Chemistry Worksheets for Transition Metal Reactions
Dive into interactive chemistry experiments with these worksheets focusing on transition metal ions, precipitation reactions, and identification of negative ions. Explore the solubility rules, reactions with various metal ions, and the properties of different anions. Each worksheet guides you through hands-on activities to deepen your understanding of chemical reactions and ion characteristics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
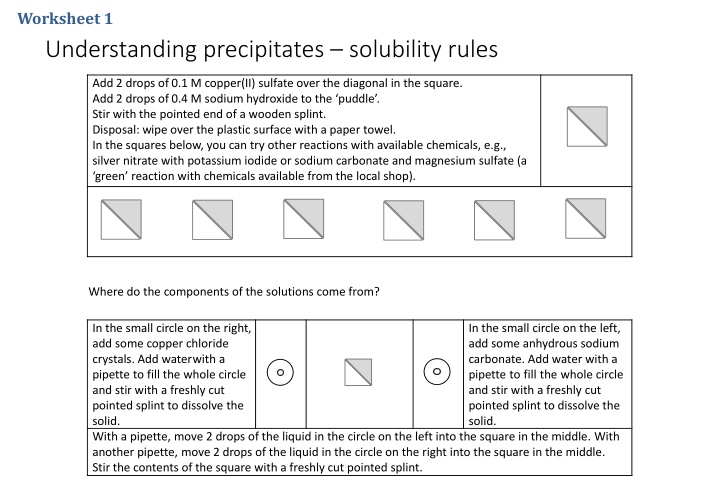
Worksheet 1 Understanding precipitates solubility rules Add 2 drops of0.1 M copper(II) sulfate overthe diagonal in the square. Add 2 drops of0.4 M sodium hydroxide to the puddle . Stir with the pointed end of a wooden splint. Disposal: wipe overthe plastic surface with a paper towel. In the squares below, you can try other reactions with available chemicals, e.g., silver nitrate with potassium iodide or sodium carbonate and magnesium sulfate (a green reaction with chemicals available from the local shop). Where do the components of the solutions come from? In the small circle on the right, add some copper chloride crystals. Add water with a pipette to fill the whole circle and stir with a freshly cut pointed splint to dissolve the solid. With a pipette, move 2 drops of the liquid in the circle on the left into the square in the middle. With another pipette, move 2 drops of the liquid in the circle on the right into the square in the middle. Stir the contents of the square with a freshly cut pointed splint. In the small circle on the left, add some anhydrous sodium carbonate. Add water with a pipette to fill the whole circle and stir with a freshly cut pointed splint to dissolve the solid.
Worksheet 2 Chemistry of transition-metal ions 1 (with sodium hydroxide) Wear eye protection Addition of 0.4 M sodium hydroxide solution Place 2 drops of 0.1 M salt solution in each circle across the central line. Along the top row, add one drop of 0.4 M sodium hydroxide solution. Stir with a pointed wooden splint. Along the second row, add 6 drops of 0.4 M sodium hydroxide solution. Stir with a pointed wooden splint. MnII FeII FeIII CoII NiII CuII ZnII
Worksheet 3 Chemistry of transition-metal ions 2 (with 2 M ammonia) Wear eye protection Ensure good room ventilation Addition of 2 M ammonia solution Place 2 drops of 0.1 M salt in each circle across the central line. Along the top row, add 1 drop of 2 M ammonia solution. Stir with a pointed wooden splint. Along the second row, add 6 drops of 2 M ammonia solution. Stir with a pointed wooden splint. MnII FeII FeIII CoII NiII CuII ZnII
Worksheet 4 Identification of negative ions (anions) Use 0.1 M to 0.2 M potassium or sodium salts in the relevant squares. Wear eye protection Potassium/ sodium chloride Potassium/ sodium iodide Potassium/ sodium carbonate Potassium/ sodium sulfate Potassium/ sodium bromide Potassium/ sodium nitrate Add 2 drops of the relevant solution to each of the squares above. Add 2 drops of 0.4 M nitric acid and 1 drop of 0.05 M silver nitrate. Stir mixtures with a with a pointed wooden splint. Record observations before adding 2 drops of 2 M ammonia. Potassium/ sodium nitrate Potassium/ sodium chloride Potassium/ sodium iodide Potassium/ sodium carbonate Potassium/ sodium sulfate Potassium/ sodium bromide Add 2 drops of the relevant solution to each of the squares above. Add 1 drop of universal indicator solution. To any solution that is alkaline, add 1 drop of 1 M hydrochloric acid and look for bubbles of carbon dioxide. Potassium/ sodium nitrate Potassium/ sodium chloride Potassium/ sodium iodide Potassium/ sodium carbonate Potassium/ sodium sulfate Potassium/ sodium bromide Add 2 drops of the relevant solution to each of the squares above. Add 2 drops of 0.4 M nitric acid and add 1 drop of barium chloride or nitrate to each square and stir mixture with a with wooden splint.