Channel Measurement Procedure for WLAN Sensing in IEEE 802.11-20
Explore the channel measurement procedure for WLAN sensing outlined in the IEEE 802.11-20 document. Learn about potential measurement options and background principles essential for effective sensing. Discover feedback mechanisms and implicit/explicit sensing approaches for improved WLAN operations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
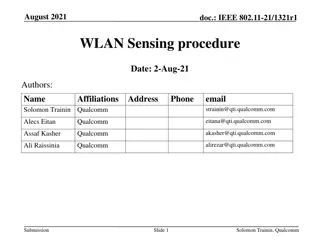
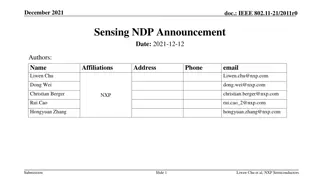
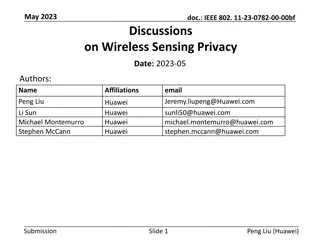
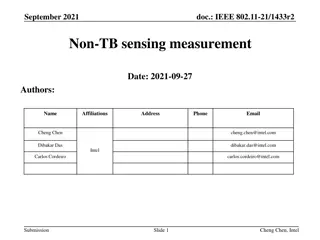
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Follow-ups on Channel Measurement Procedure for WLAN Sensing Date: 2020-06-13 Authors: Name Affiliation Address Phone Email Chenchen LIU liuchenchen1@huawei.com Meihong Zhang Huawei Rui Du Yingxiang Sun Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 1
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Abstract In this contribution, we discuss the channel measurement procedure for WLAN sensing Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 2
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Outline Background of WLAN sensing Potential Channel measurement procedure Option1: Feedback from the responders Option2:No feedback Option3: Threshold based NDP feedback Summary References Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 3
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Background of WLAN sensing Basic principle Signal reflected from the target carriers info of the target(e.g. velocity, location, etc.) Advantages Ubiquitous Device-free Privacy High precision field of view intruder detection Fall detection Gesture recognition Gesture recognition Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 4
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Background of WLAN sensing Sensing based on channel sounding Explicit Implicit Channel direction not crucial(reciprocal in general) Typical use cases only track changes over time Periodicity Some use cases like intruder detection might need a reliable periodicity of CSI feedback Most of the feedbacks over a period may be highly correlated With those principles in mind, let consider the channel measurement procedure for WLAN sensing Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 5
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Option1: Feedback from the RSTAs TX STA and RX STA diversity is very important in the sensing applications [2] The ISTA broadcast the NDP to all the RSTAs The RSTAs feedback the sensing measurement report to the ISTA Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 6
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Option1: Feedback from the responders An example of the sensing procedure with feedback from multiple RSTA One or more sequences NDPA NDP Trigger SIFS SIFS SIFS ISTA Sensing Measurement Report 1 RSTA1 Sensing Measurement Report 2 RSTA2 Sensing Measurement Report n RSTAn Problems: If the CSI as feedback, huge amount of data to feedback If sensing results as feedback, the RSTAs may have limited ability to resolve angles and perform complex algorithm Some coordination is needed Slide 7 Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Option2: No feedback The ISTA trigger each RSTA to send the NDP to the ISTA[3] The ISTA receive the NDP from each RSTA and do the sensing measurement within itself Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 8
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Option2: No feedback Examples of the sensing procedure with no feedback from the RSTA Freqeuncy Freqeuncy NDP TF NDP TF NDP TF Sensing Sounding Sensing Sounding Sensing Sounding Nss=4 Nss=3 Nss=2 time ISTA RSTA2 time ISTA RSTA1 ISTA Nss=1 SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS Problems: ISTA may need some processing time before processing the next NDP Full bandwidth is not utilized for OFDMA Complexity at the ISTA Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 9
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Option 3: Threshold based feedback The ISTA set the threshold[4] for each RSTA, and periodically transmit the NDP to all RSTAs The RSTA measure the CSI and compare it with previous measurement result If the CSI difference exceeds the threshold, the RSTA sends a NDP to the ISTA(schedule may needed). Otherwise, the RSTA store measurement result and feedback nothing The ISTA do the sensing measurement within itself based on the NDP send by the RSTA Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 10
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Option3: Threshold based feedback An example of the sensing procedure with threshold based NDP feedback Freqeuncy TF Sensing Soundin g Sensing NDPA TF NDP Sensing Poll NDP CTS- to- RSTA1 RSTA1 Nss=1 time ISTA ISTA ISTA ISTA SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS Problems: May cause some delay for certain application(negligible in most case) Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 11
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Comparison Channel measurement procedure Pros Cons Option1:From the responders Simple measurement Large overhead, limited processing ability Option2: No feedback No feedback needed Interference or longer airtime Option3: Threshold based Small overhead Latency Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 12
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Summary In this contribution, three channel measurement procedures for WLAN sensing and their corresponding pros and cons are discussed. Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 13
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 References [1] CSI-based Wi-Fi Sensing: Results and Standardization Challenges, doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1769 [2] Wi-Fi Sensing: Cooperation and Standard Support, doc.: IEEE 802.11-19/1416r0 [3] A Channel Measurement Procedure for WLAN Sensing, doc.: IEEE 802.11- 20/0842r0 [4] Z. Wu, Y. Han, Y. Chen and K. J. R. Liu, "A Time-Reversal Paradigm for Indoor Positioning System," in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 1331-1339, April 2015 Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 14
June 2020 doc.: IEEE 802.11-20/xxxxr0 Backup Threshold could be TRRS Chenchen LIU et al., Huawei Submission Slide 15