Cellular Network Architecture Components and Evolution Overview
Explore the fundamental components of cellular network architecture, such as Mobile Switching Centers (MSC), Base Stations (BS), and more, along with the evolution from 2G to 4G LTE networks. Gain insights into how these networks handle voice, data, and internet communications.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
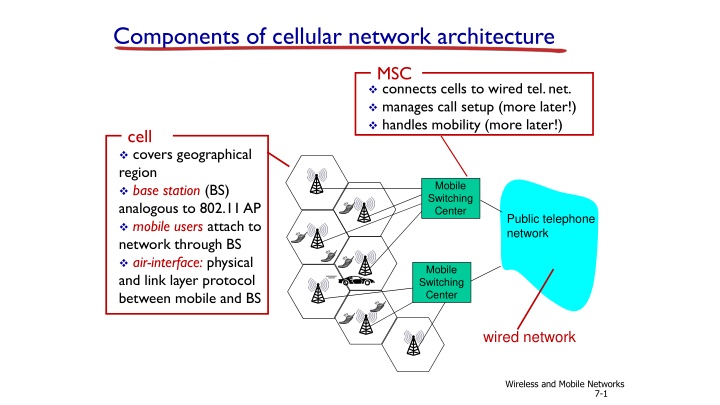
Components of cellular network architecture MSC connects cells to wired tel. net. manages call setup (more later!) handles mobility (more later!) cell covers geographical region base station (BS) analogous to 802.11 AP mobile users attach to network through BS air-interface: physical and link layer protocol between mobile and BS Mobile Switching Center Public telephone network Mobile Switching Center wired network Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-1
Cellular networks: the first hop Two techniques for sharing mobile-to-BS radio spectrum combined FDMA/TDMA: divide spectrum in frequency channels, divide each channel into time slots CDMA: code division multiple access time slots frequency bands Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
2G (voice) network architecture Base station system (BSS) MSC G BTS BSC Public telephone network Gateway MSC Legend Base transceiver station (BTS) Base station controller (BSC) Mobile Switching Center (MSC) Mobile subscribers Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-3
3G (voice+data) network architecture MSC G Public telephone network radio network controller Gateway MSC G Public Internet SGSN Key insight: new cellular data network operates in parallel (except at edge) with existing cellular voice network voice network unchanged in core data network operates in parallel GGSN Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-4
3G (voice+data) network architecture MSC G Public telephone network radio network controller Gateway MSC G Public Internet SGSN GGSN radio interface (WCDMA, HSPA) core network General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Core Network public Internet radio access network Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-5
3G versus 4G LTE network architecture MSC G Public telephone network radio network controller Gateway MSC 3G G Public Internet SGSN GGSN HSS 4G-LTE MME G G Public Internet S-GW P-GW radio access network Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) Evolved Packet Core (EPC) Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-6
4G: differences from 3G all IP core: IP packets tunneled (through core IP network) from base station to gateway no separation between voice and data all traffic carried over IP core to gateway Mobility Management Entity (MME) Home Subscriber Server(HSS) (like HLR+VLR) Packet data network Gateway (P-GW) Serving Gateway (S-GW) UE eNodeB (base station) HSS (user element) MME G G Public Internet data S-GW P-GW radio access network Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) Evolved Packet Core (EPC) Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-7
