Chemical Bonds: Covalent, Ionic, and Metallic
Explore the fascinating world of chemical bonds, including covalent bonds where atoms share electron pairs (e.g., water), ionic bonds where oppositely charged ions attract (e.g., sodium chloride), and metallic bonds formed between positively charged atoms sharing free electrons (e.g., copper wire). Learn about the forces holding atoms together and the types of bonds that exist in various substances.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
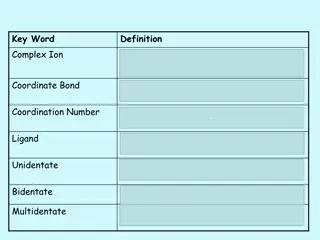
Chemical Bonds A force of attraction that holds two atoms together
Types of Chemical Bonds Covalent Ionic Metallic
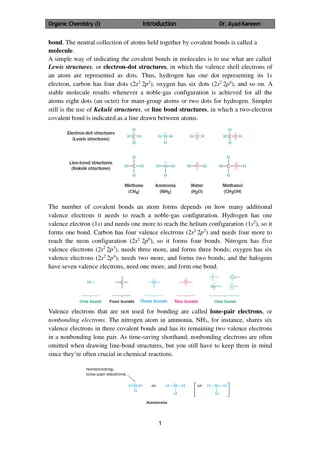
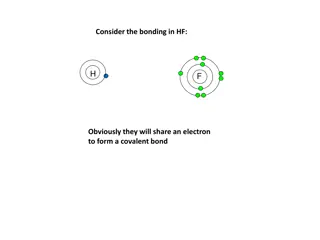
Covalent Bonds A type of bond where atoms share electron pairs Example: Water H2O. Hydrogen and oxygen atoms share electrons.
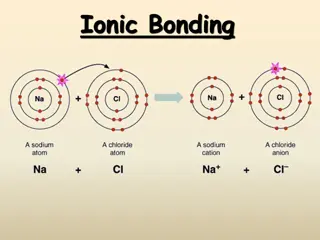
Ionic Bond In ionic bonding opposites attract. The bond occurs when positively charged and negatively charged ions interact. In this example, one atom may lose an electron while the atom it bonds with gains an electron. Example: Sodium Chloride
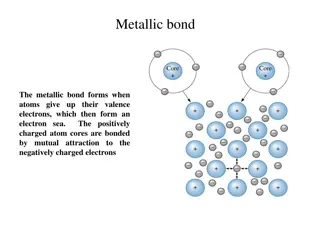
Metallic Bond A type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared Example: Copper wire