Contrasting Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Structures
Explore the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, categorized by the presence or absence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, with a proper nucleus and various organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts, are found in plants, animals, and fungi. On the other hand, prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, being simpler structures primarily seen in unicellular organisms such as bacteria and archaea.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
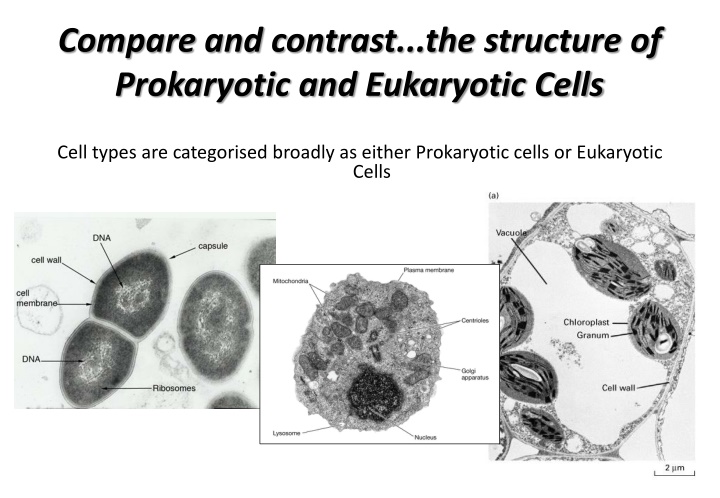
Compare and contrast...the structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Cell types are categorised broadly as either Prokaryotic cells or Eukaryotic Cells
A cell whose major organelle s are contained within membranes Eukaryotic Cells Have a proper Nucleus Usually have Mitochondria, Golgi Apparatus, Chloroplasts etc Eukarotes include Animals, Plants and Fungi
Cells contain no Nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane-bound organelles http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5a/Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg/300px-Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg.png Mainly unicellular organisms Generally less complex than the Eukaryotes Components float freely within the cytoplasm Bacteria and Archaea