Central Action for Assessing Exposure to Risk Factors
The Ministry of Health's project focuses on assessing risks to health workers and implementing prevention plans. It involves improving risk knowledge systems, supporting safety self-assessment, and coordinating prevention efforts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
29 ottobre 2019 Ministero della Salute CCM central action for assessing the impact of exposure to risk factors and targeted prevention plans in the health sector Giuseppe Campo, Diego de Merich Department of Medicine, Epidemiology, Occupational and Environmental Hygiene
Presentation topics 1. The CCM project for the health and safety of health workers 2. The picture of risks and events harmful to workers in the health sector 3. Support action for companies in the sector for risk assessment
The National Plan for Prevention, among its strategies, outlines: Improving the systems of risk knowledge and damage from work, also through the implementation of surveillance systems, including Informo and Malprof; improving the effectiveness of control activities and compliance by the recipients of the rules. Support for self-assessment of the level of safety in risk management and in the organization of company safety by employers.
The Project GENERAL OBJECTIVE: Activation of a monitoring network for the investigation of risk factors for health professionals and identification of a model of targeted prevention intervention to support companies. SPECIFIC OBJECTIVE 1: Deepening of work risk factors, through surveillance systems, ad hoc surveys and systematic review of scientific literature, for the establishment of an observatory on health and safety issues in the health sector. SPECIFIC OBJECTIVE 2: Multicentric study for a model of assistance by the local health authorities in supporting companies for the implementation of effective prevention measures, through the sharing of improvement solutions, good practices and tools for risk assessment (VdR).
The Central Action The project activities started in January 2019 with the analysis of the available archives (Inail database, Informo surveillance systems, Malprof, Monitoring networks such as the SIROH Program) and through the review of the literature. In parallel, the type of interventions by the ASL Services was defined according to a proactive approach, oriented to support the world of work, for the transfer of prevention tools to companies.
2. The picture of risks and events harmful to workers in the health sector
The European context A report by the Bilbao Agency (Eu-Osha) shows how the health sector employs about 10% of workers in the European Union, where women represent 77% of the workforce. The percentage of occupational accidents in the health sector, with about 30% more than the average, is among the highest in the European Union. With such a large portion of the workforce employed in this sector, and in anticipation of a growing need for health workers in the future, the potential impact of risk conditions is considerable and raising awareness of these issues is a priority for the EU itself. -Osha.
Healthcare personnel are exposed to various risks during the course of daily activities, such as biomechanical overload, incongruous postures, uncoordinated and / or repeated movements. Incorrect work postures are often taken in the care of the patient's bed, but also in the surgical field or during laboratory and rescue activities. Musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limbs and neck (DMAS) represent the most widespread form of occupational disease in Europe, responsible for 45% or more of all occupational diseases; in the health sector, for these disorders, there is the second highest rate of incidence among work-related diseases, immediately after the building sector. Workers are also exposed to risks related to the use of chemicals (disinfectants, anesthetic gases, detergents, ...) as well as medicines that, especially in preparation, can come into contact with the skin or penetrate the respiratory tract and cause local reactions or systemic, such as skin diseases, nasal diseases, sinus, ocular diseases and asthma.
Health Sector reports of occupational diseases with a positive causal link for pathology and gender (2005-14) - Malprof System source In Italy in recent years, the reports of sickness to INAIL for the health professions pass from 1985 cases in 2013 to 1956 in 2018 Altre patologie 391 9,8 5,4 27,6 Totale 3.996 100 100 100
Sistema Malprof The PRR (Proportional Reporting Ratio) compares the weight of the pathology in question on the total number of pathologies in the health sector with the corresponding weight in the remaining Ateco sectors; in addition, the 95% confidence interval was also calculated. The table shows the diseases with PRR greater than 1, which represent an alarm bell regarding possible occupational exposures.
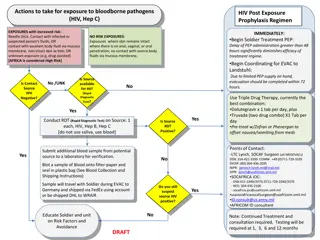
The use of some work tools, such as needles, syringes, scalpels and other devices with a needle or cutting edge, involves a risk of percutaneous exposure (puncture or cutting) with possible haematic transmission of biological agents, immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B and C viruses, present in the blood of patients such as the human The Italian Occupational Risk Study of HIV and other blood-borne pathogens (SIROH), coordinated by the Spallanzani Institute, is a research project that for 25 years and with the voluntary contribution of the operators of 120 hospitals throughout Italy, allows to realize a study of occupational hazards at biological risk with a significant impact in terms of prevention.
I dati del network SIROH, 2010-18 il numero medio di punture per ospedale si ridotto del 60%, soprattutto per gli aghi cavi pieni di sangue (-75%); il numero medio di punture con aghi di sicurezza per ospedale minimo (2,5 per anno). Questo anche in virt del recepimento (con D.Lvo 19/2014) della Direttiva 2010/32/UE sulla prevenzione delle punture e tagli nel settore ospedaliero e sanitario Nei casi di puntura, vengono identificate le modalit degli incidenti con dispositivi di sicurezza: 50% prima che l attivazione del meccanismo di sicurezza fosse possibile; 15% durante l attivazione, 20% per mancata attivazione da parte dell operatore; 7% per un malfunzionamento del meccanismo di sicurezza. In una recente indagine Siroh-Gfk Eurisko, Il 68% degli infermieri dichiara di effettuare nella routine quotidiana almeno una manovra a rischio di puntura
Professions and work organizations In addition to medical staff (doctors, nurses, laboratory technicians, etc.), support and technical personnel, as well as a whole range of professionals, including trainees and apprentices, are also exposed to risks. The cleaners, a non-negligible percentage of workers in the health sector, are exposed to dangers and risks that vary according to the specific workplace. Shift work, changing work patterns, night work, organizational factors and relationships with colleagues can be a source of stress and other occupational diseases. Last but not least, the phenomenon of the aging of the working population and its consequences on health and safety must be considered. With regard to needle-stick infections, research conducted in the United States has recorded that incidence rates among nurses with greater seniority are higher than those of less experienced colleagues.
3. Support action for companies in the sector for risk assessment
Targeted Prevention Plans Multicenter between standard of assistance, characterized by a succession of coordinated actions: study in collaboration Regioni Inail and for a a. Assistenza a) sharing of tools for Vdr and training for companies; b) self-assessment and control of risk factors; Vigilanza/Audit b. c) verification of the effectiveness of the implemented interventions Efficacia c. 16
A S S I S T A N C E 1. Objectives of the PMP, Self-assessment form, sharing tables pursuant to art.7 DL 81/08 2. Invitation letter to companies on the PMP illustrative seminar and tools for the Vdr 3. Integrated training for accident / near miss analysis and review Risk assessment Phases S U P E R V I S O R Y 4. Self-assessment of companies with the dedicated card and actions 5. Supervision / Audit in companies in the PMP sector / theme and detection of the solutions adopted by them following the prescriptions of Targeted E F F E C T I V E N E S S Plans 6. Investigation on the perception of risks by workers affected by the PMP via risk perception questionnaire 7. Final Seminar and PMP Effectiveness Verification through "Indicator Sheet". 17
Nord Est Nord Ovest 12 PMP realizzati nello studio Rete Regioni-Inail e comparti Centro o Piemonte: manifatturiero o Lombardia: logistica, fonderie o Veneto: agricoltura o P. A. Trento: forestale o Friuli Venezia Giulia: RSA o Toscana: pesca o Lazio: economia circolare o Puglia: polveri di legno, edilizia o Calabria: agricoltura o Sicilia: cantieristica navale Sud Isole 16
Specific objective of the CCM project Standardization of targeted intervention model Participatory planning with local health authorities, companies, social partners, professional associations. Transfer of corporate audit tools to the Vdr process Effectiveness verification interventions PMP Healthcare Phases for assistance and audit of local health authorities of the Dissemination of results
Strumenti a supporto delle aziende sanitarie per l autovalutazione Realizzazione piattaforma web per le aziende VERIFICA SPP/MC NEAR MISS INFORTUNIO AUDIT
Ats Milano Sorveglianza sanitaria; Rischio aggressioni Asl SGSL e fattori organizzativi Viterbo Temi PMP Sanit Asl Modelli organizzativi gestionali (MOG) Civitav. Asl Moviment. Man. pazienti (MMP); Cancerogeni Messina Sirgis Puglia SGSL; MMP; Rischio biologico