Communication Network Overview
Explore the fundamentals of communication networks, including switched networks, virtual circuits, datagrams, and the layers of network communication protocols. Discover key concepts such as service abstraction, API usage, and reliable data transmission. Dive into the world of Internet mapping and understand the intricate workings of traceroute. Uncover the layers of network communication and the services they provide for seamless data transfer across different nodes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazires, Phil Levis, John Jannotti
Communication Communication Network Network Switched Switched Communication Communication Network Network Broadcast Broadcast Communication Communication Network Network Point Point- -to to- -point network point network Packet Packet- -Switched Switched Communication Communication Network Network A hybrid of circuits and packets; headers include a circuit identifier established during a setup phase Circuit Circuit- -Switched Switched Communication Communication Network Network Virtual Circuit Network Virtual Circuit Network Datagram Datagram Network Network
Traceroute map of the Internet, ~5 million edges, circa 2003. opte.org
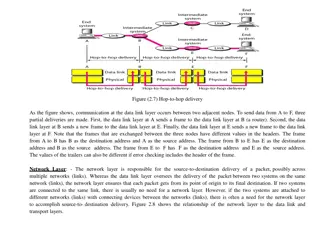
Application Protocol Transport Protocol Network Protocol Link-Layer Protocol
Layer N+1 Service: abstraction provided to layer above API: concrete way of using the service Protocol: rules for communication within same layer Layer N Layer N uses the services provided by N-1 to implement its protocol and provide its own services Layer N-1
Service: user-facing application. Application-defined messages Application Service: multiplexing applications Reliable byte stream to other node (TCP), Unreliable datagram (UDP) Transport Service: move packets to any other node in the network IP: Unreliable, best-effort service model Network Service: move frames to other node across link. May add reliability, medium access control Link Service: move bits to other node across link Physical
socket bind listen socket bind* connect accept
htonl() htons() ntohl() ntohs() sa_family sockaddr struct sockaddr_in6 struct sockaddr sockaddr_storage
sendto(int s, const void *msg, int len, int flags, const struct sockaddr *to, socklen t tolen); recvfrom(int s, void *buf, int len, int flags, struct sockaddr *from, socklen t *fromlen); udpecho.c send recv sendto recvfrom
int n; if ((n = fcntl(s, F_GETFL)) >= 0) fcntl(s, F_SETFL, n|O_NONBLOCK);