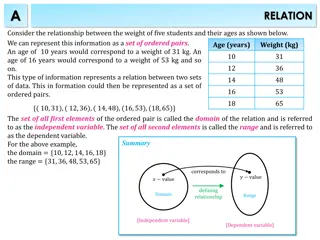
Bloom's Taxonomy and Promoting Higher-Order Thinking in Education
Explore the history and theory of educational objectives, including Benjamin Bloom's cognitive taxonomy. Learn to address concerns about lower-order thinking by fostering higher-order thinking skills such as creating, evaluating, and analyzing. Discover the importance of engaging students in deeper cognitive processes for effective learning outcomes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
History of educational objectives Theory of mastery-learning and higher order thinking Taxonomy of educational objectives (COGNITIVE, AFFECTIVE AND PSYCHOMOTOR) Organizing educational objectives according to their cognitive complexity BENJAMIN BLOOM 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 1
Bloom's Revised COGNITIVE Taxonomy 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 2
Concerns Students are engaged only in lower-order thinking; i.e. they receive, or recite, or participate in routine practice. In no activities during the lesson do students go beyond simple reproduction of knowledge. Students are primarily engaged in routine lower-order thinking for a good share of the lesson. Almost all students, almost all of the time are NOT engaged in higher- order thinking. (Department of Education, Queensland, 2002, p. 1) 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 3
Creating Evaluating Analysing Applying Understanding Remembering 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 4
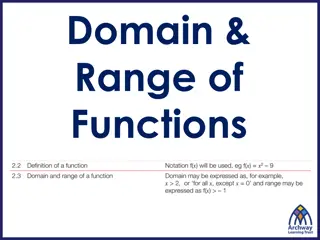
BLOOM S REVISED TAXONOMY Applying Using information in another familiar situation L O W E R Implementing, carrying out, using, executing Understanding Explaining ideas or concepts O R D E R Interpreting, summarising, paraphrasing, classifying, explaining Remembering Recalling information Recognising, listing, describing, retrieving, naming, finding 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 5
Higher-order thinking.. Creating Generating new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things Designing, constructing, planning, producing, inventing. Evaluating Justifying a decision or course of action Checking, hypothesising, critiquing, experimenting, judging Analysing Breaking information into parts to explore understandings and relationships Comparing, organising, deconstructing, interrogating, finding 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 6
A good teacher makes you think even when you dont want to. (Fisher, 1998, Teaching Thinking) 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 7
Questions for Remembering What happened after...? How many...? What is...? Who was it that...? Can you name ...? Find the definition of Describe what happened after Who spoke to...? Which is true or false...? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 8
Questions for Understanding Can you explain why ? Can you write in your own words? How would you explain ? Can you write a brief outline...? What do you think could have happened next...? Who do you think...? What was the main idea...? Can you clarify ? Can you illustrate ? Does everyone act in the way that .. does? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 9
Questions for Applying Do you know of another instance where ? Can you group by characteristics such as ? Which factors would you change if ? What questions would you ask of ? From the information given, can you develop a set of instructions about ? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 10
Question for Analysing Which events could not have happened? If. ..happened, what might the ending have been? How is...similar to...? What do you see as other possible outcomes? Why did...changes occur? Can you explain what must have happened when...? What are some or the problems of...? Can you distinguish between...? What were some of the motives behind..? What was the turning point? What was the problem with...? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 11
Questions for Evaluating Is there a better solution to...? Judge the value of... What do you think about...? Can you defend your position about...? Do you think...is a good or bad thing? How would you have handled...? What changes to.. would you recommend? Do you believe...? How would you feel if. ..? How effective are. ..? What are the consequences..? What influence will....have on our lives? What are the pros and cons of....? Why is ....of value? What are the alternatives? Who will gain & who will loose? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 12
Questions for Creating Can you design a...to...? Can you see a possible solution to...? If you had access to all resources, how would you deal with...? Why don't you devise your own way to...? What would happen if ...? How many ways can you...? Can you create new and unusual uses for...? Can you develop a proposal which would...? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 13
Remembering The learner is able to recall, restate and remember learned information. Recognising Listing Describing Identifying Retrieving Naming Locating Finding Can you recall information? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 14
Understanding The learner grasps the meaning of information by interpreting and translating what has been learned. Interpreting Exemplifying Summarising Inferring Paraphrasing Classifying Comparing Explaining Can you explain ideas or concepts? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 15
Applying The learner makes use of information in a context different from the one in which it was learned. Implementing Carrying out Using Executing Can you use the information in another familiar situation? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 16
Analysing The learner breaks learned information into its parts to best understand that information. Comparing Organising Deconstructing Attributing Outlining Finding Structuring Integrating Can you break information into parts to explore understandings and relationships? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 17
Evaluating The learner makes decisions based on in-depth reflection, criticism and assessment. Checking Hypothesising Critiquing Experimenting Judging Testing Detecting Monitoring Can you justify a decision or course of action? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 18
Creating The learner creates new ideas and information using what has been previously learned. Designing Constructing Planning Producing Inventing Devising Making Can you generate new products, ideas, or ways of viewing things? 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 19
Sample Unit : Space Remembering . List space words (Alphabet Key). List the names of the planets in our universe. List all the things an astronaut would need for a space journey. Understanding Teacher asks what does an astronaut do???. Make a model of the planets in our solar system. Applying What sort of instruments would you need to make space music? Make a list of questions you would like to ask an astronaut. 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 20
Analysing Make an application form for a person applying for the job of an astronaut. Or Compare Galileo s telescope to a modern telescope. Evaluating Compare the benefits of living on Earth and the moon. You can take three people with you to the moon. Choose and give reasons. Or Choose a planet you would like to live on- explain why. Creating Write a newspaper report for the following headline: Spaceship out of control . Or Design an advertising program for trips to the moon. 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 21
Your beliefs become your thoughts, Your thoughts become your words, Your words become your actions, Your actions become your habits, Your habits become your values, Your values become your destiny. Mahatma Gandhi 4/4/2025 Dr. Ms. Vini Sebastian, Asst. PRof. SXIE 22