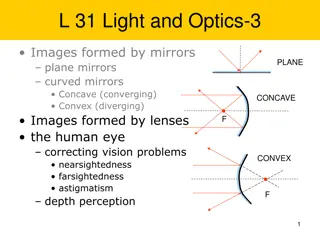
Convex and Concave Mirrors: Properties and Uses
A convex mirror, or diverging mirror, bulges towards the light source and reflects light outwards, resulting in virtual images that cannot be projected on a screen, appearing smaller than the object. Common uses include vehicle mirrors for a wider field of view. In contrast, concave mirrors focus light inward to a focal point, forming images that can vary in size based on object distance. Concave mirrors are used in various applications, offering magnification when objects are placed between the focal point and the mirror.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A convex mirror or diverging mirror is a curved mirror in which the reflective surface bulges towards the light source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards, therefore they are not used to focus light. Such mirrors always form a virtual image, since the focal point (F) and the centre of curvature are both imaginary points "inside" the mirror, that cannot be reached. As a result, images formed by these mirrors cannot be projected on a screen, since the image is inside the mirror. The image is smaller than the object, but gets larger as the object approaches the mirror. CONVEX MIRROR
USES OF CONVEX MIRROR The passenger-side mirror on a car is typically a convex mirror. Convex mirrors are preferred in vehicles because they give an upright (not inverted), though diminished (smaller), image and because they provide a wider field of view as they are curved outwards. These mirrors are often found in the hallways of various buildings . They are usually mounted on a wall or ceiling where hallways intersect each other, or where they make sharp turns.
C ON C A VE M IRROR A concave mirror, or converging mirror, has a reflecting surface that is recessed inward. Concave mirrors reflect light inward to one focal point. They are used to focus light. Unlike convex mirrors Concave mirrors show different image types depending on the distance between the object and the mirror. These mirrors are called "converging mirrors" because they tend to collect light that falls on them, refocusing parallel incoming rays toward a focus.
CONCAVE MIRROR In a concave mirror reflection of light takes place at the concave surface or bent-in. Commonly used terms about Spherical mirrors
VIRTUAL IMAGE FORMED BY CONCAVE MIRROR -> When an object is placed between the focal point and the pole the image formed is virtual, upright and magnified
FORMATION OF IMAGES IN DIFFERENT CASES OBJECT AT FOCAL POINT- Reflected rays are parallel and never meet, so no image is formed.
OBJECT BETWEEN FOCUS AND CENTRE OF CURVATURE- Real image Inverted (vertically) Magnified (larger) Object at center of curvature- Real image Inverted (vertically) Same size Image formed at centre of curvature
IMAGE FORMATION BY CONCAVE MIRROR 1. For a real object very far away from the mirror, the real image is formed at the focus. -> In concave mirror the image formed is - Upright if virtual - Inverted if real - Image is real if an object is far away - Image is virtual if object is placed near
FORMATION OF VIRTUAL IMAGE IN CONCAVE MIRROR