Chemistry Fundamentals: Atoms, Energy, Reactions, and Elements
Explore the basics of chemistry including atomic structure, energy interactions, significant figures, element properties, and reaction types. Dive into topics like states of matter, conversion factors, molecular bonds, and energy changes. Learn about diatomic elements, metalloids, and the formation of ions. Discover the significance of charge, mass, and particle symbols in chemical reactions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
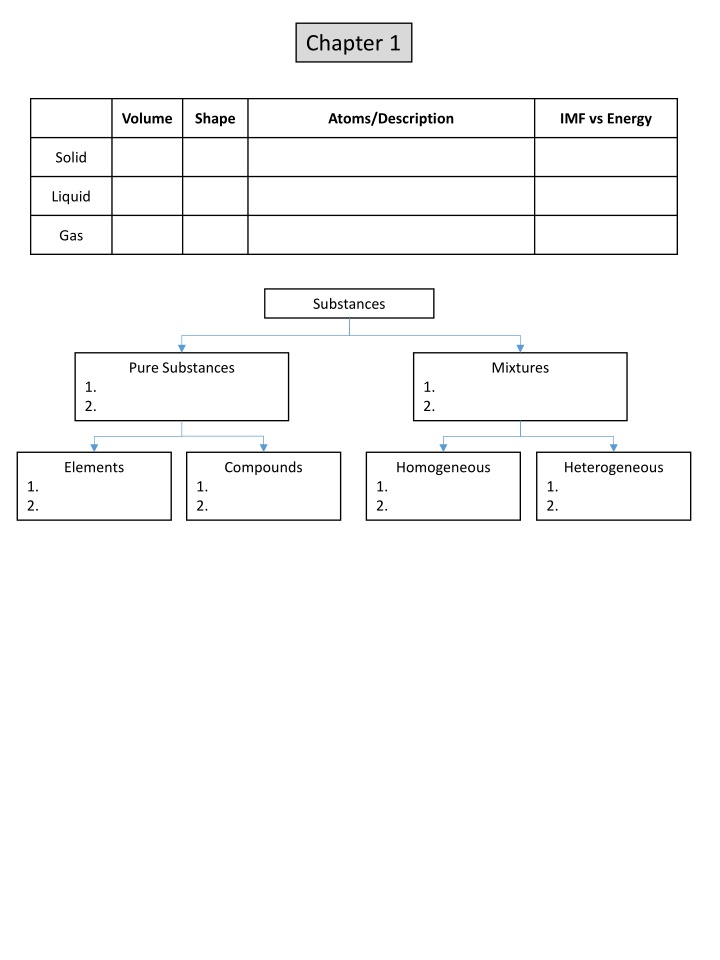
Chapter 1 Volume Shape Atoms/Description IMF vs Energy Solid Liquid Gas Substances Pure Substances Mixtures 1. 2. 1. 2. Elements Compounds Homogeneous Heterogeneous 1. 2. 1. 2. 1. 2. 1. 2.
Chapter 2 5 Rules for Significant Figures (SF) Math with Significant Figures (SF) Add/Sub 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mult/Div Examples Examples Notation for Scientific Notation Rules for Conversion Factor (CF) Tops/Bottoms Metric System Examples Typical Units (US and Metric) SN to Standard Mass: Volume: Standard to SN Length: Special Conversion Factors: Advanced Conversions - Examples Conversion Factor for mass volume Square s and Cubes: Multiple Units: Conversion Factor for (volume length cubed):
Chapter 2 Example Conversions Simple Example Conversions Metric Example Conversions Squares/Cubes Example Conversions Multiple Units Example Conversions Density Example Addition and Subtraction Example Multiplication and Division Practice Problems Chemhaven or make a few up for yourself
Chapter 3 7 Diatomics States of Elements 2 Liquids/11 Gases 7 Metalloids + how do you determine m or nm Metals vs. Nonmetals (5 properties) 1 2. 3. 4. 5. Covalent or Molecular Ionic Formed by Between Bond Strength Melting Point Solubility Conductivity Structure
Chapter 4 q = ms T (Dfn. each term and give typical units) Rearrange to solve for other variables: Write an Exothermic Reaction (ie which side of the equation does energy show up on?) Write an Endothermic Reaction (ie which side of the equation does energy show up on?) Exothermic: - Draw a graph showing the energy change in an exothermic reaction. Label x-axis, y-axis, Reactants, Products, Transition State, Activation Energy, and Energy Change in the reaction Endothermic: - Draw a graph showing the energy change in an exothermic reaction. Label x-axis, y-axis, Reactants, Products, Transition State, Activation Energy, and Energy Change in the reaction Example: Solve for S Example: Solve for q Example: Solve for T Example: Solve for m Practice Problems Chemhaven or make a few up for yourself Conservation of Energy:
Chapter 5 Relative Charge Relative Mass Particle Symbol Location Important Electron Proton Neutron Draw a reaction showing the formation of a Cation: Draw a reaction showing the formation of an Anion:
Chapter 6 Rules for Ionic Fixed: Examples: Rules for Ionic Variable: Examples: Examples: Rules for Molecular: Memorize the 10 common Acids: Examples: Come up with a system/set of rules to follow (name to formula) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Come up with a system/set of rules to follow (formula to name 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Practice Problems Chemhaven or make a few up for yourself
Chapter 8 5 Types of Reactions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. How to Recognize them: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Things to Memorize: 1. 7 Diatomics - 2. State of Elements - 2 (l), 11 (g) 3. 10 Common Acids 4. 8 common molecular gases 5. 3 Decomposition Reactions 7 Steps to complete a reaction: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Practice Problems Chemhaven or make a few up for yourself Example: AB Example: DD (ppt) Example: DD (g) Example: SD - cations Example: AS - Anions Example: Combustion
Chapter 9 Types of Problems: 1. g A g B 2. Limiting Reactant 3. Excess Reactant 4. Theoretical Yield 5. Percent Yield 6. Molarity/Titrations (2 Types) Conversion Factors: Molecular Weight (MW) can you calculate it? Mol/mol ratio Ehere does it come from? Molarity (M = mol/L) Can you write out a flow chart : Example Problem: Given grams of 2 reactants and a chemical equation: 1. Calculate the LR. 2. Calculate Theoretical Yield of both products 3. Calculate ER left over. 4. Determine Percent Yield of a product 5. Determine amount of energy used/released. Molarity Type I: Given a chemical equation, mL and M of A and M of B calculate how many mL of B reacted: Molarity Type II: Given a chemical equation, mL and M of A and mL of B calculate the M of B:
Chapter 10 Rutherford Model Atom (Picture/Description) Bohr Model Atom (Picture/Description) De Broglie Model Atom (Picture/Description) Schrodinger Model Atom (Picture/Description) Energy level filling for orbitals (1s2, 2s2 ) 4 Quantum Numbers (what they describe) n l ml ms Box model (Rules for filling orbitals) Valence Electrons (Dfn, importance) 1. 2. 3. Practice: Write the electron configuration and box model for an Element.
Chapter 11 Ionic vs. Polar Covalent vs Covalent Bonds Lewis Structures see flowchart 1. Count valence electrons 2. Trial structure 3. Fill octets 4. If you run out of electrons, share 5. Determine shape/angle and NP/DP Dfn: Dipolar(DP) Molecule + example Dfn: Nonpolar (NP) Molecule + example Which Shape/Angle are always DP? Which Shape/Angle can be NP? Ionic Bonding: Show formation of an ionic bond using (1) Lewis Structures, (2) Electron Configurations and (3) Words. Molecular Bonding: Show formation of an ionic bond using (1) Lewis Structures, (2) Electron Configurations and (3) Words. Practice Problems Chemhaven or make a few up for yourself Periodic Trends Across a row Size (I or D) Down a column Size (I or D) Across a row Ionization Energy (I or D) Down a column Size Energy (I or D) Cations are (bigger or smaller) vs neutral atoms Anions are (bigger or smaller) vs neutral atoms Review your Lab 11 Flashcards # atoms Bonded # lone pairs Shape Bond Angle
Chapter 12 3 Problem Types: Proportionalities (Boyles, Charles etc. Laws) (DP/IP) 1. Ratio Problems/Pistons 2. PV=nRT Problems 3. PV=nRT + mol/mol ratio ?1?1 ?1?1 ?2?2 ?2?2 P and V: P and T: P and n: V and T: V and n: = TEMPERATURE IS ALWAYS IN ???? Practice Problems Chemhaven or make a few up for yourself PV=nRT (typical units and alternative units) P = V = n = T = Example: Ratio Problems Example: PV=nRT Problems Example: PV=nRT + mol/mol ratio Problesm