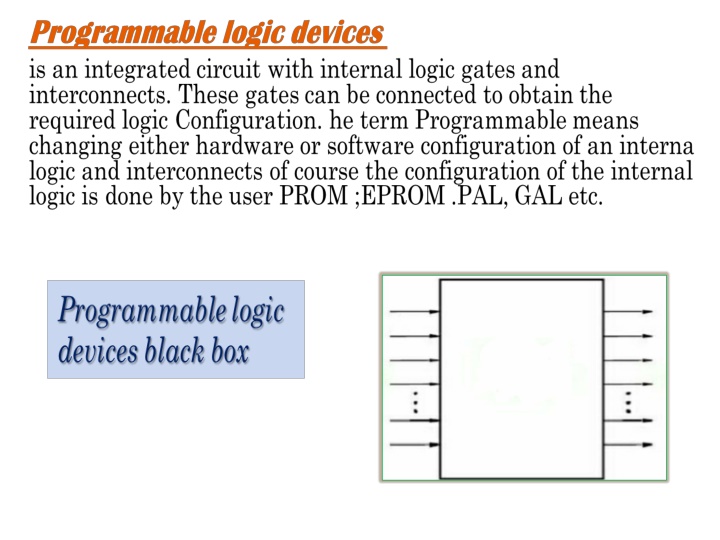
Complex Programmable Logic Devices: Advantages, CPLD vs. FPGA, and Differences Explained
Discover the advantages of CPLDs, comparisons between CPLDs and FPGAs, and key differences in a detailed analysis. Learn about the flexible and easy-to-implement growth of CPLDs, along with their applications and best practices in design.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Advantages Flexible, easy to implement Growth in any environment Exact transfer of complicated materials YBCO) Variable growth rate Epitaxial at low temperature Atoms arrive in bunches, allowing for much more controlled deposition Greater control of growth(e.g., by varying laser parameters) Dis Advantages Uneven coverage High defect or particulate concentration Not well suited for large-scale film growth Program mable Logic Simple Programmable Logic Device(SPLD) PLA or PAL Fixed internal routing, deterministic propagation delays Complex Programmable Logic Device(CPLD) Multiple SPLDs onto a single chip Programmable interconnect Field Programmable Gate Array(FPGA) An array of logic blocks Large number of gates, user selectable interconnection, delays depending on design and routing Programmable A high ratio of flip-flops to logic resources(FPLDSJ FPDLS CPLD SPLD FPGA
(CPLDs) CPLDs were pioneered by Altera, first in their family of chips called Classic EPLDs, and then in three additional series, called MAX 5000, MAX 7000 and MAX 9000 The CPLD is the complex programmable Logic Device which is more complex than the SPLD This is build on SPLD architecture and creates a much larger design. Consequently, the SPLD can be used to integrate the functions of a number of discrete digital ICS into a single device and the CPLD can be used to integrate the functions of anumber of SPLDS into a single device. CPLDs utilize nonvolatile memory such as EPROM EEPROM, and flash memory When considering a complex programmable logic device for use in design, there is some following architecture issues can be taken into account The programming technology The function block capability The I/O capability Best applications Wide functions Fast arithmetic Complex counters Complex state machines PAL/GAL or TTL integration Non-volatile
Advantages Of Cplds 1_Ease of Design: 2_With use of HDL& CPLD development tools Reduced Board Area: 3_As uses VLSI& available in tiny sizes. Cost of ownership: 4_Due to less maintenance 5_ Lower Development Costs Some of the families of CPLD from different retailers include Altera MAX 7000 and MAX 9000 families Atmel ATF and ATV families Lattice isp LSI family Lattice (Vantis) MACH family Xilinx XC9500 family