Comprehensive Overview of Composite Materials in Civil Structures
This informative content delves into composite materials used in civil structures, covering topics such as timber, concrete, pre-stressed concrete, and asphalt. Learn about the properties, advantages, and applications of these materials in engineering studies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Composite Materials in Civil Structures Year 12 Engineering Studies Civil Structures
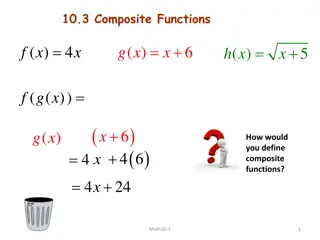
Recap What we know already A composite material is a combination of two or more materials with different physical and chemical properties. This is generally done to increase strength and reduce weight. Common engineering composites include: concrete glass reinforced polymer (fibreglass) carbon reinforced polymer (carbon-fibre) timber and timber products
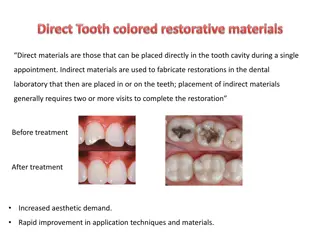
Timber Timber is a natural composite made from long cellulose fibres (a polymer) held together by a much weaker substance called lignin Laminated beams multiple pieces of timber glued together to form a long continuous beam Advantages: - environmentally friendly (more economical use of available resources) - stronger (able to eliminate or minimise defects) - longer lengths achievable - can be formed into curves - more stable than solid timber (less prone to shrinkage and twisting) How to make Laminated Wood Beams {www downloadshiva com} YouTube
Concrete Constituents: aggregate, sand and cement Properties: - high compressive strength - weak in tension - formability - durability Reinforced Concrete Steel mesh or bars are embedded to provide tensile strength. Reinforcing is positioned in the section of the slab or beam that will experience tensile loads, particularly under bending.
Pre-stressed Concrete Concrete that has a pre-induced compressive load by placing the steel reinforcing under a tensile load either before or after curing. Pre-tensioned steel reinforcing placed under a tensile load and concrete poured around the pre-tensioned reinforcing. Once the concrete has cured, the tensile load is released pulling the surrounding concrete into compression Post-tensioned concrete is formed with sleeves. Once the concrete has cured, steel bars are inserted through the sleeves and tensioned placing the surrounding concrete into compression When a load is applied the pre-induced compressive load must be overcome before the concrete experiences tensile stresses https://practical.engineering/blog/2019/3/9/what-is- prestressed-concrete
Asphalt Constituents: aggregate and bitumen Properties - stability and durability. - flexibility and fatigue resistance - slip resistance - impermeable - workability https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yBWP2QI4oaA
Geotextiles Geotextiles are woven or non-woven fabrics which are used to provide to soil stabilisation, separation, filtration, reinforcement, protection, or drainage of soils in construction and engineering applications. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1cwJ9bCgu6I https://www.geofabrics.co/geotextiles