Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2
Essential concepts in Chemistry Unit 2, including the formation of Esters, Fats and Oils, and Soaps. Learn about reactions, structures, properties, and applications of these compounds.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
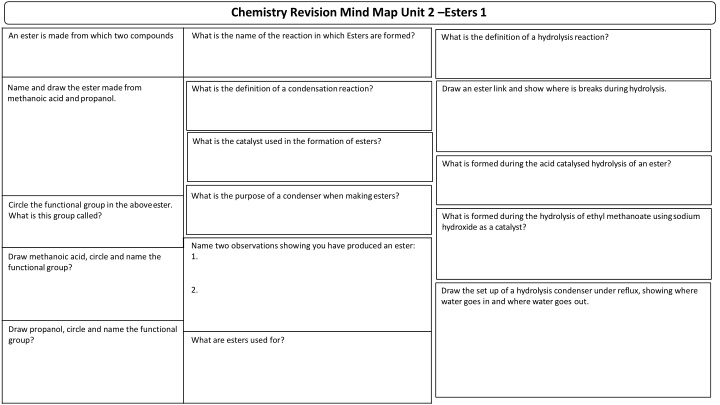
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2 Esters 1 What is the name of the reaction in which Esters areformed? An ester is made from which two compounds What is the definition of a hydrolysisreaction? Name and draw the ester madefrom methanoic acid andpropanol. Draw an ester link and show where is breaks duringhydrolysis. What is the definition of a condensationreaction? What is the catalyst used in the formation of esters? What is formed during the acid catalysed hydrolysis of anester? What is the purpose of a condenser when makingesters? Circle the functional group in the aboveester. What is this groupcalled? What is formed during the hydrolysis of ethyl methanoate usingsodium hydroxide as acatalyst? Name two observations showing you have produced an ester: 1. Draw methanoic acid, circle and name the functionalgroup? 2. Draw the set up of a hydrolysis condenser under reflux, showing where water goes in and where water goes out. Draw propanol, circle and name the functional group? What are esters used for?
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2 Fats and Oils 2 What is the name of the reaction in which fats and oilsare formed? Fats and oils belong to which familyof compounds? Will more bromine solution need to be added to fats or oils to decolourise the bromine solution?Why? Fats and oils are made from which two reactants? Why do edible oils have a lower melting points than fats? You may wish to use a diagram to aid your explanation, you must use the words, unsaturation and Van Der Walls forces (intermolecularforces). Is the following compound saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated? C17H31COOH When a fat or oil is hydrolysed what is produced? Draw the structure for glycerol: What is the name of the reaction called when an oil is converted into a fat? (also known as hardening) What is the systematic name for glycerol? Fats and oils are important for 2 reasons: 1. How many moles of fatty acids (carboxylic acids) will one mole of glycerol reactwith? 2. What is the test of unsaturation? Draw an esterlink:
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2 Soaps3 The alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils produce what? Draw a diagram and label the steps to show how soapworks. What term is used to describe water containing high levels is dissolved metalions? Draw the structure of a soap molecule and label the hydrophilic/polar(ionic) part andthe hydrophobic/covalentpart. When soap is used in hard water areas what is produced? What is used instead of soap in hard water areas?Why? What is an emulsifier? Hydrophilicmeans What is an emulsion? Hydrophobicmeans An emulsifier used in food is made my reacting edible oils with glycerol. The hydroxyl groupsare hydro whereas the fatty acid chains are hydro dissolve in . and dissolve in The hydrophilic part of soap dissolvesin what? an R1 and R2 shows the long fatty acidchain. The hydrophobic part of soap dissolvesin what? Circle and label the hydrophobicand Hydrophilicpart
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2 Proteins 4 Proteins are important for 2 reasons: 1. What is the name of the chemical reaction in which proteinsare made? What is eliminated? The body cannot make all amino acids required for protein synthesis. What is the name given to amino acids which much be acquired through the diet? During digestion protein can be broken down to amino acids, what is this reactioncalled? Draw the section of the protein made from the following3 amino acids. 2. What bond is broken during proteinhydrolysis? Proteins which are biological catalysts are called what? Proteins can form sheets, spirals and complex shapes. What holds these chains inplace? Proteins are made from what buildingblock? When proteins are heated what happens to the intermolecularbonds? Circle and name the 2 functional groups inthe amino acidbelow: When proteins are heated, the protein changed shape, what isthis called? Circle the peptide link in the above diagram of the section of protein. Draw a peptide linkbelow What causes the texture of food to change when it is cooked?
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2 Oxidation of Alcohols 5 Draw and name the functional group ofan alcohol. Why does propane-1,2,3-triol have a higher boiling point andis more viscous than ethane-1,2-diol? Which two oxidising agents can be used to oxidise primary and secondaryalcohols? Draw 2,2-dimethylpropan-1-ol Primary alcohols are oxidisedto: Draw the oxidation products of butan-1-ol. (is this primary secondary, or tertiary?) Secondary alcohols are oxidisedto: What is a primary alcohol? Draw anexample When hot copper (II) oxide is added to a primary or secondary alcohol the observationis: Draw the oxidation products of butan-2-ol. (is thisprimary secondary, or tertiary?) What is a secondary alcohol? Draw an example When acidified potassium dichromate is added to a primary or secondary alcohol the observationis: You can distinguish between a ketone and carboxylic acidby: What is a tertiary alcohol? Draw anexample Why can 2-methyl propan-2-ol not beoxidised? Oxidation has what effect on the oxygen to hydrogen ratio? (O:H)
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2 Aldehydes and Ketones 6 Draw and name the functional group ofan aldehyde andketone. Draw an isomer of pentanal What colour change would you observe when you add Fehling ssolution to an aldehyde? What is the difference between an aldehyde and a ketone? What colour change would you observe when you add Tollen s reagent to an aldehyde? Draw an isomer of 2-methylpropanal What colour change would you observe when you add acidified dichromate to an aldehyde? Draw 4-methylhexan-2-one Aldehydes are usedfor: What compound can be oxidised to a carboxylicacid? Draw 2-methylpropanal Oxidation from the air results in oxidation of food, what is a disadvantage of this? What three oxidising agents can be used to differentiate between an aldehyde and aketone? What are antioxidants: 1. 1. What is anisomer? 2. 2. 3. 3.
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2 Fragrances7 Essential oils are volatile what does this mean? Draw the structure of an isoprene unit (2-methylbuta-1,3- diene). If a terpene contains 40 carbons, how many isoprene units is it made from? Essential oils are non-water soluble, what is another word to describethis? Write the molecular formula for a terpene consisting of 4 isoprene units. Draw apparatus to extract essential oils in a lab and list the key points Circle an isoprene unit in the terpenebelow: List 4 uses of essential oils: 1. 2. 3. 4. What name is given to the key component in most essential oils? How many isoprene units make uplimonene? What is the general formula for a terpene? What is theisoprene rule? Name the molecule in which Terpenesare based.
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 2 Skin Care 8 Name the high-energy form ofradiation present in sunlight. What is a freeradical? H2 and Cl2 reacts explosively in the presence of UV (H2 + Cl2 2HCl) write the initiation, propagation and termination reactions. Free radical chain reactions include which threesteps: Exposure to UV light results in what happening tobonds? 1. 2. 3. List 3 negative impacts of UV radiation. 1. Decide if each of the following are initiation, propagationor termination. 2. 3. 1. How can you prevent skin damage caused by UV radiation? 2. What is a free radical scavenger? During UV exposure, UV light breaksbonds. What is formed? List three everyday items free radical scavengers are added to: 1. 3. 2. 3.

![[PDF⚡READ❤ONLINE] Zen Mind, Beginner's Mind: 50th Anniversary Edition](/thumb/20459/pdf-read-online-zen-mind-beginner-s-mind-50th-anniversary-edition.jpg)