Buffer Solutions Overview: Definitions, Examples, and Math
Fundamentals of buffer solutions including definitions, strengths, preparation methods, example systems, and mathematical calculations using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. Discover how buffers work, their capacity, and effectiveness through practical examples.
Uploaded on Feb 25, 2025 | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
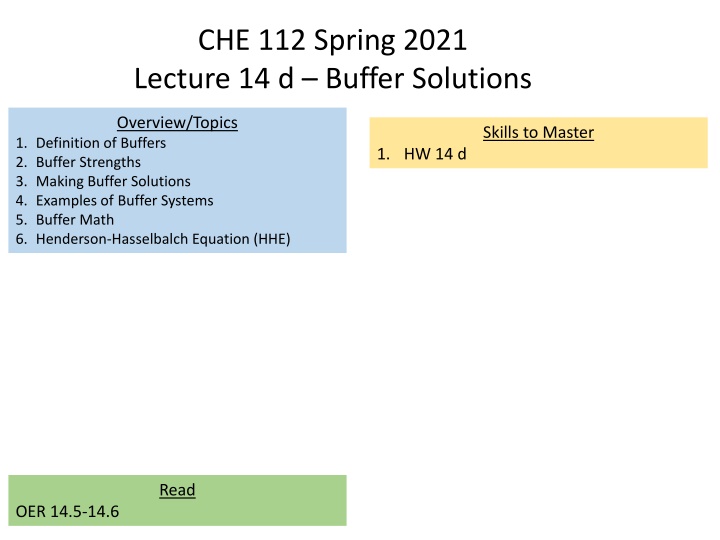
CHE 112 Spring 2021 Lecture 14 d Buffer Solutions Overview/Topics Skills to Master 1. Definition of Buffers 2. Buffer Strengths 3. Making Buffer Solutions 4. Examples of Buffer Systems 5. Buffer Math 6. Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation (HHE) 1. HW 14 d Read OER 14.5-14.6
Buffers o Solutions that are resistant to changes in pH o wa + salt of conjugate base o wb + salt of conjugate acid Salt = anion of SA cation of SB Weak Acid Salt of Weak Acid Replace H with Metal Ion
How Buffers Work Acid + Base = Salt + Water HC2H3O2 + NaOH NaC2H3O2 + H2O Salt CB + Acid = Weak Acid + Salt NaC2H3O2 + HCl HC2H3O2 + NaCl Equilibrium H3O+ (aq) + C2H3O2- (aq) HC2H3O2 (aq) + H2O (l)
You Try It: Which of the following is a Buffer Systems? (a) H2SO4 / Na2SO4 (b) HF / KF (c) NH3 / NH4Cl (d) NaOH / KOH (e) HC2H2O2 / HF You Try It: To make a buffer system you could add which of the following to HNO2: (a) HNO3 (b) NaNO2 (c) NaOH (d) Mg(NO2)2 (e) KC2H3O2
Buffer Capacity Buffer Effectiveness o DP to [ ] o DP to Volume o Ratio of [A]:[B] o Most effective near 1 o Acceptable 0.1-10 o pKa = +/- 1 of desired pH
Review Ch. 13 Buffer Math 1. Write eqn 2. ICE chart 3. Choose x 4. Solve 5. Calc. pH 1. pH HF 2. Initial pH of Buffer 3. pH after addition of base 4. pH after addition of acid 0.1 M HF Ka (HF) = 7.1 x 10-5 pH of pure HF Solution:
0.1 M HF + 0.1 M NaF Ka (HF) = 7.1 x 10-5 pH Initial Solution:
0.1 M HF + 0.1 M NaF Ka (HF) = 7.1 x 10-5 Add 0.01 M NaOH pH after addition of Base: Compare to 0.01 M NaOH alone
0.1 M HF + 0.1 M NaF Ka (HF) = 7.1 x 10-5 Add 0.01 M HCl pH after addition of Acid: Compare to 0.01 M HCl alone
Summary: Solution pH Pure 0.1 M HF: 2.07 Buffer 0.1 M HF and 0.1 M NaF 4.15 After adding Base: 4.23 After adding Acid: 4.06
Buffer vs No Buffer: o Calculate the [HCl] required to have the same pH as a 0.1 M HF + 0.1 M (4.15) o Calculate the pH after addition of 0.01 M NaOH o Compare the Buffered system and Non-buffered system
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation Buffer Shortcut ?? = ???+ log[????] [????] Double Check! [Acid] > [Base] then pH < pKa [Acid] = [Base] then pH = pKa [Acid] < [Base] then pH > pKa
Example: What is the pH of a buffer made from 0.2 M NH3 and 0.3 M NH4Cl? From Appendix Kb = 1.8 x 10-5
Example: Prepare a buffer with pH = 4.0 From Appendix Compound pKa 3.77 Formic Acid Lactic Acid 3.85 Ascorbic Acid 4.10 Benzoic Acid 4.20
Example: Prepare a buffer with pH = 9.0 From Appendix
Important Buffer Systems Not on exam
Ocean Acidification Not on exam