Comparison of Demographic Characteristics and HRQoL in TBI Patients
This study compares demographic characteristics and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) outcomes in traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients. It analyzes factors such as TBI severity, age at survey, time since TBI, functional status, and the impact of decompressive craniectomy on HRQoL scales. The findings suggest differences in neurorehabilitation duration and functional status at discharge between responder and non-responder groups. Additionally, decompressive craniectomy shows varied effects on HRQoL aspects in TBI patients.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
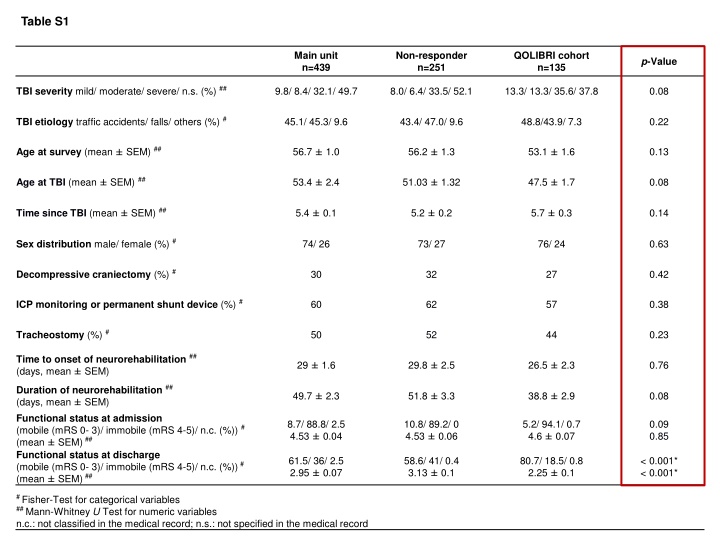
Table S1 Main unit n=439 Non-responder n=251 QOLIBRI cohort n=135 p-Value TBI severity mild/ moderate/ severe/ n.s. (%) ## 9.8/ 8.4/ 32.1/ 49.7 8.0/ 6.4/ 33.5/ 52.1 13.3/ 13.3/ 35.6/ 37.8 0.08 TBI etiology traffic accidents/ falls/ others (%) # 45.1/ 45.3/ 9.6 43.4/ 47.0/ 9.6 48.8/43.9/ 7.3 0.22 Age at survey (mean SEM) ## 56.7 1.0 56.2 1.3 53.1 1.6 0.13 Age at TBI (mean SEM) ## 53.4 2.4 51.03 1.32 47.5 1.7 0.08 Time since TBI (mean SEM) ## 5.4 0.1 5.2 0.2 5.7 0.3 0.14 Sex distribution male/ female (%) # 74/ 26 73/ 27 76/ 24 0.63 Decompressive craniectomy (%) # 30 32 27 0.42 ICP monitoring or permanent shunt device (%) # 60 62 57 0.38 Tracheostomy (%) # 50 52 44 0.23 Time to onset of neurorehabilitation ## (days, mean SEM) 29 1.6 29.8 2.5 26.5 2.3 0.76 Duration of neurorehabilitation ## (days, mean SEM) Functional status at admission (mobile (mRS 0- 3)/ immobile (mRS 4-5)/ n.c. (%)) # (mean SEM)## Functional status at discharge (mobile (mRS 0- 3)/ immobile (mRS 4-5)/ n.c. (%))# (mean SEM)## 49.7 2.3 51.8 3.3 38.8 2.9 0.08 8.7/ 88.8/ 2.5 4.53 0.04 10.8/ 89.2/ 0 4.53 0.06 5.2/ 94.1/ 0.7 4.6 0.07 0.09 0.85 61.5/ 36/ 2.5 2.95 0.07 58.6/ 41/ 0.4 3.13 0.1 80.7/ 18.5/ 0.8 2.25 0.1 < 0.001* < 0.001* # Fisher-Test for categorical variables ## Mann-Whitney U Test for numeric variables n.c.: not classified in the medical record; n.s.: not specified in the medical record
Table S1. Demographic and basic characteristics Demographics and basic characteristics in the main unit (n=439), non-responders (n=251), and the QOLIBRI cohort (n=135). Group differences were statistically tested between non-responders (n=251) and the QOLIBRI cohort (n=135) using the Fisher-Test for categorical or the Mann-Whitney U test for numerical parameters as indicated. Patients of the QOLIBRI cohort were slightly younger when experiencing TBI (p=0.08), needed shorter neurorehabilitation (p=0.08) and gained better functional status at discharge from neurorehabilitation with a mean modified Rankin Scale of 2 (p<0.001), indicating slight disability with good mobility and independence in activities of daily living though unable to carry out all previous activities.
Table S2. Decompressive craniectomy and HRQoL regarding all QOLIBRI scales. The QOLIBRI total score, the two key aspects, namely satisfaction and restrictions, as well as all six subscales were descriptively compared between DC+ and DC- patients using the Mann-Whitney U test. p-value## 0.2 QOLIBRI total score 0.19 Level of satisfaction 0.28 Cognition 0.35 Self 0.33 Daily life & autonomy 0.25 Social relationships 0.14 Level of restrictions 0.93 Emotion 0.025* Physical problems ## Mann-Whitney U Test for DC- (n=98) versus DC+ (n=37)
Table S3. Decompressive craniectomy and HRQoL. HRQoL (mean SD) of the QOLIBRI cohort were in line with previous data.[1, 2] In comparison to previous results not reporting on DC patients who underwent DC reported better HRQoL. QOLIBRI cohort DC- n=98 QOLIBRI cohort DC+ n=37 QOLIBRI cohort1 n=135 QOLIBRI validation cohort2 n=795 QOLIBRI item QOLIBRI total score 64.6 18.2 65.5 22.6 68.8 23 64.3 22.4 Cognition 61.3 21.8 62.4 27.2 65.7 28.3 61.1 26.8 Self 60.0 22.0 61.1 25.6 64.1 25.1 59.9 25.8 Autonomy 66.4 22.4 63.5 31.0 66.3 32.8 62.5 30.4 Relation 63.7 22.6 69.3 23.7 71.6 25.1 68.4 23.3 Emotion 71.7 24.7 75.0 23.9 75 24 74.9 24 63.2 24.1 Physical 67.9 23.5 66.1 24.1 73.6 22.8
Table S4 Mild TBI with initial GCS 13-15 DC- (n=12) DC+ (n=6) p-value## Age at TBI (mean SD) 60.2 13.5 years 50.5 23.4 years 0.81 Time since TBI (mean SD) 5.2 2.7 years 5.5 3.8 years 0.96 Age at survey (mean SD) 65.2 12 years 55.8 21.7 years 0.54 Time to onset of neurorehabilitation (mean SD) 24.7 9.3 days 21.5 8.4 days 0.45 Duration of neurorehabilitation (mean SD) 48.8 34.5 days 40.2 29.3 days 0.81 Functional status at admission (mRS; mean SD) 4.8 0.5 4.7 0.5 0.76 Functional status at discharge (mRS; mean SD) 2.5 0.9 2.3 1 0.66 Moderate TBI with initial GCS 9-12 DC- (n=11) DC+ (n=7) p-value## Age at TBI (mean SD) 59.2 11.8 years 50.7 20.6 years 0.59 Time since TBI (mean SD) 7.6 2.3 years 5.7 2.8 years 0.15 Age at survey (mean SD) 66.7 13.3 years 56.4 18.2 years 0.28 Time to onset of neurorehabilitation (mean SD) 20.9 13.2 days 24.9 12.2 days 0.62 Duration of neurorehabilitation (mean SD) 32.4 31.8 days 15.7 8.7 days 0.15 Functional status at admission (mRS; mean SD) 4.5 0.7 4.6 0.5 0.96 Functional status at discharge (mRS; mean SD) 2.1 1.3 1.9 0.9 0.92 ## Mann-Whitney U Test for numeric variables
Severe TBI with initial GCS 3-8 DC- (n=38) DC+ (n=10) p-value## Age at TBI (mean SD) 36.8 17.4 years 37.8 20.3 years 0.93 Time since TBI (mean SD) 5.4 3.4 years 6.5 2.7 years 0.36 Age at survey (mean SD) 42.2 16.6 years 44.5 20.9 years 0.97 Time to onset of neurorehabilitation (mean SD) 28.4 42.5 days 32.1 17 days 0.06 Duration of neurorehabilitation (mean SD) 41 33.9 days 49.6 34.1 days 0.54 Functional status at admission (mRS; mean SD) 4.7 0.5 4.5 1.3 0.9 Functional status at discharge (mRS; mean SD) 2.1 1 2.7 1.6 0.31 TBI not classified DC- (n=37) DC+ (n=14) p-value## Age at TBI (mean SD) 53.1 20.4 years 45.6 16.6 years 0.22 Time since TBI (mean SD) 5.2 2.9 years 5.5 2.6 years 0.83 Age at survey (mean SD) 58.4 19.3 years 51.1 15.6 years 0.16 Time to onset of neurorehabilitation (mean SD) 26.2 24.4 days 27 8.5 days 0.15 Duration of neurorehabilitation (mean SD) 37.5 37.6 days 35.8 28.6 days 0.74 Functional status at admission (mRS; mean SD) 4.4 1.2 4.9 0.4 0.17 Functional status at discharge (mRS; mean SD) 2 1.3 3 1.4 0.03* ## Mann-Whitney U Test for numeric variables
Table S4. Decompressive craniectomy and characteristics according to initial classified TBI severity Decompressive craniectomy was indicated in all TBI severity groups, pointing out secondary deterioration. Functional status of at least moderate disability at admission to neurorehabilitation underline the secondary deterioration. TBI: traumatic brain injury; GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale; SD: standard deviation; mRS: modified Rankin Scale.
Table S5. TBI injury patterns and reasons for decompressive craniectomy Decompressive craniectomy in mild TBI patients with initial GCS 13-15 (n=6) Admission to intensive care unit at neurorehabilitation center mRS at admission to neurorehabilitation mRS at discharge from neurorehabilitation Day of DC after TBI Reimplantat- ion of bone flap after TBI Reason for DC DC due to traumatic EDH, SDH, SAH, contusions DC with duraplasty due to evacuation of traumatic SDH, evacuation of right frontal contusion bleeding DC due to evacuation of traumatic SDH with herniation DC due to midline shift of 8 mm, no herniation; twice rebleeding with evacuation including osmotherapy (mannitol 20%) and Triple H therapy due to progressive brain swelling 0 2 months yes 5 2 0 6 months yes 5 3 0 3 months yes 5 2 0 3 months yes 4 2 DC due to traumatic SDH, right temporal EDH, right temporo-parietal contusion bleeding, SAH, several contusions 0 2 months yes 4 1 DC due to traumatic SDH, EDH, SAH 6 2 months no 5 4
Decompressive craniectomy in moderate TBI patients with initial GCS 9-12 (n=7) Admission to intensive care unit at neurorehabilitation center mRS at admission to neurorehabilitation mRS at discharge from neurorehabilitation Day of DC after TBI Reimplantat- ion of bone flap after TBI Reason for DC DC due to evacuation of traumatic SAH, SDH < 1 cm and contusion bleeding DC due to contusion bleeding bitemporal and SAH DC due to evacuation of traumatic SDH left frontal, SAH, bilateral contusion bleeding Initial osteoplastic trepanation at day 0 post-TBI for evacuation of left frontal hematoma; 10 days post-TBI bifrontal DC and duraplasty due to refractory intracranial hypertension despite maximal pharmacotherapy 1 2 months yes 5 1 0 1 months yes 4 1 0 2 months no 5 1 10 1.5 months yes 5 3 DC due to midline shift with herniation and traumatic SDH 0 2 months yes 5 2 Initial osteoplastic trepanation with evacuation of hematoma, DC at 3 days post-TBI due to progressive brain edema with midline shift, but no herniation and bulky hematoma; 8 days post-TBI rebleeding, mannitol due to persistent raised ICP 3 1.5 months no 4 3 DC bifrontal due to raised intracranial pressure of 50 mmHg not 1 months no 4 2 specified
Decompressive craniectomy in severe TBI patients with initial GCS 3-8 (n=10) Admission to intensive care unit at neurorehabilitation center mRS at admission to neurorehabilitation mRS at discharge from neurorehabilitation Day of DC after TBI Reimplantat- ion of bone flap after TBI Reason for DC DC due to traumatic right SDH with evacuation and duraplasty, rebleeding and second evacuation 5 days post-TBI DC due to multiple intracerebral bleedings, cerebellar hematoma, diffuse axonal injury DC due to bifrontal contusion bleeding, traumatic EDH, SAH DC bilateral due to malignant brain edema after contusion of corpus callosum and midbrain 1 3 months yes 5 1 2 7 months yes 5 4 0 5 months yes 5 3 2 1 months no 4 4 DC with duraplasty due to evacuation of traumatic frontal-temporo-parietal SDH, contre-coup contusion, significant midline shift 0 3 months Yes 5 1 DC with duraplasty due to traumatic SAH, bitemporal contusion bleeding, diffuse axonal injury, SDH 0 3 months yes 5 4 DC due to traumatic SAH, bilateral contusions, brain edema, midline shift and herniation 0 2 months no 5 5 DC due to traumatic right SDH, brain edema, midline shift of 11 mm, ICH, contusion bleeding 0 2 months no 1 1 not DC, reason not specified 5 months no 5 3 specified DC with duraplasty due to refractory intracranial hypertension (ICP > 20 mmHg), pharmacotherapy with mannitol and thiopental, evacuation of traumatic SDH, debridement of contusions 0 2 months yes 5 1
Decompressive craniectomy in not classified TBI patients with no documentation of initial GCS (n=14) Admission to intensive care unit at neurorehabilitation center mRS at admission to neurorehabilitation mRS at discharge from neurorehabilitation Day of DC after TBI Reimplantat- ion of bone flap after TBI Reason for DC DC due to intracranial hypertension, brain edema, traumatic bilateral SDH, SAH, diffuse contusions, midline shift DC due to traumatic ICH, bilateral contusions, SAH, ICP probe for 19 days post-TBI, normalized ICP at day 11 post- TBI DC due to traumatic SDH, SAH, brain edema and raised ICP for at least 11 days post-TBI DC due to traumatic SAH, SDH, contusions 0 3 months yes 5 4 9 3 months yes 5 1 0 1.5 months yes 4 1 0 3 months yes 5 2 DC due to traumatic EDH, SDH with evacuation, diffuse axonal injury, midline shift of 1.5 mm n.s. 4 months no 5 4 DC due to brain edema and subfalxial herniation, traumatic SAH, SDH, ICH; second surgery due to rebleeding and evacuation of EDH 9 1.5 months no 5 4 DC with duraplasty due to evacuation of traumatic SDH, EDH, contusions, brain edema, midline shift 5 mm 0 9 months no 5 3 DC due to traumatic bifrontal SDH, diffuse contusions 0 3 months no 4 2 DC with duraplasty due to traumatic SAH, ICH, EDH, intraventricular hemorrhage 0 3.5 months yes 5 5 DC due to traumatic SDH, bifrontal contusions 0 2 months no 5 5 DC due to contusion bleeding, ICP probe, at day 2 post-TBI second evacuation of hematoma 0 1.5 months no 5 3
Admission to intensive care unit at neurorehabilitation center mRS at admission to neurorehabilitation mRS at discharge from neurorehabilitation Day of DC after TBI Reimplantat- ion of bone flap after TBI Reason for DC DC due to refractory intracranial hypertension of 40 mmHg 0 4 months no 5 5 DC due to refractory intracranial hypertension despite pharmacotherapy not 3 months yes 5 4 specified DC with duraplasty due to contusions, expansion of DC at day 4 post-TBI 3 2 months no 5 1