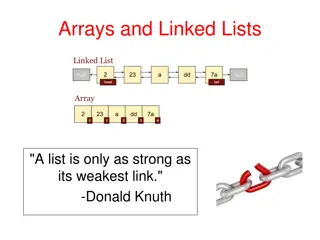
Chare Arrays: Indexed Collections for Scientific Applications
Chare arrays provide a unique and efficient way to manage collections of chares in scientific applications. Each element in the collection has a distinct index and proxy, allowing for easy indexing and dynamic insertion/deletion. Learn about declaring, constructing, and utilizing chare arrays in this informative tutorial series.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Everything around you is made up of Matter. What is Matter? Matter Anything that has mass and takes up space.
It can exist as a solid, liquid, gas or plasma. It may be possible to break some kinds of matter down into other kinds of matter with different properties. For example, water (H2O) can be broken down into hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen and oxygen in the above example cannot be broken down any further because they are elements. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uy0m7jny v6U
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substance by any chemical or physical means. The smallest particles of an element that have the characteristics of that element are atoms Elements are substances made up of only one kind of atom. . https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QH2td6OEON4 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qmC7b6USj40 How did it start? Aristotle Proposed the idea that all matter is made from Air, Fire, Water and Earth. Different combination of these led to different "stuff".
Democritus ____________________, Greek philosopher that was first to understand and call the movement of particles atoms. Democritus believed that if matter was divided to smaller pieces there would be a point in which it could not be divided further. He said matter was made of indivisible (cut in half continually and eventually you can t cut anymore) particles called atoms atomos
John Daltons Atomic Theory came from many experiments. Compounds consist of atoms which combines in whole number ratios The main parts were: 1.All ______________ are composed of atoms. Atoms cannot be divided or destroyed. 2.________ of the same element are exactly alike. 3. Atoms of different elements are different. 4.The atoms of two or more elements can join together to form ________________________. elements Atoms compounds
Thomsons model was next, stating that there were small negative charged particles ________ evenly embedded throughout a positive sphere. electrons Cookie dough Rutherford then came up with the idea that most of the __________ of an atom (and all its positive charges) were in a central atomic nucleus surrounded by electrons. Empty space contains electrons mass Bohr hypothesized that electrons traveled in fixed __________around the nucleus. Chadwick, concluded that the nucleus contained positive ___________ and neutral ______________. protons orbits Fixed orbits neutrons Today scientists believe that electrons do not follow fixed paths, but rather occur in certain areas around the nucleus At any given time. They are currently looking at the Quark Theory (there are an infinite number of possibilities for what makes matter.) Electron Cloud Order of discovery ..D D T R B C Did Dr. Thomson really bake cookies?
An atom is composed of subatomic particles. Three important kinds of subatomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. An exception is hydrogen which does not have neutrons. mass charge protons approx. 1 amu + neutrons approx. 1 amu 0 electrons 1/1836 amu - Protons and neutrons are located in a central area called the nucleus. Electrons move about the nucleus. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vi91qyjuknM http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vi91qyjuknM
Protons = 2 up quarks + 1 down quark Neutrons = 2 down quarks + 1 up quark
It is more accurate to represent the space occupied by electrons as a cloud. The electrons are likely to be located somewhere within the cloud in an energy level. The mass of subatomic particles is too small to be conveniently measured in grams so atomic mass units (amu) are used instead. One amu is approximately 1.7 X 10-24g. Protons and neutrons have a mass of approximately 1 amu. The mass of an electron is much less. The total mass of an atom is due mostly to the mass of protons and neutrons.
Charge is a state in which particles are either attracted to each other or they repel each other. Two particles that are attracted to each other have opposite charges (positive and negative). Particles that repel each other have the same charge; they are both either positive or they are both negative. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yE8rkG9Dw4s Protons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge. Particles with positive charges are attracted to particles with negative charges. Two particles with the same charge (both positive or both negative) will repel each other. Atoms are neutral. The number of electrons (negatively charged) is equal to the number of protons (positively charged), therefore the overall charge is zero.
The number of protons and neutrons together equal the______________. Both are in the nucleus and this is where most of the mass of an atom is. It takes 1,847 electrons to equal the mass of one proton. mass number The number of protons tells you what type of atom you have. The number of protons is equal to a number called ____________________. Therefore if you know any one of the following, the name of the element, the # of protons, or the atomic number, you can determine the other two. Element Protons Atomic Number Neutrons Atomic Mass / # Oxygen 8 ___ Nitrogen ___ 7 Boron ___ ___ Atomic number 8 ___ ___ 6 14 11
The ______________________ of an atom is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. If you know the mass number and the atomic number of an atom, you can calculate the number of neutrons. Mass Number Number of neutrons = Mass Number minus Atomic Number Not all the atoms of an element have the same number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called _________________. Nearly all elements have isotopes, some of which are radioactive. The mass of an element listed on the periodic table is the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of that element. Isotopes Carbon dating Living organisms on Earth contain carbon. Carbon -12 makes up 99% of this carbon. Carbon-13 and carbon-14 make up the other one percent. Which isotopes are archaeologists most interested in when they determine the age of carbon-containing remains?
Because most elements have more than one isotope, each element has an average atomic mass. The _______________________ of an element is the weighted-average mass of the mixture of its isotopes. Average Atomic Mass How many electrons are found in a neutral atom of carbon? ________ What would the charge be on the carbon atom if it lost four electrons? ____________________________ How does neutron count affect atomic charge? _____________________ six + 4 ; protons = 6, electrons=2 It has no effect.