Cell Structure Function and Theory
Explore the fascinating world of cell biology with a focus on structure, function, and the cell theory. Learn about prokaryotes, eukaryotes, organelles, and cell membranes. Dive into the history of cell discovery and the importance of cells in all living organisms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
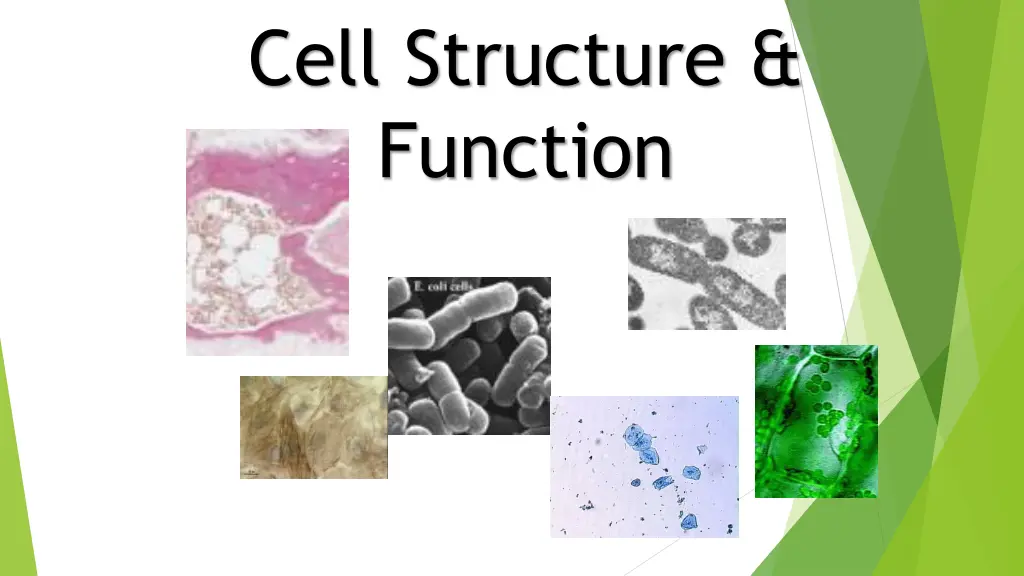
Cell Structure & Function bone-cells cells cells
1.State the cell theory. (A) 2.Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. (B) 3.Describe the structure and function of the nucleus, cytoskeleton, cell wall and cell membrane. (B) 4.Describe the structure and function of the various cell organelles.(A/B) 5. Describe the relationship between the structure & function of the cell membrane. (B) 1.Describe passive transport. (B) 2.Describe active transport. (B) 3.Using microscope.
Wednesday (A-Day)_ __ 11/08/17 Agenda: Cells!!!! Notes Cell Types Poster ENZYME LAB DUE All cells have a nucleus. T or F The cell theory is important because Eukaryotes are cells that What is an organelle? Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis? Learning Target(s) What you should be able to do by the end of today: 1.State the cell theory. (A) 2.Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. (B) 3.Describe the structure and function of the nucleus, cytoskeleton, cell wall and cell membrane. (B) 4.Describe the structure and function of the various cell organelles.(A/B) Warm Up: Cell Pre-Assessment: Cells are the basic unit of life. T or F Cells from plants and animals look the same. T or F
A little history 1600s: van Leeuwenhoek used microscope to study nature 1665: Hooke used microscope to look at plant tissue & cork; called them cells 1838: Schleiden concluded that all plants were made of cells 1839: Schwann concluded that animals are made of cells 1855: Virchow studied cell reproduction and concluded that cells come from cells
What is a cell? The basic unit of ALL living organisms. cells Scale of Life
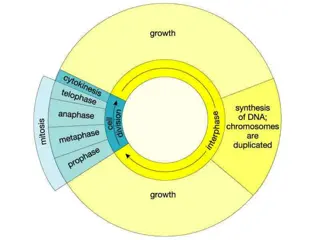
Cell Theory cells All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things. New cells are made from existing cells. bone-cells
Cell Types Poster Your partner and you are going to create a poster that shows one type of cell. The objective of this assignment is to show you how many different types of cells there are. Choose one cell off of Mrs. C s list and put your name next to it. You will now look up the cell your chose online. You and your partner will begin creating a picture of the cell. You will also need to label the important (organelles) cell parts as well. When you have completed the drawing, you will explain, either to the side or underneath the drawing, how your cell is different than the general cells we labeled.
Types of cells: is?168439875654 Prokaryotes bone-cells Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes is?168439875654 Unicellular No nucleus Asexual reproduction Example: bacteria
Eukaryotes bone-cells Unicellular or multicellular Nucleus present Organelles present Sexual reproduction Examples: plants, animals, people
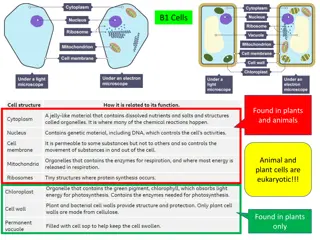
All cells have: Cell membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Cell wall (plants only)
Cell Membrane The skin of the cell. Protects cell from outside environment. Regulates flow of water, nutrients & waste.
Cytoplasm Material inside the membrane (not including the nucleus). Contains many important structures.
Other cell parts to know: Cell Wall Found outside cell membrane Supports & protects cell Plant cells only!!! Cytoskeleton Maintains shape Movement Nucleus Organelles
Nucleus The brain of the cell. Controls cell functions. Contains DNA. Surrounded by nuclear envelope.
Organelles Little organs Specialized parts of the cell. Examples: ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, lysosomes, vacuoles
Cell Membrane Functions: Provides protection and support. Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Takes in food and water. Eliminates waste. Allows the cell to maintain homeostasis.
The cell membrane is semi-permeable. Some substances can pass through it, while others cannot. Most biological membranes are semi- permeable.
Parts of the Cell Membrane Phosopholipid bilayer: the core of the membrane; forms a strong barrier between the cell and the outside Protein channels: form pumps to move material through membrane Carbohydrates: identify the cell; on the outside
Concentration How many molecules are in a given volume. (How crowded the molecules are.) Concentration = Amount of solute Volume of Solution Every cell is surrounded by liquid and has a liquid interior (cytoplasm) that are solutions of many different substances. High Concentration Low Concentration
Passive Transport: movement from an area of high concentration to areas of lower concentration (getting less crowded); does not require energy Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion: molecules that are too large to pass through the cell membrane go through protein channels Osmosis: the diffusion of water
Osmosis in Cells Hypotonic: the solution outside has a lower solute concentration that inside the cell. Isotonic: the concentration of solutes is the same both in and out of the cell Hypertonic: the solution outside has a higher solute concentration than inside the cell
Active Transport: movement from an area of low concentration to areas of higher concentration (getting more crowded); requires energy Exocytosis: when a vesicle fuses with the cell membrane to take material out Endocytosis: brings material into the cell when a pocket in the membrane breaks off, forming a vesicle 1.) Phagocytosis: large particles taken in 2.) Pinocytosis: small particles taken in
Cell Specialization Cells in multicellular organisms are interdependent. Cells in multicellular organisms are specialized to perform particular functions in the organism.
Cell The basic unit of life.
Tissue A group of cells that perform a particular function. Four types: Connective Epithelial Muscle Nervous
Organs A group of tissues working together to perform a particular function. Examples: Heart Stomach Lungs
Organ System A group of organs working together. Examples: Nervous system Circulatory system Digestive system
Organism Any living thing.