Carbohydrates: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
Explore the world of carbohydrates in this detailed guide covering nomenclature, classification, monosaccharides, isomerism, and more. Discover the different types of saccharides and their significance in organisms, along with detailed formulas and structures. Learn about aldoses, ketoses, and various sugar isomerisms, providing a foundational understanding for students studying biochemistry or related fields.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CARBOHYDRATES F.Y.B.Sc, PAPER II UNIT 1
INTRODUCTION Abundant class of biomolecules Saccharides ORGANISM WATER CARBO HYDRATE PROTEIN LIPID ASH PLANT 60 30 5 1 4 ANIMAL 60 1 20 15 4
NOMENCLATURE HYDRATES OF CARBON CX(H20)Y Deoxyribose C5H1004 Rhamnose C6H1205 Glucosamine C6H1305N
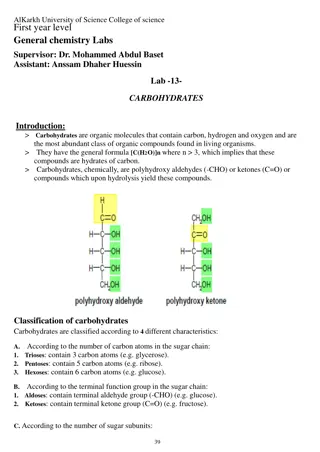
NOMENCLATURE Formaldehyde CH20 Acetic acid C2H204 Lactic acid C3H603 Polyhydroxy aldehyde or Polyhydroxy ketones, derivatives or substances that yield one of these compounds on hydrolysis.
CLASSIFICATION MONOSACCHARIDE CARBOHYDRATES OLIGOSACCHARIDE POLYSACCHARIDE
MONOSACCHARIDE Mono= one, saccharon= sugars Simple sugars Free aldehyde group (-CHO) Ketone group (=CO) 2 or more hydroxyl group, CnH20n
MONOSACCHARIDE FORMULA ALDOSES (ALDO SUGAR) KETOSES (KETO SUGAR) DIHYDROXY ACETONE ERYTHRULOSE TRIOSES C3H603 GLYCEROSE TETROSES C4H804 ERYTHROSE PENTOSES HEXOSES C5H1005 C6H1206 RIBOSE GLUCOSE RIBULOSE FRUCTOSE HEPTOSES C7H1407 GLUCOHEPTOSE SODOHEPTUL OSE
MONOSACCHARIDE Glycerose Aldotriose Ribulose Ketopentose Glucose Aldohexose Aldoses suffix oses Ketoses suffix uloses
ISOMERISM ETHYL ALCOHOL DIMETHYL ETHER
ISOMERISM ISOMERISM STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM STEREOISOMERISM CHAIN GEOMETRICAL POSITIONAL OPTICAL FUNCTIONAL GROUP
POSITIONAL ISOMERISM ISO PROPYL CHLORIDE N PROPYL CHLORIDE
FUNCTIONAL GROUP n PROPANOL ETHYL METHYL ETHER
FORMATION OF ALPHA AND BETA D GLUCOSE
FORMATION OF AND D GLUCOSE
FORMATION OF ALPHA & BETA D FRUCTOSE.
FORMATION OF AND D FRUCTOSE
OLIGOSACCHARIDE DISACCHARIDE: SUCROSE, LACTOSE, MALTOSE TRISACCHARIDE: RAFFINOSE, MALTOTRIOSE TETRASACCHARIDE: STACHYOSE
DISACCHARIDE C1 C1/C2 GLYCOSIDIC LINKAGE NON REDUCING DISACCHARIDE C1 C4/C6 GLYCOSIDIC LINKAGE REDUCING
MALTOSE Two D-Glucose 1,4 glycosidic linkage.
SUCROSE Common sugar. Plant origin. 1, 2 glycosidic linkage. Non reducing sugar.
LACTOSE Milk sugar. Animal origin. 1,4 galactoside. Reducing sugar.
POLYSACCHARIDE POLYSACCHARIDE HOMOPOLYSACCHARIDE HETEROPOLYSACCHARIDE
POLYSACCHARIDE POLYSACCHARIDE NON NUTRITIVE POLYSACCHARIDE NUTRITIVE POLYSACCHARIDE
STARCH AMYLOSE 250-1000s STARCH AMYLOPECTIN 30
HEPARIN N ACETYL GLUCOSE AMINE HEPARIN GLUCURONIC ACID
BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES CARBOHYDRATE AS MAJOR NUTRIENT AND AS STORAGE FORM OF CELL FUEL GLUCOSE STARCH GLYCOGEN
BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES CARBOHYDRATES AS STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS. HEPARIN COENZYMES----NIACIN, NICOTINAMIDE VITAMIN C (ASCORBIC ACID) ANTIFREEZE PROTEIN
BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES PROTECTIVE FUNCTION CELLULOSE CHITIN MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDE
REACTIONS OF MONOSACCHARIDES BENEDICTS TEST MOLISCH TEST REDUCING SUGARS