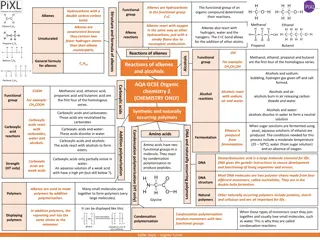
Comparing Alkenes and Alkanes for GCSE
The characteristics and differences between alkenes and alkanes in this resource designed for GCSE level science students. Learn about their molecular structures, reactions, and importance in the study of hydrocarbons. Engage with visual aids like Venn diagrams to deepen your understanding of these fundamental concepts in chemistry.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
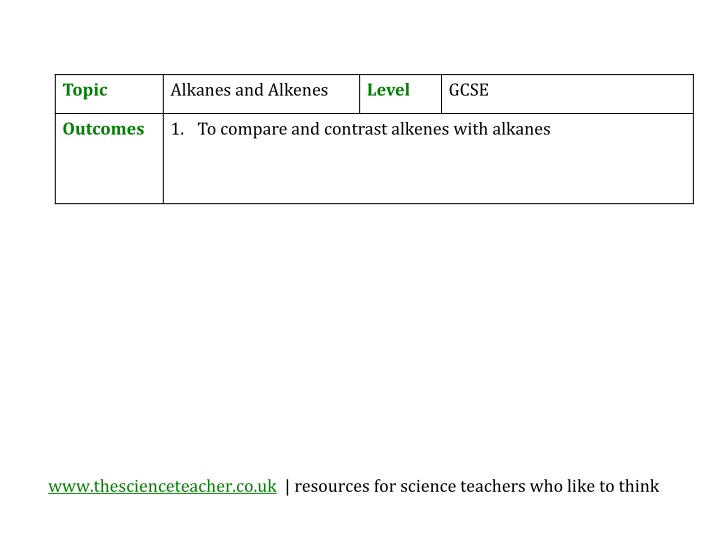
Topic Alkanes and Alkenes Level GCSE Outcomes 1. To compare and contrast alkenes with alkanes www.thescienceteacher.co.uk | resources for science teachers who like to think
Alkanes and Alkenes: teaching compare and contrast
Alkenes Alkanes Neither alkene or alkane
Complete the Venn diagram using these terms Have only single bonds Saturated Contains oxygen Double bond Has the molecular formula C20H42 Hydrocarbon Carbon atoms form 3 bonds Formed by cracking Contains strong ionic bonds Very high melting point Covalently bonded Extracted from crude oil Used as fuels Reacts with bromine water Decolourises bromine water Renewable General formula CnH2n React with steam to produce ethanol Reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water Belong to a homologous series