Comprehensive Information on Liver Cancer Classification and Treatment Guidelines
Explore the detailed parameters and classifications of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), including patient symptoms, liver function tests, tumor spread indicators, and treatment options such as ablation, sorafenib, resection, transplantation, and more. Understand the stages of HCC according to BCLC, APASL, and HKLC systems, aiding in treatment decisions and assessing prognosis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
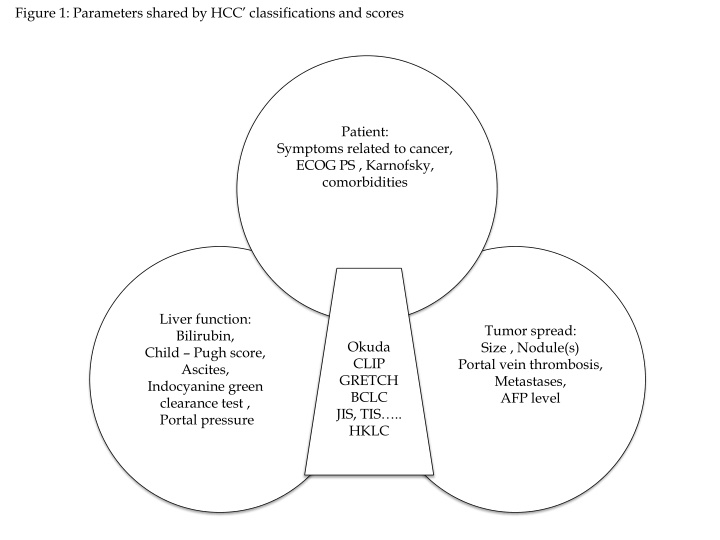
Figure 1: Parameters shared by HCC classifications and scores Patient: Symptoms related to cancer, ECOG PS , Karnofsky, comorbidities Liver function: Bilirubin, Child Pugh score, Ascites, Indocyanine green clearance test , Portal pressure Tumor spread: Size , Nodule(s) Portal vein thrombosis, Metastases, AFP level Okuda CLIP GRETCH BCLC JIS, TIS .. HKLC
Figure 2: BCLC system Hepatocellular carcinoma Very early stage (0) Single < 2cm Child Pugh A , PS 0 Early stage (A) Single or 3 nodules < 3cm Child Pugh A , PS 0 Intermediate stage (B) Multinodular Child-Pugh A-B, PS 0 Advanced stage (C) Portal invasion Extrahepatic spread Child-Pugh A-B, PS 1-2 Terminal stage (D) Child-Pugh C PS 3-4 Potential candidate for Liver transplantation Single Three nodules 3cm Portal pressure bilirubin non oui Normal Increased Associated disease No Yes Ablation Ablation Sorafenib Resection Transplantation Best Supportive care (10%) TACE Palliative treatments (20% - 40%) Curative treatments (30-40%) OS <3 months OS >60 months OS >20 months OS >11 months
Figure 3: APASL guideline on the treatment algorithm for HCC HCC Confined to the liver Main portal vein patent Extrahepatic metastasis Main portal vein tumor thrombus Child A/B Child C Resectable yes no Sorafenib or systematic therapy trial Resection / RFA (for < 3cm HCC) Solitary tumor 5 cm 3 tumors 3cm No venous invasion Tumor > 5 cm > 3 tumors Invasion of hepatic /portal vein branches Child A Child B Child C Child A/B Child C Local ablation Transplantation TACE Supportive care
Figure 4: HKLC Classification ECOG 2-4 / Child C ECOG 0-1, Child A-B No EVM EVM Early Tumors no EVM Others tumors/ EVM Early Tumor 5cm, 3 nodules no intrahepatic venous invasion Intermediate Tumor 1) 5cm, >3 nodules or with intrahepatic venous invasion 2) >5cm, 3 nodules and no intrahepatic venous invasion Locally advanced Tumor 1) 5cm, >3 nodules and with intrahepatic venous invasion 2) >5cm, >3 nodules or/and intrahepatic venous invasion 3) Diffuse tumor Child B Child A ECOG 0, Child A ECOG 1 , Child B Child A Child B Stage Vb Stage I Stage IIa Stage IIb Stage IIIa Stage IIIb Stage IVa Stage IVb Stage Va Resection/ LT/ ablation LT BSC Resection TACE Systemic therapy Systemic Therapy / BSC EVM: Extrahepatic vascular invasion/metastasis, BSC: best supportive care
Figure 5:Histograms of evolution of median OS following NIACE score in BCLC stage C patients from a multicenter French study treated by Sorafenib (black bars center 2, grey bars center 3, white bars center 4) 35 BCLC C center 2 30 30 BCLC C center 3 Sorafenib 25 Survival time (months) BCLC C center 4 20 20 20 17 16 P<.0001 15 15 13 15 13 13 10 9 10 8 8 7 7 6 5 5 5 5 4 4 5 3 3 3 0 0 1 1.5 2.5 3 4 4.5 5.5 6 7 NIACE score Patients, n 1 1 9 - 8 5 7 4 11 3 9 19 18 16 25 9 11 20 21 10 14 8 10 12 16 10 - 2 3 3 NIACE score results
Figure 6:Histograms of evolution of median OS following NIACE score in HCC patients from a multicenter French study treated by TACE (grey bars center 1, black bars center 2) 45 41 TACE center 1 39 40 38 33 35 Survival time (months) 30 TACE center 3 26 21 25 21 21 P<.0001 20 15 13 15 10 10 10 7 5 3 5 0 NIACE score 0 1 1.5 2.5 3 4 4.5 5.5 6 7 47 10 26 55 52 4 35 16 25 - 21 6 9 - 10 - 2 - 3 - Patients, n NIACE score results
Figure 7: Prognostic scores designed to TACE, an aid to the decision making process: in Practice BCLC B HCC, Child pugh grade A / B7 BCLC A HCC (not suitable for surgery or RFA) BCLC C HCC (sectorial portal vein thrombosis) TACE treatment: No absolute contraindication HAP score: A / B State score 18 points NIACE score 3 Absolute contraindication to TACE: alternative therapy or supportive care HAP score: C / D State score < 18 points NIACE score > 3 First TACE CT scan and /or MRI Progressive disease new lesion(s) and /or growth of existing lesion Stable disease or Response ART 2,5 ABCR >2 ART 0 1,5 ABCR 2 alternative therapy or supportive care, according to: Untreatable Progression? Child-Pugh grade? ECOG PS? Second TACE Similar diagram Objective: achieve disease control
Figure 8: Nomogram for HCC Recurrence after RFA Point 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Number of tumor 0 4,3 10 Single Two Three Size of the largest tumor 0 4 6,3 2 cm 2,1-3,0 3,1-5,0 cm cm Serum Albumin 0 3,8 <4 4 0 3 Meld score meld<8 meld 8 Blood Platelet count 3 0 <150.00 0 150.000 Total points 0 5 10 15 20 23,8 Recurrence- free Survival 84% 73% 62% 45% 29% 19%
Figure 9: Histograms of evolution of median OS following NIACE score in HCC patients from a multicenter French study treated by surgery / RFA (grey bars center 5, black bars center 1) 65.5 70 61 Survival time (months) Surgery center 5 60 50 44.5 Surgery / RFA center 1 38 40 30 24.5 P<.0001 21 19 17 16 17 20 15 15.5 6.5 10 6 0 0 1 1.5 2.5 3 4 4.5 5.5 6 7 87 58 5 6 36 18 3 5 14 7 1 3 - 4 - 3 Patients, n NIACE score results