Biology for a Changing World: Bee Decline and Trophic Interactions
Explore the importance of honeybees, pollinators, and trophic interactions in ecosystems. Learn about keystone species, energy transfer, and the impact of waste. Understand the critical role of bees in plant reproduction and food chains.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Biology for a Changing World, 2e Clicker Questions Chapter 22
Why are scientists so worried about honeybee colony collapse disorder? A. Bees are keystone species in their communities. B. Commercial crops require bees. C. Flowering plant reproduction relies on pollinators like bees. D. All of the above.
Why do pollinators have such a critical role in communities? A. Pollinators visit many flowers so they can spread parasites in the community. B. Producers have a parasitic relationship with pollinators, which would be disrupted if pollinators disappeared. C. Many producers rely on pollination to reproduce. Without pollinators, these plants could go extinct, which would reduce the food supply for consumers.
Which species is more likely to be a keystone species in its community? A. Species A, where the removal of this species causes major changes in the numbers of Species B, C, D, E, F, G, & H. B. Species B, where the removal of this species causes minor changes in the numbers of Species A, B, D, E, & F.
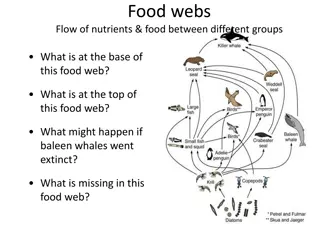
A zebra eats grass and a lion eats a zebra. What best describes these interactions? A. Simplified food chain B. Complex food web C. Symbiosis D. Keystone species
Which species is a producer? A. The lion B. The zebra C. The grass D. None of these are producers.
Which species is a consumer? A. The lion B. The zebra C. The grass D. Both the lion and the zebra are consumers.
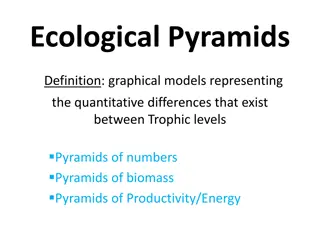
How much energy produced by the grass is transferred to the lion? A. 100% B. 90% C. 50% D. 1%
Waste contributes to energy loss between trophic levels. What parts of the zebra can t be eaten by lions? A. Hooves B. Bones C. Hair D. All of the above.
Which diet is most energy efficient? A. Herbivore B. Carnivore C. Omnivore D. They are all equally energy efficient
A zebra eats grass, and the lion eats the zebra. Which is not a correct categorization of these interactions? A. Lion eats zebra = predation B. Zebra eats grass = predation C. Zebra eats grass = commensalism D. All of these are correct
What might happen to the grass population if lions disappeared? A. The grass population would probably decrease. B. The grass population would probably increase. C. The grass population would probably stay the same.
A bird builds a nest in a tree. The bird gains shelter from the tree. The tree does not pay a cost or get a benefit from the bird nesting there. How would you describe their relationship? A. Parasitism B. Mutualism C. Commensualism D. All of the above.
Two species compete for the same prey. How would you describe their relationship? A. Mutualism B. Predation C. Keystone species D. Competition