Cells and Organisms: The Basics Explained
Delve into the world of cells and organisms, exploring the differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms, the Cell Theory, and the exploration of cells through research. Discover the characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in this comprehensive guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
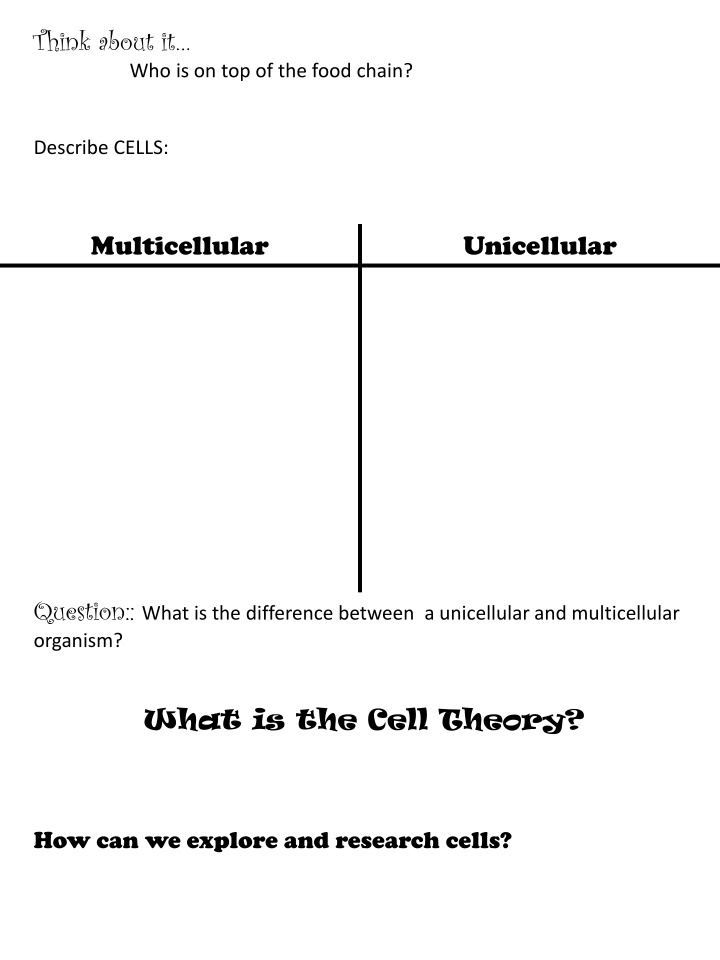
Think about it Who is on top of the food chain? Describe CELLS: Multicellular Unicellular Question:: What is the difference between a unicellular and multicellular organism? What is the Cell Theory? How can we explore and research cells?
Think about it Who is on top of the food chain? Describe CELLS: Multicellular Unicellular Question:: What is the difference between a unicellular and multicellular organism? What is the Cell Theory? How can we explore and research cells?
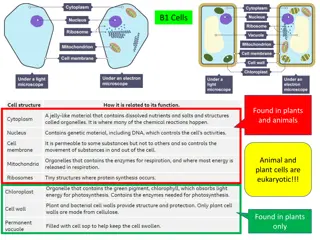
Think about it Who is on top of the food chain? All living things are made up of _____________. *Cells are microscopic building blocks *Everything that is alive has cells! Multicellular Unicellular Multicellular means _____________. Unicellular means ______________. Multi = ____________ Uni= ______________ Plants, Fungi and _________________ are multicellular. ___________________ are an example of a unicellular organism. Have specialized parts and organs that have specific roles they are in charge of. Unicellular organisms are only made of 1 cell so that 1 cell has to do it all!! These parts and organs are called ____________________. Have to rely on their one cell to get the job done! Question:: What is the difference between a unicellular and multicellular organism? The Cell Theory: 1. All things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic building block of life. 3. All cells come from other cells. How can we see these cells? We can view cells through a ____________________________________.
Think about it Who is on top of the food chain? All living things are made up of _____________. *Cells are microscopic building blocks *Everything that is alive has cells! Multicellular Unicellular Multicellular means _____________. Unicellular means ______________. Multi = ____________ Uni= ______________ Plants, Fungi and _________________ are multicellular. ___________________ are an example of a unicellular organism. Have specialized parts and organs that have specific roles they are in charge of. Unicellular organisms are only made of 1 cell so that 1 cell has to do it all!! These parts and organs are called ____________________. Have to rely on their one cell to get the job done! Question:: What is the difference between a unicellular and multicellular organism? The Cell Theory: 1. All things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic building block of life. 3. All cells come from other cells. How can we see these cells? We can view cells through a ____________________________________.
TWO TYPES OF CELLS: PROKARYOTES AND EUKARYOTES What do they have in common? Prokaryote Eukaryote What are at least three characteristics prokaryotic cells have? What are at least three characteristics eukaryotic cells have?
TWO TYPES OF CELLS: PROKARYOTES AND EUKARYOTES What do they have in common? Prokaryote Eukaryote What are at least three characteristics prokaryotic cells have? What are at least three characteristics eukaryotic cells have?
Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Ribosomes Ribosomes DNA/RNA DNA/RNA Have NO _____________ Contain a _____________ No membrane bound ______________________ Have membrane bound _______________________ Small and Simple Some are single celled, most are multicellular. Two major groups- archaebacteria and eubacteria Generally ________________ than prokaryotes Unicellular Plants, animals, fungi and protists are examples ______________ are prokaryotes 4 main parts -cell membrane -cytoplasm -nucleus -organelles What are at least three characteristics prokaryotic cells have? Why is bacteria considered a prokaryotic organism? What is 1 cool fact about bacteria you did not know? Illnesses caused by bacteria Salmonella sp. : found in raw chicken and eggs. (recently found in Peanut Butter) Staphylococcus aureus: causes staph infections E.Coli What are at least three characteristics eukaryotic cells have?
Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Ribosomes Ribosomes DNA/RNA DNA/RNA Have NO _____________ Contain a _____________ No membrane bound ______________________ Have membrane bound _______________________ Small and Simple Some are single celled, most are multicellular. Two major groups- archaebacteria and eubacteria Generally ________________ than prokaryotes Unicellular Plants, animals, fungi and protists are examples ______________ are prokaryotes 4 main parts -cell membrane -cytoplasm -nucleus -organelles What are at least three characteristics prokaryotic cells have? Why is bacteria considered a prokaryotic organism? What is 1 cool fact about bacteria you did not know? Illnesses caused by bacteria Salmonella sp. : found in raw chicken and eggs. (recently found in Peanut Butter) Staphylococcus aureus: causes staph infections E.Coli What are at least three characteristics eukaryotic cells have?