Coexistence of 802.11ah and 802.15.4g in S1G Band
Explore the coexistence challenges between IEEE 802.11ah and IEEE 802.15.4g operating in the Sub-1 GHz (S1G) band, addressing issues like spectrum allocation, multiple system deployment, and coexistence mechanisms for improved interoperability.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
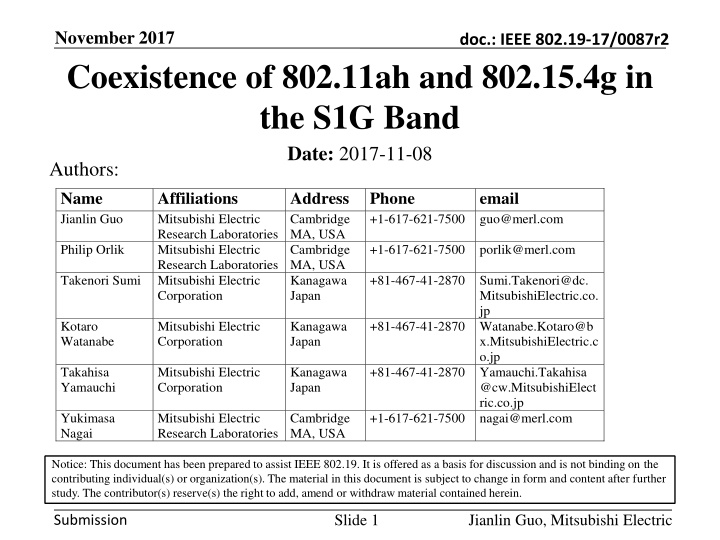
November 2017 Coexistence of 802.11ah and 802.15.4g in the S1G Band Date: 2017-11-08 Authors: doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 Name Jianlin Guo Affiliations Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Address Cambridge MA, USA Cambridge MA, USA Kanagawa Japan Phone +1-617-621-7500 guo@merl.com email Philip Orlik +1-617-621-7500 porlik@merl.com Takenori Sumi +81-467-41-2870 Sumi.Takenori@dc. MitsubishiElectric.co. jp Kotaro Watanabe Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Kanagawa Japan +81-467-41-2870 Watanabe.Kotaro@b x.MitsubishiElectric.c o.jp +81-467-41-2870 Yamauchi.Takahisa @cw.MitsubishiElect ric.co.jp +1-617-621-7500 nagai@merl.com Takahisa Yamauchi Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Kanagawa Japan Yukimasa Nagai Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Cambridge MA, USA Notice: This document has been prepared to assist IEEE 802.19. It is offered as a basis for discussion and is not binding on the contributing individual(s) or organization(s). The material in this document is subject to change in form and content after further study. The contributor(s) reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material contained herein. Slide 1 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric Submission
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 Abstract Presentation to IEEE 802.19 Working Group to raise awareness of coexistence issues between IEEE 802.11ah and IEEE 802.15.4g in the Sub-1 GHz (S1G) Band Slide 2 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric Submission
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 Motivation 802.15.4g based smart utility devices have been deployed o Operate in the Sub-1 GHz (S1G) band 802.11ah is also designed to operate in the S1G band o 802.11ah channel is at least 1 MHz wide Spectrum allocation in S1G band can be narrow o Japan allocates 5.6 MHz spectrum for smart meter system as specified in ARIB STD-T108, Version 1.0 (Feb 14 2012). Channel hopping can be limited o Multiple systems may be deployed with high node density, e.g., LoRa and SigFox also operate in the S1G band As a result, 802.11ah and 802.15.4g coexistence issue needs to be investigated and addressed Slide 3 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric Submission
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 Coexistence Mechanisms of 802.11ah and 802.15.4g 802.11ah coexistence mechanism o An S1G STA uses energy detection (ED) based CCA with a threshold of -75 dBm per MHz to improve coexistence with other S1G systems including 802.15.4 and 802.15.4g o If a S1G STA detects energy above that threshold on its channel, then the following mechanisms might be used to mitigate interference Change of operating channel Sectorized beamforming Change the schedule of RAW(s), TWT SP(s), or SST operating channels Defer transmission for a particular interval RAW = Restricted access window TWT = Target wake time SP = Service period SST = Subchannel Selective Transmission 802.15.4g coexistence mechanism o Define three PHY types MR-FSK MR-OFDM MR-O-QPSK o Define common signaling mode (CSM) for coexistence between devices using different 802.15.4g PHYs Slide 4 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric Submission
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 Are Standard Defined Coexistence Mechanisms Sufficient? A NS-3 simulation system is developed to evaluate coexistence of 802.11ah network and 802.15.4g network IEEE document 802.11-11/0905r5 provides guidelines on evaluation methodology o Application such as smart utility, location of devices, overlapped network, propagation model, etc. One 802.15.4g network o 1 PANC located as (0, 0) o 55 nodes are uniformly placed in circle centered at (0, 0) with 56 meters of radius Three overlapped 802.11ah networks o 3 APs are located at (28, 0), (-14, 24.248) and (-14, -24.248) o Each AP associates with 18 STAs o STAs of each AP are uniformly placed in circle centered at AP location with 42 meters of radius Simulation results show that 802.11ah network can severely interfere with 802.15.4g network Slide 5 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric Submission
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 802.11ah and 802.15.4g Node Placement 802.15.4g PANC: black square 802.15.4g nodes: black stars 802.11ah APs: {red, green, blue} diamonds 802.11ah STAs: {red, green, blue} dots Submission Slide 6 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 Propagation Model ITU-R P.1411-8 model for propagation between terminals from below roof-top height to near street level Lurban = 0 for suburban LoS NLoS(suburban) NLoS(urban) ED Threshold(11ah) ED Threshold(15.4g) -30 11ah Receiver Sensitivity: -77dBm TX power: 13dBm 920 MHz band -40 15.4g Receiver Sensitivity: -88dBm -50 Rx Power[dBm] -60 11ah: 42m -70 11ah ED Threshold: -75dBm -80 15.4g ED Threshold: -80dBm 15.4g: 56m -90 -100 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Distance[m] Submission Slide 7 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 Simulation Results of 802.11ah and 802.15.4g Coexistence Data packet generation rate o 802.15.4g: 1 packet per minutes with 256 bytes payload o Variable 802.11ah packet generate with 256 bytes payload PHY data rate o 802.15.4g: 100kbps, 802.11ah: 3000kbps Data packet delivery rate (PDR) o 802.11ah network achieves more than 85% of PDR for four scenarios o However, 802.15.4g network PDR decreases to about 40% when 802.11ah network packet generation rate is 216/s, i.e., 4 packets/s by each STA, to about 20% when 802.11ah network packet generation rate is 270/s, i.e., 5 packets/s by each STA 802.15.4g PDR 802.11ah PDR What are the causes of 802.11ah interference on 802.15.4g? Submission Slide 8 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 802.11ah Interference Cause I Interference caused by higher ED threshold of 802.11ah o 802.11ah ED threshold: -75dBm o 802.15.4g ED threshold: -80dBm 802.15.4g receiver sensitivity (RS) o -88dBm Consequences o Readable 802.15.4g packets with receiving power level within the range [802.15.4g RS, 802.11ah ED Threshold] are ignored by 802.11ah ED CCA mechanism, which result in 802.15.4g packet collision o 802.11ah devices access channel more, which result in 802.15.4g packet drop due to channel access failure Submission Slide 9 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 802.11ah Interference Cause II Interference caused by faster backoff mechanism of 802.11ah o 802.11ah smaller time scales vs 802.15.4g larger time scales 62.5 ksymbols/s Consequences o 802.11ah device may start packet transmission when 802.15.4g device performs CCA- to-TX turnaround, which causes data packet collision o 802.11ah device may start packet transmission when 802.15.4g device is waiting for ACK packet, which causes ACK packet collision Submission Slide 10 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 September 802.15 WG Straw Poll (1) Do you think there are issues when 802.11ah network and 802.15.4g network are forced to coexist in the Sub-1 GHz band when channel hopping is not available or severely restricted? Yes:23 No:0 Abstain:3 Submission Slide 11 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 September 802.15 WG Straw Poll (2) Would you like to participate in the resolution of coexistence of 802.11ah network and 802.15.4g network? Yes:10 No:3 Abstain:12 Submission Slide 12 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 September 802.15 WG Straw Poll (3) Should IEEE 802.15 and/or 802.19 and/or 802.11 Working Group address issues (if any) in 802.11ah and 802.15.4g coexistence? 802.15: 6 802.19: 18 802.11: 16 Abstain: 6 None of above: 0 Submission Slide 13 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 November 802.19 WG Straw Poll (1) Should IEEE 802.19 Working Group create a study group or interest group to study coexistence between 802.15.4g and 802.11ah in the Sub-1 GHz band? Yes: No: Abstain: Submission Slide 14 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric
November 2017 doc.: IEEE 802.19-17/0087r2 References 1. IEEE Standard 802.15.4g-2012 (Amendment to IEEE Standard 802.15.4- 2011) IEEE Standard 802.11ah-2016 (Sub-1 GHz Operation) IEEE 802.11-11-05-00ah/0905r45, TGah Functional Requirements and Evaluation Methodology L. Tian, S. Deronne, S. Latre, and J. Famaey, An IEEE 802.11 ah Module for NS-3, in Proceedings of the Workshop on ns-3. ACM, 2016, pp. 49 56 NS-3 version 3.23 2. 3. 4. 5. Submission Slide 15 Jianlin Guo, Mitsubishi Electric