Condensation reactions
Aldol condensation, Benzoin condensation, and Perkins condensation are condensation reactions commonly used with carbonyl compounds to synthesize new molecules. Aldol condensation involves the formation of unsaturated compounds, while Benzoin condensation is specific to aromatic aldehydes. Perkins condensation results in aryl acrylic acids, such as cinnamic acid and Coumarin. Explore the mechanisms and applications of these reactions in organic synthesis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
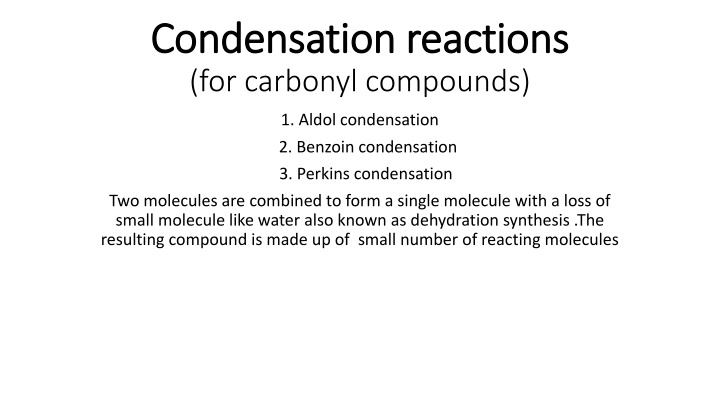
Condensation reactions Condensation reactions (for carbonyl compounds) 1. Aldol condensation 2. Benzoin condensation 3. Perkins condensation Two molecules are combined to form a single molecule with a loss of small molecule like water also known as dehydration synthesis .The resulting compound is made up of small number of reacting molecules
1. Aldol condensation (for carbonyl compounds) 1. Aldol condensation (for carbonyl compounds) CHO/CO in the presence of base: NaOH/K2CO3/ or acid: Hcl undergoes condensation reaction to form syrupy liquid ( -hydrogen involved) 2 CH3-CHO ------CH3 -CH(OH)-CH2-CHO Yield: (50%) Reaction takes place in 2 steps with the formation of carbaion On heating Aldol eliminates H2O to form unsaturated compound Example:3-hydroxy-butanal, yield- CH3-CH=CH-CHO [crotonaldehyde] Aldol condensation occur between identical or different CHO/CO compounds In case of acetaldehyde CH3CHO Yield- -hydroxy ketone In presence of Ba(OH)2 2(CH3)2CO --------(CH3)2C(OH)CH2 CO-CH3
2. Benzoin condensation 2. Benzoin condensation Two mole of Bezaldehyde reflexed with aq.ethanolic KCN to form benzoin [MP:137 0C] C6H5CHO+ C6H5CHO -------C6H5-CH(OH)CO-C6H5 (85%) Benzoin is mono - hydroxy, mono ketone Only suitable for the conversion of aromatic aldehyde CN- act as a good Nucleophilic attacker and also as a good leaving group
3. Perkins condensation reaction 3. Perkins condensation reaction Aromatic aldehyde reacts with aliphatic anhydride (Ac2o) with 2 - hydrogen atom in the presence of sodium acetate [CH3COONa]- to form -aryl acrylic acid Example : synthesis of cinnamic acid [Aryl- , unsaturated acid] C6H5CHO+ (CH3 COO)3O--------C6H5-CH=CH-COOH Alkali salt act of acid as a weak base Another example: synthesis of Coumarin is carried out by heating sodium salt of salicylaldehyde with Ac2o
Synthesis of Coumarin Synthesis of Coumarin