Business Process Engineering: Process Flow Measures & Analysis
Explore the core concept of business process engineering through process flow measures and analysis. Learn about The Little's Law, its application in different scenarios, and how it impacts businesses. Dive into practical examples like the coffee shop and admission flow at Marshall for a comprehensive understanding.
Uploaded on | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
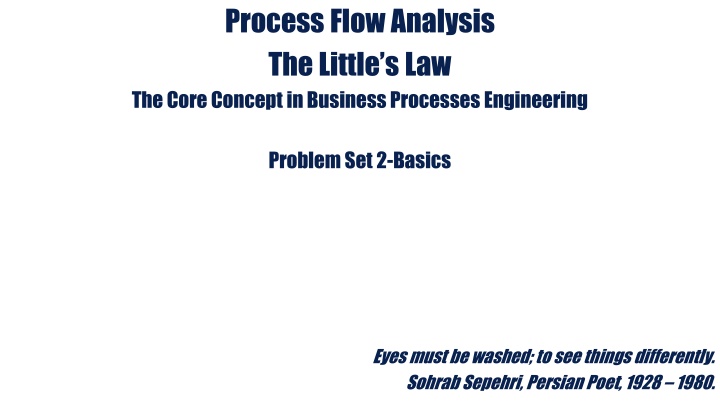
3. Process Flow Measures Process Flow Analysis The Little s Law The Core Concept in Business Processes Engineering K1 . The Coffee Shop 1 Problem Set 2-Basics Eyes must be washed; to see things differently. Sohrab Sepehri, Persian Poet, 1928 1980.
3. Process Flow Measures E1. Admission Flow Similar to Coffee Shop 2 Marshall provides higher education to executives and receives about 1000 applications per month. The evaluation starts with a preliminary classification: Group A: Applicants with desired recommendations, working experience, etc. (50% of the applicants) Group B: Other applicants. (50% of the applicants) Applicants in group A will be further considered through an advanced review. Applicants in group B will be rejected. On average there were are 200 applications in the preliminary review stage, and 100 applications in the advanced review stage a) How long does group A spend in the application process? b) How long does group B spend in the application process? c) How long is the average process time?
3. Process Flow Measures E1. Difference Between R and I 3 Throughput is 1000 per month, inventory in the first process is 200. Lets assume a month is 30 days. Then I can state: R=1000/30 = 33.33 per day but I in the first process is still 200. Now suppose a day is 8 hours. Then I can state: R= 33.33/8 = 4.167 per hour but I is still 200. I can also state: R=4.167/60 =0.0694 per minutes but I is still 200. Assuming a year to be 12 month, R = 12000 per year, but I is still 200. In all these cases, Inventory in processes A and B are 200 and 100, respectively.
3. Process Flow Measures E1. Admission Flow 4 Accept Process 100 50% 1000 200 50% Reject Process a) How long do the applicants spend in the preliminary stage? RT=I T = I/R=200/1000 = 0.2 month Applicants spend 0.2(30) = 6 days in the first stage Applicants from group B receive an answer in 6 days on average
3. Process Flow Measures E1. Admission Flow 5 b) How long do the applicants from group A spend in the advanced review stage? I =100 , R = 1000(0.5) = 500 TR= I T=I/R T= 100/500 = 0.2 Applicants from group A spend 0.2(30) = 6 days on average in the advanced review stage. Applicants from group A receive answer in 12 days (6 + 6) on average.
3. Process Flow Measures E1. Admission Flow 6 c) What is the average processing time? 0.5(6)+0.5(12) = 9 days Is there an alternative way to calculate the average waiting time? Do it------ Little s Law holds for complicated systems.
3. Process Flow Measures E2. Bank Loan The Same as the Previous Example 7 Bank XYZ receives 20 loan requests per hour on average. Each loan request goes through an initial processing stage, after which an accept or reject decision is made. Approximately 80% of the loans are accepted, and these require additional processing. Rejected loans require no additional processing. Suppose that on average 5 loans are in the initial processing stage, and 25 (accepted) loans are in the additional processing stage. 20 Accept 80% 25 5 20% Reject a)What is the average processing time required for a loan b)What is the average processing time required for a rejected loan? c) What is the average processing time required for an accepted loan (including the initial processing stage)?
3. Process Flow Measures E2. Bank Loan 8 a) What is the average processing time required for a loan request? R = 20 loans/hour I = 5+25 = 30 loans Average processing time = Throughput Time RT= I T = I/R = 30/20 = 1.5 hours b) What is the average processing time required for a rejected loan? R = 20 loans/hour I = 5 loans Average processing time = Throughput Time RT= I T = I/R = 5/20 = 0.25 hours
3. Process Flow Measures E2. Bank Loan 9 c) What is the average processing time required for an accepted loan (including the initial processing stage)? Initial Stage: As computed for rejected applications the time for the initial process is T = I/R = 5/20 = 0.25 hours Additional Processing Stage: R = 20 0.8 = 16 loans/hour, I = 25 loans T = I/R = 25/16 = 1.5625 Average Total Processing Time = = 0.25 + 1.5625 = 1.8125 hours
3. Process Flow Measures E3. Fresh Juice and Fruit 10 Consider a roadside stand that sells fresh oranges, and fresh orange juice. Every hour, 40 customers arrive to the stand, and 60% purchase orange juice, while the remaining purchase oranges. Customers first purchase their items. Customers that purchased oranges leave immediately after purchasing their oranges. Any customer that ordered orange juice must wait while the juice is squeezed. There are 3 customers on average waiting to purchase either oranges or orange juice, and 1 customer on average waiting for orange juice to be squeezed. 40 3 0.6(40) = 24 1 How long on average must customers that purchase fresh orange juice wait?
3. Process Flow Measures E3. Fresh Juice and Fruit 11 40 24 3 1 How long on average must customers that purchase fresh orange juice wait? In the ordering process RT =I 40T = 3 T = 3/40 hours T = 60(3/40) = 4.5 minutes In the juice squeezing process RT =I 24T = 1 T = 1/24 hours T = 60(1/24) = 2.5 minutes Average waiting time = T = 4.5 + 2.5 = 7 minutes
3. Process Flow Measures E4. Call Center 12 3. A call center employs 1000 agents. Every month 50 employees leave the company and 50 new employees are hired. a) How long on average does an agent work for this call center? Now suppose the cost of hiring and training a new agent is $1000. The manager of this call center believes that increasing agents salary would keep them working longer term in the company. The manager wants to increase the average time that an agent works for the call center to 24 months, or 2 years. b) If an agent works for the call center for 24 months on average, how much can the company save on hiring and training costs over a year? Hint: first determine the current annual cost for hiring and training, then determine the new annual cost for hiring and training. c) How much the monthly salary of each agent can be increased?
3. Process Flow Measures E4. Call Center 13 1000 Agents 50/month 50/month a) How long on average does an agent work for this call center? R = 50 people/month I = 1000 people Average working time = Throughput Time = I/R = 1000/50 = 20 months or 20/12 = 1.67 years Suppose the cost of hiring and training a new agent is $1000. The manager of this call center believes that increasing agents salary would keep them working longer term in the company. The manager wants to increase the average time that an agent works for the call center to 24 months, or 2 years.
3. Process Flow Measures E5. Call Center 14 b) If an agent works for the call center for 24 months on average, how much can the company save on hiring and training costs over a year? Hint: first determine the current annual cost for hiring and training, then determine the new annual cost for hiring and training. 1000 Agents 1000 Agents 50/month ?/month 50/month ?/month 20 months 2 years Current annual cost for hiring and training: Throughput Rate = 50 people/month = 600 people/year Annual hiring and training cost is 600 (1000) = $600,000
3. Process Flow Measures E5. Call Center 15 New annual cost for hiring and training: Average working time = Throughput Time = 24 months = 2 years Throughput Rate R= I/T = 1000 people / 2 years = 500 people/year 41.7 per month Annual hiring and training cost is 500 (1000) = $500,000 Annual saving on hiring and training cost is $600,000-$500,000 = $100,000 c) How much the monthly salary of each agent can be increased? Average # of employees = 1000 Annual saving on hiring and training cost = $100,000 Monthly saving = $8,333.33 8333.33/1,000 = $8.33 per employee/month
3. Process Flow Measures Practice. Compute the Flow Time 16 D 30% B T = 18 T = 15 70% 40% 10% 100% F 100% A T = 10 T = 10 40% 60% 30% E 20% C T = 16 T = 12






















