Bioactivation Reactions in Drug Design
Discover the concept of bioprecursor prodrugs, metabolic reactions, and activation reactions in drug design. Explore examples like sulfation activation and decarboxylation activation, showcasing how inactive compounds are transformed into active drugs for therapeutic purposes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
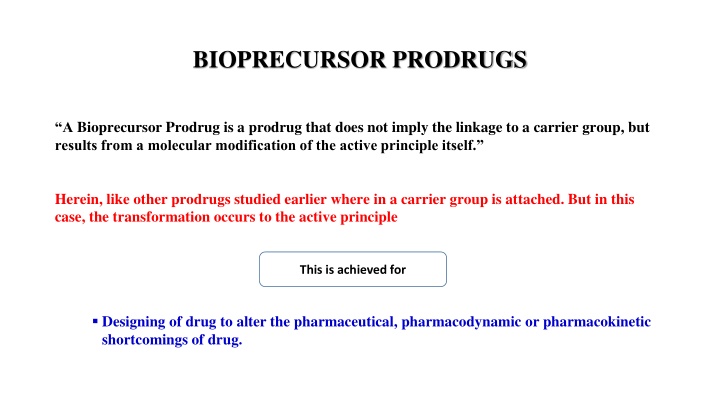
BIOPRECURSOR PRODRUGS A Bioprecursor Prodrug is a prodrug that does not imply the linkage to a carrier group, but results from a molecular modification of the active principle itself. Herein, like other prodrugs studied earlier where in a carrier group is attached. But in this case, the transformation occurs to the active principle This is achieved for Designing of drug to alter the pharmaceutical, pharmacodynamic or pharmacokinetic shortcomings of drug.
O Metabolic reaction + O H2 N S O NH2 H2 N N H2 N NH2 N S O NH2 NH2 NH2 Sulphanilamide (Antibacterial) Prontosil (Inactive) In this case the drug Prontosil which is in inactive state...But upon metabolic reaction it is converted into an active drug sulphonilamide which is used as an antibacterial.
CONTENTS contain some of the activation reactions which include Proton activation. Nucleotide activation. Hydrolytic activation. Phosphorylation activation. Elimination activation. Sulfation activation. Oxidative activation. Decarboxylation activation. Reductive activation. Let us discuss these activation reaction one by one ..
SULFATION ACTIVATION The hypotensive and hair growth activities of minoxidil require a sulfotransferase catalyzed sulfation to form minoxidil sulfate. Minoxidil sulfate is more potent than minoxidil. O- - SO3 N+ N+ H2 N NH2 H2 N NH2 N N Sulfotransferase N N Minoxidil Minoxidil sulfate
DECARBOXYLATION ACTIVATION Dopamine increases systolic and pulse blood pressure and renal blood flow. L- -glutamyltranspeptidase, catalyses the transfer of L-glutamyl group from the N-terminus of one peptide to another, in kidney cells. COO- H + H3 N OH N OH + L- -Glutamyl transpeptidase H3 N COO- COO- O OH OH L- -Glutamyl-L-dopa L-Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase + H3 N OH OH Dopamine






















