Coordination Compounds: Isomerism Insights
Explore different types of isomerism in coordination compounds by Dr. Atul Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry. Dive into coordination, stereo, and geometrical isomerisms with detailed examples and images, shedding light on ligand placements and spatial arrangements around the central metal atom or ion. Discover the complexities and possibilities within coordination number variations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Coordination Compounds by Dr. Atul Kumar Singh Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry M. L. Arya College, Kasba Purnia -854330 India
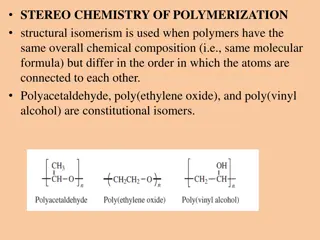
Coordination isomerism This type of isomerism arises due to different placement of ligands in bridged complex. For example
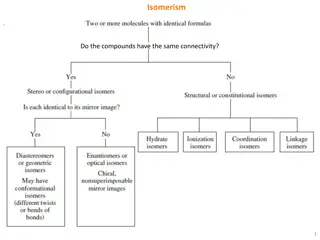
Stereo-isomerism This type of isomerism arises when they contain the same ligands in their coordination spheres but different arrangement in space.
Geometrical isomerism This type of isomerism is also referred as cis- and trans- isomerism. This type of isomerism arises due to ligands occupying different positions around the central metal atom or ion. The ligands occupy positions either adjacent (Cis) or opposite to one another(trans). Geometrical isomerism of compound with coordination number 4 and 6 is common but not possible with coordination number 2 and 3.
Geometrical isomerism in complexes with coordination number 4 Complexes with coordination number 4 either have tetrahedral geometry or square planer geometry .
Geometrical isomerism in Mabcd Complexes Complexes of the type Mabcd have three isomers
Geometrical isomerism in M(ab)2 Complexes M(ab)2 Complexes of the type containing unsymmetrical bidentate ligands. Complexes of the type Ma3b can not show geometrical isomerism because all spatial arrangements are equivalents.