Communication Process Components and Models
Communication involves the transfer of information, thoughts, and emotions from one person or group to another. This process includes various components such as the sender, message, channel, receiver, decoding, and feedback. Understanding these components and the communication process model is essential for effective and unambiguous communication. Factors like emotion, culture, and the medium used can influence communication success. Nonverbal signals and potential barriers should also be considered for successful communication outcomes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
WHAT IS COMMUNICATION? THE WORD COMMUNICATION REFERS TO ANY ACT BY WHICH WE TRANSFER INFORMATION, THOUGHT, EMOTION, ETC. FROM ONE PERSON OR GROUP OF PEOPLE TO ANOTHER. THE WORD "COMMUNICATION" (WHICH "COMMUNICARE" MEANING TO MAKE COMMON) IS USED IN COMMON TALK, USUALLY, TOMEANSPEAKINGORWRITINGORSENDINGAMESSAGETOANOTHERPERSON. COMES FROM THE LATIN WORD
COMPONENTS OF COMMUNICATION
1.SENDER-THEPERSONWHOISSENDINGTHEMESSAGE. 2. ENCODING- ORGANISING THE MESSAGE CONTENT INFO APPROPRIATE VER BAL OR NONVERBALMEDIUMDEPENDUNGONTHECONTACTOFCOMMUNICATION. 3. MESSAGE- THE INFORMATION, IDEA, THOUGHT, EMOTION, ETC. WE WANT TO CONNETTERTI. 4. CHANNEL- IT IS THE MODE OR WAY THE MESSAGE FLOWS, LIKE FACE-TO-FACE COMMUNICATION,TELEPHONICCONVERSATION,WRITTENMAIL,ETC.
5.RECIEVER-PERSONFORWHOMTHEMESSAGEISINTENDED. 6. DECODING- INTERPRETATION OR CONVERSION OF THE SENT MESSAGE INTO INTELLIGIBLELANGUAGE. 7. FEEDBACK- THIS REFERS TO THE RESPONSE OF THE RECEIVER IN REFERENCE TO THE MESSAGESENTTOHER/HIMBYTHESENDER. ALL THE COMPONENTS OF COMMUNICATION ARE INFLUENCED BY MANY OTHER FACTORS SUCH AS EMOTION, CULTURAL PRACTICES, MEDIUM USED ETC. FOR AN EFFECTIVE,ACCURATEANDUNAMBIGUOUSCOMMUNICATION,WENEEDTOPONDERUPON ALLTHEABOVECOMPONENTSOFCOMMUNICATION.
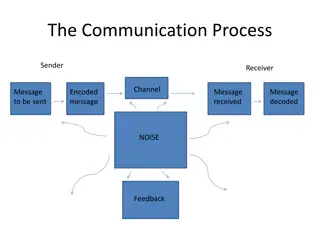
THE PROCESS OF COMMUNICATION IN THE GIVEN DIAGRAM, WE HAVE IDENTIFIED THE COMPONENTS OF COMMUNICATION THATPLAYDIFFERENTROLESINTHEPROCESSOFCOMMUNICATION. THE PROCESS OF COMMUNICATION IS A CYCLIC PROCESS THAT BEGINS WITH THE SENDERANDENDSWITHTHESENDERAGAININTERMSOFFEEDBACKORRESPONSEVIA THERECEIVER.
THEMODELOFCOMMUNICATIONPROCESSCANBEPRESENTEDASBELOW: SENDER SSELECTIONOFMESSAGE ENCODINGOFMESSAGE SELECTIONOFCHANNEL MESSAGE RECEIVED BY THE RECEIVER/LISTENER DECODING OF MESSAGE PROVIDING THEFEEDBACKTOTHESENDER. HOWEVER, WE SHOULD KEEP IN MIND THAT THE PROCESS OF COMMUNICATION IS NOT SMOOTHANDWITHOUTANYBARRIER.
IN EVERY STEP CODING OF MESSAGE BY THE SENDER, PROCESS OF TRANSMISSION, MODE OF COMMUNICATION, RECEIVING AND DECODING OF MESSAGE AND FINALLY FEEDBACK THEMESSAGEMAYGETDISTURBEDORINTERFEREDBYVARIOUSFACTORS THATWENEEDTOUNDERSTANDINORDERTOCOMMUNICATEEFFECTIVELY. ALONGWITHTHESE,WEALSONEEDTOUNDERSTANDNONVERBALSIGNALS. IF WE ARE NOT CAUTIOUS ABOUT ALL THESE FACTORS, WE MAY END UP UN HAVING A COMMUNICATIONFAILURE.