamine-induced vasodilatation in the brain vasculature , e.g. Migraine Pheochromocytoma A small vascular tumor of the adrenal medulla, causing irregular secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine, leading to attacks of raised blood pressure, palpitations, and headache Used with -blockers (never alone) >= noitcirtsnocosav sesuac ti enola esuaceb , tnaw ew tahw fo tceffe etisoppo eht si hcihw PB sesaercni detavele eht traeh eht tcetorp srekcolb rewol srekcolb - blood pressure from NE. -
Thanks to Team 439 ! ADRs of -blockers Note: if no receptors are written then both receptors are involved Mnemonic: C THE BALD FISH Cold extremities Coronary spasm Variant angina is a type of angina where common atherosclerotic risk factors do not usually apply. 2 ) 2 ) ( ( due to vasoconstriction ( blood flow). in variant angina patients c T Triglycerides (TG) Hypertriglyceridemia 2 ) ( Hypotension Heart failure Hypoglycemia Hallucinations gurd eht fi was lipophilic 1 ) 1 ) 2 ) ( ( H ( E Erectile dysfunction & impotence 2 ) ( due to blood flow (vasoconstriction). Bradycardia or heart block Bronchoconstriction (Both are less pronounced with -blockers with ISA) 1 ) ( ( B 2 ) contraindicatedin asthma &emphysema A L Arrhythmia Lack of energy Depressionif the drug was lipophilic Disturbanceof GIT D F Fatigue I Intermittent claudication (limping) 2 ) ( due to vasoconstriction s Sodium Retention H - 2 adverse effects are only with non-selective srekcolb However, the cardioselectivity of 1 blockers decreases at high doses. - Thus, regular monitoring of blood glucose (especially in diabetic pts) is recommended. . All srekcolb mask hypoglycemic manifestations i.e. tachycardia, sweating COMA. Precautions Sudden stoppage will give rise to a withdrawal syndrome: rebound angina, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction & hypertension. Why? due to up-regulation of -receptors Prolonged blockade can cause a compensatory rise in receptors. Abrupt termination then leads to increased sympathetic activity (rebound reaction). To prevent withdrawal manifestations the drug is withdrawn gradually. Applies to 2 classes of drugs: ( ) . sdioretsocitroc + srekcolb -
Propranolol (prototype) Labetalol Carvedilol Drug . Non-selective Ends in lol only mixed No ISA & no local anesthetic effect Antioxidant action Patients who have heart failure have COP. Normally, when there is a decrease in COP, the sympathetic system gets activated which stimulate eht ,FH sah tneitap eht esuaceb naht troffe erom gnitrexe si traeh esuac lliw hcihw lamron lliw hcihw traeh eht ot yhportrepyh ro gniledomer elbisreverri ot dael esehT .setycoym eht ni segnahc & lufmrah era segnahc sudden death. A drug with antioxidant activity the chance of these changes to occur which the risk of sudden death. rekcolb & 1 Non-selective 1 & Ends in lol only mixed With ISA Has local anesthetic effect Rapid acting Non-selective competitive blocker of Membrane stabilizing action / quinidine-like / local anesthetic effect Sedative actions (because it s lipophilic) / No ISA 2 & 1 blocker tuB .)aidracyhcat( 1 MAO the risk of Lipophilic: Completely absorbed 70 metabolism 90 Cross BBB Excreted in urine Given p.o or parenteral % destroyed during 1st pass hepatic Given & o.p IV - P.K % 95 - protein bound Membrane Stabilization: kcolB slennahc aN myocardium has local anesthetic + antiarrhythmic effects. Blocking the Na channels will the generation of impulses from the pacemaker, so it arrhythmia & give a local anesthetic action. - effects) CNS Effect: ,noitca evitades sah tremors & anxiety used to protect against social performance type anxiety. direct depressant to General ( tceffE gnikcolb antiarrhythmic Does NOT alter serum lipids or blood glucose Peripheral vasodilation - Action BP CVS Inhibit heart properties cardiac output Anti-ischemic action work + O2 consumption Antiarrhythmic effects excitability, automaticity & conductivity + by membrane stabilizing activity Propranolol has now been replaced by cardioselective - blockers cardiac 1
Propranolol (prototype) Labetalol Carvedilol Drug Blood Vessels: Vasoconstriction specially to muscles, other organs except brain cold extremities Bronchi: ni yllaiceps msapsohcnorB susceptible patients Intestine: Intestinal motility Metabolism: Liver: Glycogenolysis Hypoglycemia Pancreas: Glucagon secretion Adipocytes: Lipolysis Skeletal muscles: glycolysis Peripheral & central nervous systems: ,tceffe citehtsena lacol tremors, & anxiety . blood flow 2 Does NOT alter serum lipids or blood glucose Peripheral vasodilation Action - BP Antihypertensive action (blood pressure) yb Inhibiting heart properties cardiac output edakcolb system nisnetoigna niner( aldosterone system) Presynaptic inhibition of NE release from adrenergic nerves Inhibiting sympathetic outflow in CNS : : renin & RAAS & 1 2 Hypertension Chronic glaucoma Arrhythmias Migraine [Prophylaxis; to prevent attacks] Myocardial infarction Hyperthyroidism tachycardia Angina Anxiety: (specially social & performance type) Pheochromocytoma; used with -blockers (never alone) Tremors can be managed by non- selective -blockers only as they re caused by 2 Severe hypertension in pheochromocytoma (instead of giving 2 medications to block & , labetalol is given because it s non selective) Hypertensive crisis (e.g. during abrupt withdrawal of clonidine.) Pregnancy-inducednoisnetrepyh Congestive heart failure esrever ot segnahc lacigoloisyhpohtap sti Uses Orthostatic hypotension ( 1 ) Sedation &dizziness Orthostatic hypotension Edema 1 ) ( ADRs - 1 ) ( Heart Block -blockers can precipitate heart block as they cause bradycardia Diabetic patients Masking of hypoglycemia GIVEN CAUTIOUSLY Peripheral vascular disease (e.g.Raynaud's) (safer with cardio-selective 1 blocker) Contraindications of -blockers Hypotension Alone ni pheochromocytoma htiw nevig eb tsum( eht tuo lecnac enola srekcolb fo stceffe yrotalidosav unopposed 1vasoconstriction hypertension [except blockers with 1 antagonism] )srekcolb Bronchial Asthma (safer with cardio-selective srekcolb 2 .) -
Extra Intermittent claudication: Peripheral artery disease most commonly affects the legs, but other arteries may also be involved. The classic symptom is leg pain when walking which resolves with rest. Risk factors: Diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension Summary Thanks team 439 Classific ation Adverse effect Contraindication Drug Notes Uses Contraindication -Membrane stabilizing effect - blocking effect -CNS effect Migraine prophylaxis, Hyperthyroidism, (thyrotoxicosis) Relieve anxiety (social performance), hypertension, arrythmia, myocardial infarction Propranol ol Cold extremities Erectile dysfunction Bronchoconstricti on Non selectiv e Blockers Glaucoma Timolol Hypertension in pregnant women and hypertensive emergency All mask hypoglycemic manifestation Labetolol -Diabetes -Asthma -Using alone in pheochromocytom a -Hypotension -Raynauds disease Orthostatic/postu ral hypotension Non selectiv e Antioxidant action Congestive heart failure Should be withdrawn slowly to prevent upregulation of Cadvedilol Atenolol Hypotention Heart failure Bradycardia Myocardial infarction Hypertension Bisoprolol 1 blockers Metoprolo l Short duration of action Arrythmia Esmolol
MCQS What s the drug of choice in Congestive heart failure? a- Propranolol b- Carvedilol c- Timolol d-Sotalol - Which drug that have short half-life of 10 min? 2 a-Metoprolol b-Atenolol c- Esmolol d- Propranolol - what is the main use of Bisoprolol? 3 a- Hypertension b-Angina pectoris c- MI d- CHF - Which one is true about Proranolol? 4 a-don t have sedation action b-membrane stabilization c- selecive b1 blocker d- increase the cardiac output - What s the drug of choice in Cardiac Arrhythmias? 5 a-Timolol b-Labetalol c-Bisoprolol d-Propranolol - Which drug is blocking the Na channels? 6 a-Sotalol b-Propranolol c-Carvedilol d-Acebutolol 1 - b 4 - b 6 - b 3 - a 2 - c 5 - c SAQ S - give 3 examples of contraindications of b-blockers? 1 Diabetic patient, bronchial asthma , hypotension - What s the mechanism of action of Propranolol? 2 Non-selective competitive blocker of Membranestabilizing action / quinidine-like/ local anesthetic effect Sedative actions (because it's lipophilic)/No ISA 2 & 1 - How can the Timolol treat the Glaucoma? 3 by decreasing the Aqueous humor production from ciliary body thus reduces intraocular pressure(IOP) - list 5 ADRs of b-blockers? 4 Fatigue, sodium retention, disturbance of GIT , Erectile dysfunction& impotence, heart failure
442 Pharmacology Team Leaders Othman Alabdullah Arob Alasheikh Hassan Alabdullatif Dena Alsuhaibani Members Rakan Alromayan Meshari alshathri Nasser Alghaith Alwaleed Faqihi Malik halees Nawaf Alrefaei Saad Alahmari Emad Almutairi Khaled bin arbeed Salem alrasheed Mohammed Almajhadi Mohammed aloraini Faisal adel Khalid alrasheed Faris Alseraye Fahad Alhelelah Luay Almutair Omar Alkadhi Noura bin hammad Rahaf Almutairi Jana Alhazmi Lina ALyahya Aljazi AlBabtain Atheer Alkanhal Reema Alquraini Nouf Aldhalaan Noura Alshafi Layan Aldoukhi Farah Alfayez Razan Almohanna Alanoud Almarzoqi Shahed Bukhari Tharaa Alhowaish Special thanks to: Shatha Alshabani & Abdulaziz Al manea any suggestions or Complaints: Pharmacology moc.liamg@ 442