Carbohydrates: Elements, Functions & Structure
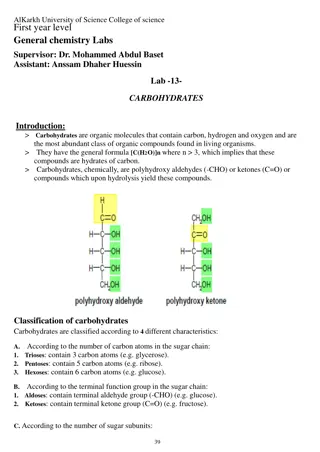
Carbohydrates are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1. They serve as energy sources and structural components in living organisms. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates, and they can form polysaccharides through dehydration synthesis. Learn more about the role of carbohydrates in energy storage and support in plants, animals, and other organisms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What elements are carbs composed of? 1. Carbon (C) 2. Hydrogen (H) 3. Oxygen(O) In a ratio of C : H : O 1 : 2 : 1 For every 1 Carbon (C) You will have 2 Hydrogens (H) Example: Glucose C6H12O6 6 1 : 2 : 1
Function in living organisms 1. Energy Storage in plants and animals Starch in plants Glycogen in animals 2. Structural support in insects, plants & Fungi Chitin in exoskeleton of insects & cell walls of fungi Cellulose in plant cell walls
Carbohydrate Monomers (Building Blocks) Mono=one Saccharide=sugar Monosaccharides: are simple sugars commonly found in rings.
Carbohydrate Monomers (Building Blocks) Glucose = C6H12O6
Front Bottom Left Carbohydrate Polymers Polysaccharides: Poly=Many, Saccharide=sugar Polysaccharides are made by linking monosaccharides (simple sugars) together.
Front Bottom Left Carbohydrate Polymers Disaccharides: Di=Two, Saccharide=sugar Disaccharides composed of 2 monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
Front Bottom Left Complex Carbs Very Large Polysaccharides Have 3 or more simple sugars linked together
Back Top Left Monosaccharides Simple Sugars 1. Glucose: commonly found in blood of animals; the immediate energy source for cells 2. Galactose: a simple sugar found in milk 3. Fructose: commonly found in fruit
Back Top Left Monosaccharides Simple Sugars Ribose & Deoxyribose are 5 carbon simple sugars that make up the backbone of RNA & DNA, respectively.
Back Top Right DISACCHARIDE EXAMPLES Carbohydrate Polymers 2. Sucrose: Table Sugar Made up of Fructose + Glucose 1. Lactose: Found in Milk Made up of Galactose + Glucose
Back Top Right DISACCHARIDE EXAMPLES Carbohydrate Polymers 3. Maltose: Forms in the digestive tract of humans during starch digestion Made up of Gluctose + Glucose
Back Bottom Polysaccharides Complex Carb (Larger polysaccharide) examples 1. Starch: Glucose (energy) stored in plants (breads, pasta, potatoes)
Back Bottom Polysaccharides Complex Carb (Larger polysaccharide) examples 2. Cellulose: Forms plant cell walls providing strength and rigidity.
Back Bottom Polysaccharides Complex Carb (Larger polysaccharide) examples 3. Glycogen: Glucose stored in the liver and muscle of animals. Used for quick energy!!!
Back Bottom Polysaccharides Complex Carb (Larger polysaccharide) examples 4. Chitin: Structural support in fungi cell walls and insect exoskeletons
Exit Ticket 1. List the three elements which compose a carbohydrate. 2. One function of a carbohydrate is ___________. 3. Glycogen, a polysaccharide, in your liver may be broken down to glucose by the process of __________. 4. Draw the basic shape that represents glucose.